News
Ministry of Human Resource Development making education Available, Accessible, Affordable and Accountable.
In pursuance to Hon’ble Prime Minister’s vision for ‘Transforming India’, Ministry of Human Resource Development took a leap forward in transforming education sector with the motto of “सबको शिक्षा, अच्छी शिक्षा ” (Education for All, Quality Education).

In pursuance to Hon'ble Prime Minister's vision for ‘Transforming India’, Ministry of Human Resource Development took a leap forward in transforming education sector with the motto of “सबको शिक्षा, अच्छी शिक्षा ” (Education for All, Quality Education).
Year 2017 has been a yet another landmark year in the field of education as 'Education For All & Quality Education' guided policy actions and decisions enabling transformation, that emphasized upon making education Available, Accessible, Affordable and Accountable.
Learning Outcomes
A frequent criticism against the RTE Act was that it did not adequately focus on issues promoting quality education in schools. Therefore, in a landmark step, the Rules to the RTE Act were amended in February 2017 to include, for the first time, the class wise, subject wise Learning Outcomes till Class VIII, thereby emphasizing the importance of quality education.
In this regard, Learning Outcomes for each class in Languages (Hindi, English and Urdu), Mathematics, Environmental Studies, Science and Social Science up to the elementary stage have been developed. These are the basic levels of learning that children should arrive at the end of each class.
Subsequently, 21 States and UTs, including Jammu and Kashmir, have incorporated the Learning Outcomes in their State Rules, while the remaining States have initiated the process, it is expected that this will be completed by the end of this year.
All the States and UTs have translated the Learning Outcomes document in their regional languages, and they are circulating these to all the teachers, and also providing them with the requisite training. Posters for display of Learning Outcomes on the schools along with leaflets on Learning Outcomes for reference of parents have been developed and circulated to all States and UTs. An amount of Rs. 91.20 crore has been released by the MHRD to all States and UTs for printing the Learning Outcomes documents, the Posters and the leaflets in regional languages, and for their distribution.
National Achievement Survey 2017-18
National Achievement Survey (NAS) which was earlier based on textbook content is now a competency based evaluation. As compared to only 4.43 lakh students who were earlier tested across Classes 3, 5 and 8, this time around 22 lakh students from around 1,10,000 schools across 700 districts of India (including rural and urban) were assessed in the year 2017-18 (November 13, 2017) making it one of the largest sample surveys of student learning achievement.
This survey is an improvement over the previous cycles of NAS as it will be completed in the one full academic year. It will reflect the scores of the students and will be able to suggest academic intervention in the same academic year. District wise Result will be generated within 2 months of test conduction. NAS Reporting will show if the students’ learning levels are as per the learning outcomes of a particular grade. It will also look for association of school, teacher and students’ background variables with students’ achievements while analysing the data.
Through NAS 2017-18, it will be for the first time that the teachers will have a tool to understand what exactly the child should be learning in various classes, how to teach this through activities and how to measure and ensure that children have reached the required level. This will also help agencies at the District, State, and National level to conduct achievement surveys and assess the health of the system to improve upon the policy directives. Adding to this, for the first time there will be detailed district-specific report cards for all the districts in the country.
Teacher Education
Major Reforms:
- Introduction of four year B.Ed. integrated programme with multiple pathways- with specialization for pre-primary, elementary, secondary and senior secondary teachers for enabling regulatory framework and orientation of all existing Teacher Education Institutions will be introduced from the academic session 2019-2020.
- Guideline on Strengthening of District Institutes of Education and Training (DIETs): As per the National Policy on Education (NPE), 1986, DIETs were envisaged for In-service as well as pre-service education. However, over the years, the focus had gradually shifted to pre-service education. Moreover, currently, there is no nodal agency with expertise in in-service training and thus to address this challenge, the Ministry of Human Resource Development has recently developed Guidelines on-strengthening of DIETs. Accordingly, States have been encouraged to do a district wise analysis before considering a reconceptualization of DIETs as per the models proposed in the MHRD Guideline on DIETs. This will also allow flexibility of getting more expertise into in-service teacher training.
- DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing): DIKSHA was launched on 5th September, 2017 by the Hon’ble Vice President of India, Shri. M. Venkaiah Naidu.

DIKSHA will accelerate and amplify solutions, experiments and innovations that are underway, and is being attempted in the areas of teacher training and professional development. States and TEIs have the autonomy and choice to repurpose and extend DIKSHA to suit their own needs and purposes. DIKSHA is for the benefit of Teachers in Schools, Teacher Educators and Student Teachers in Teacher Education Institutes (TEIs).
- Amendment of the RTE Act for Training of In-service Untrained Teachers:
In another landmark achievement, the Amendment to the Section 23(2) of the RTE Act to extend the period for training of untrained in-service elementary teachers to 31st March, 2019 has been passed by both the houses of Parliament on 1st August, 2017. The same was notified in Gazette of India on 10th August, 2017. As per the above amendment all untrained in-service elementary teachers working in Government, Government aided, and Private unaided schools should acquire minimum qualification as laid down by an academic authority, authorized by the Central Government, by 31st March, 2019.
This would ensure an improvement in the overall quality of teachers and teaching processes, and consequently learning outcomes of children. Further, it reinforces the Government's emphasis on improvement of quality of elementary education.
The training for untrained teachers is being conducted through Online Mode by National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS). The online D.El.Ed. Course has already been started from 3rd October, 2017. A unique feature of this initiative is that the study material for the course prepared by NIOS in self-instructional mode, is uploaded on the SWAYAM platform in four quadrants i.e. (1) Audio/Video lecture, (2) specially prepared reading material that can be downloaded/printed (3) self-assessment tests through tests and quizzes and (4) an online discussion forum for clearing the doubts. Three courses i.e., 501, 502 and 503 have already been uploaded on the SWAYAM Portal in 4 quadrants. The D.El.Ed. programme video lectures are also broadcast on SWAYAM PRABHA (DTH Channel no. 32).
A total of 14,02,962 in-service untrained teachers from Govt., Govt. Aided and Private Schools have registered on the NIOS portal and 13,58,000 admissions have been confirmed so far.
Distribution of tablets in Kendriya Vidyalayas
Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan has initiated a pilot project for connecting students and their teachers through tablets preloaded with relevant e content to facilitate easy classroom transaction, creation of genuine interest among students and effective learning of the students.
The students of class VIII in 25 Kendriya Vidyalayas (one KV from each Region) shall be provided with good quality Tablets on pilot basis. Every child shall be given a tablet with pre-loaded content in Maths & Science. About 5000 students and teachers shall be involved in this project. Along with the students, their teachers of Maths and Science also shall be provided with tablets for transacting the subjects.
Introduction of e-material/courses for Principals/HMs, teachers and students –
The Department is placing a lot of emphasis on the development and provision of e-content for students and also training of teachers, head masters and Principals.
The CIET-NCERT is developing e-materials and online courses for teachers and students. So far 4524 e-materials (audios, videos, interactives, images, documents, maps etc.) have been developed. They are regularly being validated and uploaded on the NROER portal and e-Pathshala portal.
NUEPA has established the National Centre for School Leadership (NCSL), which is conceptualizing and designing the Online Programme on School Leadership and Management using Moodle platform for School Heads. This e-learning course is envisioned as a Basic course and in the years to come NCSL would be designing Moderate and Advanced courses.
Two Days’ National Workshop – Chintan Shivir
This was organized by the Department of School Education and Literacy on 06-07 November, 2017. More than 350 participants from various NGOs, Private organizations, individual experts, State officials etc. participated.

Deliberations were on six themes – Digital Education for Students, Digital Education for Teachers, Value Education, Physical Education, Lifestyle Education and Experiential Education.
Presentations were made on these 6 themes to the Hon’ble Human Resource Development Minister by the participants. The recommendations are being reviewed and a detailed road map has also been prepared.
Ek Bharat Shresth Bharat – National Level Camp
A Social Science Exhibition cum National Integration Camp was organized by the Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan (KVS) at the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts, New Delhi from 31st October to 2nd November, 2017, to celebrate Ek Bharat Shresth Bharat. A total number of 1250 students of Kendriya Vidyalayas participated in this National level camp from all the 25 regions.

Enhanced allocation of funds under SSA for components promoting quality education
The allocation of SSA funds to States and UTs was revised and in 2016, 10% of the funds were allocated for components related to entitlements and promoting quality education in schools. In 2017 this was enhanced to 30%. It is expected this will further increase to around 40% by April, 2018. This is a huge departure from previous years when the funds were left untied and were utilised by States and UTs primarily for civil works and paying teacher’s salaries.
Annual grading of all States and UTs based on their achievements under the SSA and specific decisions taken during reviews by Hon’ble PM
The SHAGUN portal was launched in January 2017 to enable real time monitoring of the SSA components and various decisions on elementary education taken during the reviews by Hon’ble Prime Minister. The Online Grading of States and UTs, which measures their performance, was introduced in September/October 2017, and it will be expanded and refined further so that it is a valuable tool enabling States and UTs to assess and improve their performance.
NCERT to distribute over 6 crore textbooks
NCERT launched a portal in August, 2017 to facilitate individuals, schools, States and UTs to directly purchase textbooks. By 11th December 2017, NCERT has received orders from 3524 schools for 1.56 crore copies through this portal. Apart from this NCERT has received direct orders from NVS and other states/UTs for about 1.55 crore copies. Thus, so far (by 11.12. 2017) NCERT has received orders for about 3.11 crore copies. It is expected that NCERT will be printing and distributing over 6 crore textbooks by June, 2018.

Textbooks will be distributed through four Regional Production-cum-Distribution Centres already established at Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Guwahati and Kolkata apart from Delhi HQ. NCERT has also empanelled 905 vendors across the country for distribution of textbooks.
Awarding cleanest schools under Swachh Vidyalaya
During June 2016, DoSE&L launched the Swachh Vidyalaya Puraskar to recognize, inspire and celebrate excellence in sanitation & hygiene practice in Government Schools in the areas of water, sanitation, hand washing with soap, operations and maintenance, behavior change and capacity building.

A total of 2, 68,402 schools applied online through web portal/Mobile App for the Puraskar. The schools were selected at the district, state and national level. 643 schools were evaluated at the national level and National awards were given to 172 schools on 1st September 2017 including elementary and secondary schools in both urban and rural areas.
For 2018 the Puraskar has been extended to aided and private schools also and till 2nd week of November, 5.33 lakh Government, Aided and Private schools have submitted their applications for the Puraskar.
All schools to rollout the Automated Monitoring System at the school level under MDM
This department has put in place an automated system of data collection for real time monitoring of Mid Day Meal Scheme. Such data is being captured from schools with no cost to school Head Master/ Teacher.
Under the automated monitoring system, States/UTs have set up a suitable system of data collection (i.e. Interactive Voice Response System (IVRS)/SMS/Mobile Application/Web Application) from schools on a daily basis and using it for purpose of monitoring and timely follow up action.
All the States/UTs are pushing data on specific field in a predefined format on a real time basis to the Central Server maintained by NIC. Based on the data collected, various drill down reports are made available for real time monitoring of the scheme at National/State/District/Block level.
Improving universal access, gender parity and quality improvement in secondary education in 3479 Educationally Backward Blocks
An Innovation Fund has been set up under RMSA in order to encourage local innovative interventions for ensuring universal access, gender parity and quality improvement in secondary education in 3479 Educationally Backward Blocks. The fund is likely to be operationalised by December, 2017 and its impact should be visible by December, 2018.
So far, proposals from 23 States have been received under the project and a Video Conference with the concerned States/UTs Governments has been held under the Chairmanship of Secretary (SE&L) on 08.12.2017 in which the proposals have been considered.
Capturing Aadhaar based data of all 25 crore school students and creation of a Students Data Management and Information System (SDMIS) –
The Department is creating a database of all students in the country along with their Aadhaar details, which will help in reducing drop outs, duplicate enrolments, improve planning process and ensure efficient utilisation of resources.
Till date, data of nearly 21 crore students has been captured. By April, 2018, it is likely that the SDMIS will have captured data of all the 25 crore students, which will be updated on an annual basis thereafter.
Providing gender segregated toilets in all schools
The Prime Minister of India on 15th August 2014 announced that all government schools in the country should have toilets with separate toilets for girls within one year. The Department of School Education and Literacy launched “Swachh Bharat: Swachh Vidyalaya” campaign as a collaborative effort of the Central Government which provided funding through Centrally sponsored schemes of Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan, Swachh Bharat Kosh, and the States/Union Territories with Public Sector Undertakings and Private Corporates.
Under this initiative, 4, 17,796 toilets were constructed/made functional in 2, 61,400 schools in a period of one year up to 15th August 2015. With this, India achieved the target of providing 100% access to functional toilets in all government schools across the country.
The provision of toilet facilities in all schools has enhanced sanitation standards in schools leading to better health and hygiene among the children. ‘Swachh Vidyalaya’ was also recognized as one of the priority programmes for Prime Minister’s Excellence Award for 2016.
Scholarship:
- National Means-cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme (NMMSS)
- 3.80 lakh scholarships have been sanctioned for the last three years from 2014-15 to 2016-17.
- 3.59 lakh scholarships have been sanctioned for the current year 2017-18 as on 8.12.2017.
- National Scheme of Incentive to Girls for Secondary Scholarship (NSIGSE)
- 9.71 lakh incentive to girls have been sanctioned for the last three years from 2014-15 to 2016-17.
- 7.12 lakh incentives to girls have been sanctioned for the current year 2017-18 as on 8.12.2017.
Other achievements of the Department of SE&L
- A Bill for amending the no-detention provision under the RTE Act and allowing States to detain a student at Classes 5 and 8 has been introduced in the Lok Sabha.
- Board examinations made mandatory for 10th in all CBSE Schools.
- Mid Day Meal scheme offers food every day to 9.78 crore students in 11.40 lakh schools and 25.38 lakh cooks are employed in preparing it.
- 3 Crore illiterates became literate and passed the literacy test in adult literacy campaign.
- 93 Kendriya Vidyalayas (KVs) started during last 3 years and 19 KVs are to be started shortly.
- 62 new Navodaya Vidyalas sanctioned.
NEW EDUCATION POLICY (NEP)
In view of the vastly transformed landscape of education in India in terms of coverage, content and delivery systems, a New Education Policy is being formulated after nearly 30 years.
MHRD has embarked on an unprecedented collaborative, multi- stakeholder and multi-pronged consultation process. The consultative process has reached out to individuals across the country through more than 2.75 lakh direct consultations while also taking online inputs. The online consultation process was undertaken on www.MyGov.in portal from 26th January, 2015 to 31st October, 2015 and nearly 29000 suggestions were received on the 33 identified themes.
Over 200 thematic national workshops were held with a youth survey by the UNESCO Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Education for Peace, Sustainable Development. With regard to School Education, 1, 10,623 villages, 3250 Blocks, 725 Urban Local Bodies from 340 districts of 19 States have uploaded their Grassroots Consultation Reports on www.MyGov.in portal.
Similarly, 2741 Blocks, 962 Urban Local Bodies from 406 districts in 20 States have done the same with regard to Higher Education. A Committee for Evolution of the New Education Policy has been constituted to examine the outcome documents, recommendations & suggestions received and formulate a draft National Education Policy as well as a Framework for Action.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)
It was launched on 29th September 2015, ranks institutions based on objective and verifiable criteria. It has been made available separately for Engineering, Management, Pharmaceutical, Architecture, Humanities, Law and for Universities.

The first ranks were declared on 4th April 2016. More than 3,500 institutions have participated in the exercise, making it the highest participated ranking exercise in the World. The second India Rankings were released in April 2017.
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds)
The Ministry of HRD, has embarked on a major and new initiative called ‘Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds’ (SWAYAM), which will provide one integrated platform and portal for online courses, using information and communication technology (ICT) and covering all higher education subjects and skill sector courses to ensure that every student in the country has access to the best quality higher education at affordable cost.
The SWAYAM IT platform is indigenously developed that facilitates hosting of courses, taught in classrooms from 9th class till post-graduation in a number of disciplines that can be accessed by anyone, anywhere at any time. The three cardinal principles of Education Policy viz., access, equity and quality shall be achieved by providing high quality e-content to all learners in the country through SWAYAM.
Courses delivered through SWAYAM are available free of cost to the learners and are delivered by best of the teaching fraternity. Hon’ble President of India had officially launched SWAYAM, on July 9th, 2017. At present about 750 MOOCs (Massive open online courses) courses are listed on SWAYAM and about 330 MOOCs are running, wherein about 6 Lakhs (5, 92,178) students have registered for these courses.

(On the auspicious occasion of “Guru Purnima” on 9th July, 2017, the Hon’ble President of India Shri Pranab Mukherjee launched the SWAYAM)
SWAYAM PRABHA
It is an initiative to provide 32 high quality educational channels through DTH (Direct to Home) across the length and breadth of the country on 24X7 basis. This would enable to deliver e-education in a most cost effective manner.
The Department of Space has allotted two Transponders of GSAT-15 for the same. The subscribers of free DTH service of Doordarshan (Free dish) would be able to view these Educational channels using the same set Top Box and TV. No additional investment would be required.
These educational programmes delivered over DTH shall also be made available at YouTube as archival data. The information related to channel schedules; subject, archival link etc are available on SWAYAM Prabha portal (https://swayamprabha.gov.in/) which is developed by INFLIBNET Gandhinagar.

(Launch Of “Swayam”, “Swayam Prabha DTH Channels” & “National Academic Depository” By Hon’ble President Of India During “National Convention On Digital Initiatives” organized By MHRD From 8th July to 10th July 2017 At Vigyan Bhavan, New Delhi).
National Academic Depository (NAD)
The Government of India is committed towards bringing administrative and academic reforms using technology for delivery of efficient services to all stakeholders. A step in this direction is the initiative of digital depository of academic awards known as National Academic Depository (NAD).
The NAD has been launched by Hon’ble President of India on 9th July, 2017. NAD is an online store house of academic awards (degrees, diplomas, certificates, mark-sheets etc) lodged by the academic institutions / school boards / eligibility assessment bodies in a digital format.
NAD is on 24X7 online mode for making available academic awards and help in validating their authenticity, their safe storage and easy retrieval. As on 24th November, 2017, 74.81 lakh records have been uploaded on the NAD Portal
National Digital Library (NDL)
Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) is establishing the National Digital Library (NDL) under the National Mission on Education through Information and Communication Technology (NMEICT) with the objective to host a national repository of existing e-content available across educational institutions in the country and e-content developed under NMEICT. IIT Kharagpur has been entrusted to host, coordinate and set-up National Digital Library (NDL) of India towards building a national asset.
The objective of the project is to integrate all the existing digitized and digital contents across educational and cultural institutions/bodies to provide a single-window access to different groups of users ranging across the entire population.
NDL Portal (https: //ndl.iitkgp. ac.in) went live in February 2016 with users from selected CFTIs (Centrally Funded Technical Institutes), opened to all in February 2017 (with release of Mobile App), with daily website hits: ~30K. User base – Registered: 17+ Lakhs, Active: 7+ Lakhs, Content items, 72 Lakhs, Sources: 142 and IDR Sources: 85. Mobile App (Android): Launched in January, 2017, 3.5 Lakhs download and daily Android hits: ~20K. Training & awareness development IDR workshops: 19 and user workshops.
Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA)
The Cabinet considered and approved the proposal of establishment of HEFA in its meeting dated 12th September 2016. In order to give a big push for building up robust higher educational institutions, the Cabinet has approved creation of the Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA) with Government equity of Rs. 1,000 Cr.
The creation of HEFA will enable major investments for creation of high quality infrastructure in premier educational institutions. The HEFA would be formed as an SPV within a PSU Bank/Government-owned-NBFC (Promoter). It would leverage the equity to raise up to Rs. 20,000 Cr for funding projects for infrastructure and development of world class Labs in IITs/IIMs/NITs and such other institutions.
The HEFA would finance the academic and research infrastructure projects through a 10-yr loan. The principal portion of the loan will be repaid through the ‘internal accruals’ of the institutions. The Government would service the interest portion through the regular grant assistance.
All the Centrally Funded Higher Educational Institutions would be eligible for joining as members of the HEFA. For joining as members, the Institution should agree to escrow a specific amount from their internal accruals to HEFA for a period of 10 years. This secured future flows would be securitised by the HEFA for mobilising the funds from the market. Each member institution would be eligible for a credit limit as decided by HEFA based on the amount agreed to be escrowed from the internal accruals.
The HEFA would be jointly promoted by the identified Joint Promoter, Canara Bank and the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) with an authorized capital of Rs.2,000 crore. The Government equity would be Rs.1, 000 crore.
The HEFA would also mobilize CSR funds from PSUs/Corporates, which would in turn be released for promoting research and innovation in these institutions on grant basis.
Canara Bank was identified and appointed as Joint Venture partner on 29.12.2016 for establishment of Higher Education Financing Agency (HEFA) to manage the financing agency incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 and also registered with RBI as NBFC. An MOU was signed on 9th February, 2017 between MHRD and Canara Bank for the same. Later, Joint Venture Agreement (JVA) was also signed between MHRD and Canara Bank on 16th March, 2017.
The investment in the equity of the JVC by MHRD, GOI and Canara Bank shall be in the following proportion:
|
S. No. |
Party |
Contribution (in Rs.) |
Shareholding Percentage |
|
1. |
GoI |
Rs. 1000,00,00,000/- |
90.91 |
|
2. |
Canara Bank |
Rs. 100,00,00,000/- |
9.09 |
HEFA has now been incorporated as Section 8 Company under the Companies Act, 2013 on 31.5.2017. The following subscription of equity has so far been made to HEFA by MHRD and Canara Bank:
|
Name of the Subscriber |
Amount (Rs. In Crores) |
|
GoI, MHRD, Department of Higher Education |
250 |
|
Canara Bank |
50 |
|
Total |
300 |
The first and second meeting of the Board of Directors of HEFA was held on 12-06-2017 and 11-8-2017 respectively. HEFA is now functional and institutes have accordingly been informed along with format of application to take the benefit of HEFA on 16 -8-2017.
The third meeting of the Board of Directors of HEFA was held on 29-11-2017 in which following loan applications to HEFA were considered:
|
S. No. |
Name of the Institution |
Proposed Loan amount (Rs. in Crore) |
|
1 |
IIT – Kanpur |
391 |
|
2 |
IIT – Delhi |
200 |
|
3 |
IIT – Kharagpur |
500 |
|
4 |
IIT- Madras |
300 |
|
5 |
IIT- Bombay |
521 |
|
6 |
NIT – Surathkal |
80 |
|
|
Total |
1992 |
INDIA SURVEY ON HIGHER EDUCATION
All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) was initiated in 2011 in which data for the year 2010-11 were collected. The survey was utmost necessary as none of the sources of data on Higher education gave a complete picture of higher education in the country. Also, there were many important parameters on which data were required for policy making but either no data was available or incomplete data was available.
For the first time all the major Stakeholders in Higher Education such as Medical Council of India, University Grants Commissions, All India Council for Technical Education as well as State Governments have participated in for the data collection exercise. The entire survey was conducted through electronic mode and a dedicated portal www.aishe.gov.in was developed for this purpose, thus making the exercise completely paperless.
The survey covers all the Institutions in the country engaged in imparting higher education. Data are being collected on several parameters such as teachers, student enrolment, programmes, examination results, education finance, infrastructure etc. Indicators of education development such as Institution Density, Gross Enrolment Ratio, Pupil-teacher ratio, Gender Parity Index etc. are calculated from the data collected through AISHE. These are useful in making informed policy decisions and research for development of education sector.
During AISHE 2016-17, 96.6% University, 92.1% Colleges and 72.4% Stand-Alone Institutions uploaded the data on the portal. Final report for the AISHE 2010-11 to 2015-16 are available on MHRD website. Survey for the year 2016-17 has been completed & Survey for the year 2017-18 will soon be launched.
SWACHHTA PAKHWADA
An exercise called ‘Swachhta Rankings” of Higher Educational Institutions were held on 14th September 2017. More than 3000 institutions participated in the online submission of their levels of campus cleanliness based on some key parameters like toilet adequacy, water purity & supply, hostel kitchen facilities & cleanliness, campus greenery, method of waste disposal, garbage cleaning systems etc. The best institutions in 5 categories were awarded.

To coincide with the Swachhta Pakhwada of the Department, under the Unnat Bharat Abhiyan programme, District Collectors were asked to complete Open defecation free (ODF) with facility for solid and liquid waste management in at least 1 village adopted by the educational institution in their district. 5 Collectors of Ajmer, Warangal, Telangana, Jhabua & Indore were the top 5 Collectors who completed the task in time and were awarded at the function on 14th September 2017. More than 1400 families in the villages benefited from this campaign.
RESEARCH PARKS
Five new Research Parks at IIT Delhi, IIT Guwahati, IIT Kanpur, IIT Hyderabad, and IISc Bangalore at a total cost of Rs.75.00 crore each have been approved by the Government. Approval has also been accorded for continuation of two already approved Research Parks at IIT Bombay and IIT Kharagpur at a cost of Rs.100 crore each.
The Research Park at IIT Gandhinagar at a total cost of Rs.90 crore is being funded by the Department of Science & Technology
IMPRINT INDIA
IMPRINT India is an effort to direct research in the premier institutions into areas of social relevance. Under this, 10 domains have been identified which could substantially impact the living standards of the rural areas: (1) health care technology, (2) energy security, (3) rural urban housing design, (4) Nano technology, (5) water/river system, (6) advanced materials, (7) computer science and ICT, (8) manufacturing technology, (9) advanced security and (10) environment/climate change. Each of these domains is coordinated by one IIT.
More than 2,600 research proposals have been submitted by scientists in the priority areas of these domains. These have been examined by eminent scientists and 259 proposals for Rs. 595.89 crore have been approved for implementation. 142 research projects costing Rs. 323.17 crore with joint funding by MHRD and various participating Ministries / departments are currently under execution under IMPRINT – I. IMPRINT-II is under process for approval.
UCHCHTAR AAVISHKAR ABHIYAAN
The scheme was launched to promote industry-specific need-based research so as to keep up the competitiveness of the Indian industry in the global market. All the IITs have been encouraged to work with the industry to identify areas where innovation is required and come up with solutions that could be brought up to the commercialization level.
Under the UAY, it is proposed to invest Rs. 250 crores every year on identified projects proposed by IITs, provided the Industry contributes 25% of the project cost. For the year 2016-17, (92) projects for Rs. 285.15 crore have been approved for implementation.
IIT Madras is the National Coordinator of the scheme. (160) proposals have been received of which industry has agreed to contribute Rs. 156 Cr, making this one of the biggest ever industry-academia partnership. These research projects are expected to result in registration of patents.
Other Initiatives
- Improving Gender Balance in IITs: For improving Gender Balance in IITs, the IIT Council in its 51st meeting held on 28.04.2017, on the basis of the recommendations of a JAB Sub Committee, and decided to increase female enrolment in B.Tech. programmes of IITs from the current 8% to 14% in 2018-19, 17% in 2019-20 and 20% in 2020-21 by creating supernumerary seats.
- Premier Testing Facility: The Union Cabinet in its meeting held on 10.11.2017 approved creation of the National Testing Agency (NTA) as an autonomous and self-sustained premier testing organization to conduct all entrance examinations for higher education institutions in the country.
- Several welfare measures viz. Anti-Ragging Cell, Anti-discrimination Cell, Gender Sensitization Cell, Internal Complaints Committee for prevention of Sexual Harassment & Barrier Free access for specially abled students in all places have been introduced.
- Six new IITs at Jammu, Bhilai, Goa, Dharwad, Tirupati and Palakkad were established and operationalized at a total cost of Rs.1411 crore.
- The proposal for construction of permanent campuses of these IITs was approved by the Union Cabinet in November, 2017 at a total cost of Rs.7002.42 crore for Phase-A.
- Global Initiative for Academics Network (GIAN): The GIAN programme brings together foreign and Indian faculties to teach an academic course that provides the credit to participating students selected from the world’s leading academic institutions. Under this Scheme, foreign schemes are coming and conducting courses, out of which 802 courses have been completed. In 2017-18, a total of 156 courses have been conducted till now.
- Smart India Hackathon 2017: First time India organized Smart India Hackathon 2017 with participation of more than 42,000 engineering students working on 600 problem statement to all digital solutions from 30 ministries. Second Smart India Hackathon 2018 has been announced and about one lakh engineering students are expected to participate.
- Wi-Fi under implementation in 38 Central Universities.
- University Grants Commission (Open and Distance Learning) Regulations, 2017 have been recently notified in the month of June, 2017 keeping in view the urgent need of appropriate regulations for monitoring of higher education through the open and distance mode. The open and distance learning system in India has emerged as an important mode for providing education to diverse sections of society. These regulations provide clear directions and instructions for HEIs proposing to offer UG and PG courses through the ODL mode, along with the mechanism of approvals, assessment and monitoring.
- UGC (Institutions of Eminence Deemed to be Universities) Regulations, 2017 have been notified to create a distinct category of Deemed to be Universities, called Institutions of Eminence Deemed to be Universities, which would be regulated differently from other Deemed to be Universities so as to evolve into Institutions of world class in reasonable time period. Also, in order to assist Indian Higher Education Institutions to get a rank within the top 100 in globally renowned rankings, UGC has invited applications under the Institutions of eminence schemewherein 10 institutions from the government and 10 institutions from the private sector are to be selected. Government Institutions will get financial assistance of 1000 crores over a period of five years in addition to the grant already being received. The institutions selected from the private sector will have complete autonomy to promote innovation and creativity expected to result in producing competent graduates for the development of the country.
Major Legislative Reforms
- IIT Public Private Partnership Bill – Lok Sabha passed the Indian Institute of Information Technology Public Private Partnership Bill 2017, on 26th July 2017, that seeks to allow 15 IIITs established on a PPP model to grant degrees
- The IIIT Bill 2014 was notified in the Gazette on 05.01.2015. The Bill which was approved by the Cabinet in August, 2012 and introduced during the Budget Session had lapsed with the dissolution of the Lok Sabha. The Bill, provides independent statutory status to the four existing IIITs in Allahabad, Gwalior, Jabalpur and Kancheepuram, which are funded by the Central Government, as also to declare them to be institutions of National Importance.
- National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) which was launched on 29th September 2015, ranks institutions based on objective and verifiable criteria. It has been made available separately for Engineering, Management, Pharmaceutical, Architecture, Humanities, Law and for Universities as a whole. The first ranks were declared on 4th April 2016. More than 3,500 institutions have participated in the exercise, making it the highest participated ranking exercise in the World. The second India Rankings were released in April 2017.
- Passing of IIM Bill, 2017 by Lok Sabha Indian Institutes of Management are the country’s premier institutions imparting best quality education in management on globally benchmarked processes of education and training in management. IIMs are recognized as world-class management Institutions and Centers of Excellence and have brought laurels to the country. All IIMs are separate autonomous bodies registered under the Societies Act.
Being societies, IIMs are not authorized to award degrees and, hence, they have been awarding Post Graduate Diploma and Fellow Programme in Management. While these awards are treated as equivalent to MBAs and Ph.D, respectively, the equivalence is not universally acceptable, especially for the Fellow Programme. Therefore, after approval of the Cabinet, IIM Bill, 2017 was introduced in the Lok Sabha, under which the IIMs would be declared as Institutions of National Importance and which will enable them to grant degrees to their students. Bill has been passed in both the Houses of Parliament.
Salient Features of IIM Bill
Apart from authority to grant degrees, the Bill provides for complete autonomy to the Institutions, combined with adequate accountability. Management of these Institutions would be Board driven, with the Chairperson and Director of an Institution to be selected by the Board. A greater participation of experts and alumni in the Board is another of the important features in the Bill. Provision has also been made for presence of women and members from Scheduled Castes/Tribes in the Board. The Bill also provides for periodic review of the performance of Institutions by independent agencies, and placing the results of the same on public domain. The Annual Report of the Institutions will be placed in the Parliament and CAG will be auditing their accounts. There is also a provision of a Coordination Forum of IIMs, chaired by an eminent person, as an advisory body.
Important Achievements of NCERT
![]()
- Inclusive Education: The Council has developed the Tactile Map Book in Geography for students with visual impairments, Barkha Reading Series for All consisting of 40 booklets with additional features to aid early reading in inclusive settings has been developed in print and digital forms.
- Performance Indicators: NCERT has developed a Framework for Performance Indicators (PINDICS) for elementary school teachers and shared with States/UTs. NCERT has made PINDICs on-line.
- Rashtriya Avishkar Abhiyan (RAA): NCERT has developed Guidelines for the creation of State Resource Group for RAA. This has been shared with the states/UTs.
- Textual Material on Yoga: The Textual Materials on Yoga for students of Upper Primary and Secondary stages in English, Hindi and Urdu have been developed by NCERT.
- Veer Gatha: NCERT has developed “Veer Gatha” highlighting the sacrifices and patriotism of the war heroes of the country.
- NCERT has brought out publications on Sanitation, Cleanliness, Hygiene and Environmental Protection for students and teachers.
- North East India-People, History and Culture- a publication has been brought out by the NCERT.
- Publication and Dissemination Textbooks- More than 4.25 million copies of various NCERT publications in English, Hindi and Urdu have been brought out.
- Vocational Education: Under NSQF, the NCERT has developed students’ workbooks and modules for various job roles in different sectors such as Construction, Organic farming, Floriculturist, Micro Irrigation, Junior Software Developer, Marketing and Sales Management, etc. The NCERT is also in the process of developing curricula and student’ workbooks for another 100 job roles.
- Contribution in Pre-service Teacher Education: NCERT’s innovative and integrated pre-service teacher education courses i.e., B.Sc. B.Ed. (four year), B.A. B.Ed.(four year) and B.Ed. (two year) have now been replicated across the country since 2015.
- NCERT has conducted Yoga Olympiad and also National Role Play, Folk Dance Competition and Youth Festival for promoting health, yoga and life skills. In these programmes students and teachers from most of the states/UTs took part.
- The Council organized 44th Jawaharlal Nehru National Science, Mathematics and Environment Exhibition (JNNSMEE) at Bhopal from 10 to 16 November 2017.
- Kala Utsav: It is being organized in January, 2018 at Bhopal
Specific Targets to be achieved period up to March 2018
- Implementation of learning outcomes across the States/UTs.
- Development of e-content and digital books in all the subject areas for all the classes.
- Conducting school achievement survey for class X.
- Conducting researches related to school education and teacher education.
- Offering pre-service teacher education programmes in all regions.
- Organising need based in-service teacher professional development programmes in different subject areas across the country.
- Organization of Audio-video Festival and ICT Mela.
- Establishment of a Centre for Popularisation of Science.
- Enhancing International Educational Cooperation.
- Organising activities for promoting innovative practices.
- Organising National Outreach Programme Workshop on Practices of Inclusion.
Initiatives taken by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan

- Union HRD Minister launches Swasth Bachche-Swasth Bharat Programme of KVS – Union Minister for HRD, Prakash Javadekar inaugurated the “Swasth Bachche Swasth Bharat” programme of Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan at KV NAD, Aluva (Kochi) on 21st August 2017. The Minister unveiled the Physical Health and Fitness Profile card for more than 12 lakh students of KVS. The KVS had already done a pilot in Patna and Chandigarh Region during the academic year 2016-17. Looking at the positive results on health and fitness of School going children, the KVS decided to implement it in all the KVs of the country. Activities under this ambitious programme are selected to measure various components of physical fitness of all the students in the age group of 5 to 8 years and 9 to 19 Years. Balanced emphasis is laid down on- Diet, Personal Hygiene and Clean Environment, Suggested Daily Routine and Yoga for Peace & Harmony.

- Sh. Prakash Javadekar laid foundation stone of K.V. Shahdara – Hon’ble HRD Minister Sh. Prakash Javadekar laid the foundation stone of Kendriya Vidyalaya, GT Road Shahdara in North East Delhi on 23rd February 2017. This is the first K.V. in this area. Hon’ble Minister formally laid the foundation of the school and unveiled the plaque before the huge gathering. Hon’ble M.P. of North East Delhi Sh. Manoj Tiwari, Commissioner, K.V.S. Sh. Santosh Kumar Mall were the guests of honour on this occasion. KVS Additional Commissioner (Admin) Sh. G.K. Srivastava and Additional Commissioner (Acad) Sh. U.N. Khaware were present as the special guests on the dais.

Education
Supreme Court’s Landmark Judgment for Schools: Menstrual Health is a Fundamental Right
In a transformative judgment delivered on January 30, 2026, the Supreme Court of India has unequivocally placed menstrual health within the ambit of fundamental rights, linking dignity, education, and equality in classrooms across the country. This ruling goes beyond infrastructure mandates to address stigma, awareness, and school culture—reshaping how institutions must support adolescent girls. ScooNews breaks down what the judgment says and what it now requires every school leader to do.

In a landmark judgment that firmly connects constitutional law with everyday classroom realities, the Supreme Court of India has declared menstrual health a fundamental right, placing it squarely within the ambit of Article 21 (Right to Life with dignity) and Article 21A (Right to Education).
Delivered on January 30, 2026, by a Bench of Justices J.B. Pardiwala and R. Mahadevan, the ruling in Jaya Thakur vs Union of India goes far beyond symbolic recognition. It lays down clear, enforceable obligations for schools—government and private alike—transforming menstrual hygiene from a welfare measure into a constitutional duty.
For school leaders, this judgment marks a decisive shift: menstrual dignity is no longer optional, charitable, or discretionary. It is a core educational standard.
Why the Court Intervened
The Court acknowledged what educators and parents have long known but systems have often ignored:
lack of menstrual hygiene support is a direct barrier to girls’ education.
Absenteeism, discomfort, fear of embarrassment, inadequate toilets, and social stigma collectively push many girls out of classrooms—sometimes temporarily, sometimes permanently. By recognising menstrual health as integral to dignity and learning, the Court affirmed that no girl should ever have to choose between her education and her period.
What the Court Said
The judgment rests on three powerful principles:
- Menstrual health is inseparable from dignity and bodily autonomy, which are central to the Right to Life.
- Education cannot be meaningful if menstruation becomes a reason for exclusion, discomfort, or discrimination.
- Infrastructure alone is insufficient—social stigma, silence, and male insensitivity must also be addressed.
In a telling observation, the Court noted that “ignorance breeds insensitivity” and warned that menstrual facilities will remain underused unless schools actively dismantle stigma.
What Schools Must Now Do
The Court’s directions are both practical and time-bound, with a three-month implementation window. They fall into two clear buckets: infrastructure and ecosystem change.
-
Physical Infrastructure: The Non-Negotiables
All schools—government and private—must ensure:
- Free provision of biodegradable sanitary pads, with a preference for discreet access such as vending machines.
- Functional, gender-segregated toilets with running water, soap, privacy, and regular maintenance.
- Disabled-friendly sanitation facilities, ensuring inclusivity for all students.
- Safe and hygienic disposal systems, including covered bins and environmentally compliant solutions.
- Creation of a Menstrual Hygiene Management (MHM) Corner stocked with emergency supplies such as spare uniforms, innerwear, and hygiene kits.
The Court made it clear that absence of these facilities amounts to denial of constitutional rights.
-
Cultural & Educational Shift: The Ecosystem Solution
Perhaps the most progressive aspect of the ruling is its insistence that menstrual health is not a “girls-only issue.”
Schools are now expected to:
- Sensitise boys about menstruation as a normal biological process, removing shame, jokes, and harassment from school spaces.
- Train male teachers and staff to respond empathetically to menstruation-related needs, without interrogation or embarrassment.
- Integrate age-appropriate, gender-responsive content on menstruation and puberty into health and wellness curricula, in line with NCERT/SCERT guidance.
- Foster a school culture where menstruation is discussed openly, respectfully, and without euphemism.
The message is unambiguous: pads without dignity do not equal access.
A Clear Warning to Private Schools
The Supreme Court issued a firm caution to private institutions:
non-compliance can lead to de-recognition.
By linking menstrual hygiene directly to the Right to Education, the Court has placed accountability squarely on school managements. Compliance is no longer a matter of reputation—it is a legal obligation.
Why This Judgment Matters
This ruling represents a rare moment where law, education, health, and gender equity intersect meaningfully.
It acknowledges that:
- Equality in education requires both facilities and acceptance
- Silence around menstruation is itself a form of discrimination
- Boys and men must be part of the solution—not bystanders
For school leaders, this is an opportunity to lead with empathy, foresight, and constitutional responsibility.
The Bottom Line
The Supreme Court has drawn a clear line:
menstrual dignity is a right, not a favour.
Schools that act decisively now will not only meet compliance requirements but will also create environments where every student feels safe, supported, and respected—every day of the month.
Education
Beyond the First Bell: 5 Key Takeaways for School Leaders from Economic Survey 2025–26
The Economic Survey 2025–26 signals a definitive pivot in India’s education strategy. While infrastructure goals have largely been met, the focus now shifts to bridging the higher secondary gap and fixing a vocational training deficit that remains under 1%. For school leaders, success is no longer measured by enrolment, but by measurable competencies, digital wellness, and global readiness.

The Economic Survey 2025–26, tabled in Parliament on January 29, 2026, presents an arresting paradox. India has successfully built one of the world’s largest schooling systems—educating 24.69 crore students—yet only six out of ten learners complete higher secondary education.
For school leaders, the Survey’s message is unambiguous: the national focus is shifting from inputs (getting children into school) to impact (ensuring they learn, progress, and stay). What follows are five findings that matter most inside the school gate.
1. The “Leaky Bucket”: Transitioning from Middle to Secondary
While primary enrolment is near-universal (90.9%), the Survey identifies a structural drop-off after Class 8.
Reality check: The Net Enrolment Rate (NER) at the secondary level stands at just 52.2%.
The rural gap: Only 17.1% of rural schools offer secondary education, compared to 38.1% in urban areas. Longer travel distances and higher costs lead to significant transition losses.
What this means for schools:
- The Survey strongly backs Composite Schools (K–12 models) to reduce dropout risk.
- Schools serving Classes 6–10 should prioritise transition counselling, parent engagement, and academic bridging.
Leader takeaway: Retention, not recruitment, is now the real leadership challenge.
2. Learning Outcomes: The PARAKH Recovery Story
Post-pandemic recovery is visible, particularly in foundational years—but learning quality remains uneven across states and school types.
Encouraging gains:
- Grade III Mathematics proficiency has risen to 65%, up from 42% in 2021.
What’s next:
- The Survey proposes a PISA-like, competency-based assessment at the end of Class 10, signalling a decisive move away from rote learning.
What this means for schools:
- Internal assessments will increasingly need to mirror National Achievement Survey (NAS) benchmarks.
- Performance-linked accountability is no longer hypothetical—it is imminent.
Leader takeaway: Assessment literacy will become as important as curriculum delivery.
3. The Skilling Crisis: Addressing the 1%
Perhaps the most candid section of the Survey exposes a stark education–employment mismatch.
The 1% problem: Only 0.97% of students aged 14–18 have received formal institutional skilling.
Structural issue: Education and skilling continue to operate in parallel silos, leaving most learners academically qualified but workplace-unready.
What this means for schools:
- Vocational exposure must be embedded within Classes 9–12, not offered as an optional or external add-on.
- Partnerships with local industry, NSDC-aligned providers, and apprenticeship platforms will become critical.
Leader takeaway: Schools that integrate skills early will future-proof their students—and their relevance.
4. Digital Exposure: Pedagogy vs. Addiction
In a significant first, the Economic Survey flags digital addiction as a threat to student wellbeing, learning focus, and social capital.
The paradox:
- 89% of rural youth now have access to smartphones.
- 75% use them primarily for social media, contributing to sleep deprivation, reduced attention spans, and anxiety.
What this means for schools:
- The Survey recommends introducing a Digital Wellness Curriculum, covering:
- Screen-time literacy
- Cyber safety
- Responsible AI and social media use
Leader takeaway: Digital fluency must now include digital restraint.
5. Global Ambitions: Stemming the Student Exodus
India is on track to become the world’s largest source of international students, with outbound numbers expected to reach 18 lakhs by 2025. Yet, international students form just 0.10% of domestic enrolment.
The strategy:
- The Survey promotes “Internationalisation at Home”—inviting foreign campuses, enabling joint degrees, and ensuring mutual recognition of qualifications.
Key enablers already in place:
- Academic Bank of Credit (ABC)
- APAAR IDs (with 2.2 crore already issued)
What this means for schools:
- Senior secondary students should be actively guided on credit portability, interdisciplinary choices, and global pathways.
Leader takeaway: Global readiness is no longer optional—it is systemic.
The Bigger Shift: Learning Over Schooling
The Economic Survey 2025–26 makes one thing clear: India’s education mission has entered its second phase. Infrastructure and access have largely been achieved. The next frontier is retention, relevance, and real learning.
For school leaders, success will no longer be measured by enrolment numbers alone, but by:
- Meaningful learning outcomes
- Student wellbeing and digital balance
- Employability and global mobility
The bell has rung. What happens after it now matters more than ever.
News
Inclusive Education Summit 2026: Designing the Future of “Learner-Centric” Education
The Inclusive Education Summit 2026 gained significant momentum on Day 2, moving from policy vision to practical implementation. Focused on “Inclusive Education Pathways,” the session highlighted the transformative PRASHAST 2.0 digital screening tool and groundbreaking state models from Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal. Industry experts from NCERT, NIOS, and UNICEF emphasized a critical shift from mere “classroom access” to “academic achievement” through Universal Design for Learning (UDL). By integrating assistive technology, specialized teacher training, and inclusive sports, the summit is redefining how India supports Children with Special Needs, ensuring that every learner has a personalized path to success.
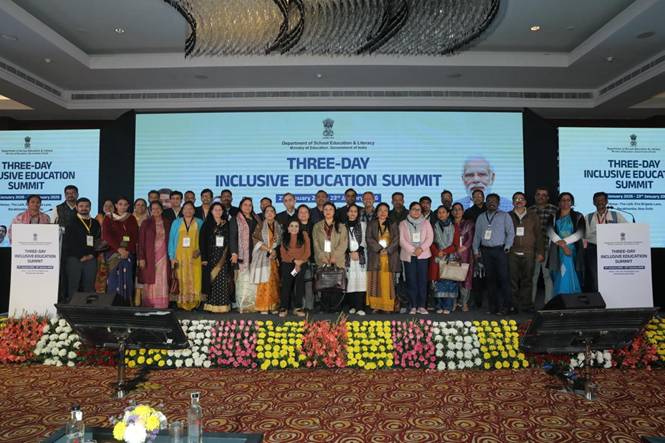

New Delhi | January 22, 2026 – As the three-day Inclusive Education Summit 2026 enters its second day, the conversation has shifted from policy theory to tangible pathways. Organised by the Ministry of Education (DoSEL) at The Lalit, New Delhi, the summit is setting a high bar for how India intends to align with NEP 2020 and the RPwD Act 2016.
While Day 1 set the stage, Day 2 focused on the “how”—the digital tools, pedagogical shifts, and inter-sectoral collaborations required to ensure no child is left behind.

1. Digital Transformation: PRASHAST 2.0 Takes Center Stage
The most significant tech highlight was the unveiling and live demonstration of PRASHAST 2.0. Introduced by Ms. Ira Singhal (Deputy Secretary, DoSEL), this revamped disability screening tool is designed to move the needle on early identification.
-
Integrated Ecosystem: The tool now integrates directly with UDISE+, allowing for real-time tracking and data-driven interventions.
-
The Goal: Moving away from guesswork toward evidence-based planning at the school level.
2. Scalable Success: Lessons from the States
The summit showcased that inclusion isn’t just a national mandate; it’s a local reality. Two states shared blueprints that other school leaders can learn from:
-
Andhra Pradesh: Highlighted the transformative impact of their 125 Autism Support Centres.
-
West Bengal: Showcased a model of strengthening resource rooms to provide child-centric interventions immediately after identification.
3. Reimagining Pedagogy and Teacher Training
A recurring theme throughout the day was that “access” to a classroom is not the same as “achievement” in learning.
-
NCERT’s New Framework: Dr. Sharad Sinha presented an 8-module framework designed to mainstream inclusive pedagogy. The focus is on training teachers to manage diverse classrooms as the norm, not the exception.
-
NCTE & NIOS: Discussions led by Prof. Pankaj Arora (NCTE) and Prof. Akhilesh Mishra (NIOS) highlighted the shift toward flexible admission systems, accessible e-content, and a national mentoring mission to support inclusive practices in everyday schooling.
4. Beyond the Classroom: Sports and Language
Inclusion was also discussed through the lens of holistic development:
-
Inclusive Sports: Representatives from Special Olympics Bharat and the Indian Blind Sports Association emphasized that sports are a primary vehicle for building confidence and independence in children with intellectual and visual impairments.
-
The Power of Words: Ms. Amita Tandon (UNICEF) reminded delegates that disability-inclusive language is the first step in reducing stigma.
Innovator’s Spotlight: Prof. Bharti Kaushik (CIET, NCERT) showcased the “Kitaab Ek, Padhe Anek” project. Based on Universal Design for Learning (UDL), this initiative allows a single textbook to offer multiple accessible pathways, proving that “one size fits all” is a thing of the past.

Key Takeaways for School Leaders
As the summit concludes its second day, the message to the Indian education fraternity is clear:
-
Screen Early: Use tools like PRASHAST 2.0.
-
Train Often: Move toward inclusive pedagogy, not just special education.
-
Build Infrastructure: Invest in resource rooms and UDL-compliant materials.
Education
AI to Become a Core Subject from Class 3: India’s Big Leap Toward a Future-Ready Generation
In a landmark move to make India’s school system future-ready, the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, has announced that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computational Thinking (CT) will be introduced as part of the school curriculum from Class 3 onwards, beginning in the academic year 2026–27.
The initiative marks a major step in preparing students for an AI-driven world, ensuring early exposure to technological literacy, ethics, and problem-solving. The curriculum, currently being developed through a consultative process with CBSE, NCERT, KVS, NVS, and States/UTs, will fall under the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) 2023, in alignment with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
A stakeholder consultation held on 29th October 2025 brought together education leaders, including Prof. Karthik Raman from IIT Madras, who heads the CBSE expert committee responsible for shaping the AI & CT curriculum. The focus is on designing a meaningful, inclusive framework that integrates AI not as an advanced elective but as a foundational skill — comparable to literacy and numeracy in importance.
Shri Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, DoSE&L, emphasised that AI education should be viewed as a universal skill closely linked to real-world applications. “Every child’s distinct potential is our priority. Policymakers must define minimum thresholds and evolve them with changing needs,” he said. He also stressed on teacher training as the backbone of successful implementation, with modules under NISHTHA, and resource materials being prepared by NCERT and CBSE.
The Ministry plans to release AI handbooks and digital resources by December 2025, followed by a grade-specific rollout supported by video-based learning materials and structured training.
By embedding AI education from the foundational years, India aims to nurture a generation that understands, creates, and applies technology ethically — transforming the vision of AI for Public Good into everyday classroom reality.
Education
Dharav Utsav to Celebrate Rajasthan’s Cultural Heritage and Local Talent

Education
Beyond the Syllabus: School Teachers’ Insights on Project-Based Learning

How classroom experiences are being reshaped through projects, inquiry, and authentic learning
As the classroom grows beyond the boundaries of textbooks and blackboards, so too does the role of the teacher, and the very meaning of learning. Project-Based Learning (PBL), once considered a niche innovation, is increasingly being embraced by educators across schools in India. But what happens when PBL moves from theory to practice?
To answer this, we turned to the people at the heart of the learning experience: teachers.
In conversations with educators from diverse school contexts, one theme was clear: PBL is not just a teaching strategy; it’s a transformation in how students learn, engage, and grow.
From Worksheets to Real-World Work: How PBL Differs from Traditional Homework
One of the clearest contrasts teachers observed was how PBL moves learning from repetition to relevance. Traditional homework often reinforces information through rote exercises. PBL, by contrast, asks students to apply their knowledge to solve problems, create products, or investigate issues that matter to them.
One teacher shared how using PBL to raise student awareness about water pollution was a hit in the class. Instead of just assigning problems, the students were made to create awareness posters, conduct surveys in their neighbourhood, and suggest solutions through group presentations. The teacher also noted how the students took the lead, and had an ownership over this project that they usually don’t showcase.
The shift from repetition to application fosters deeper engagement. Several teachers noted that students who previously struggled to stay motivated with homework showed renewed interest when asked to take on real-world challenges.
Changing Roles: Teachers as Facilitators, Not Just Instructors
Project-Based Learning also changes the role of the teacher, who went from being the sole source of knowledge to a guide who supports inquiry and exploration.
One common change teachers noticed was on how they had to let go of control in the classroom. Naturally, the students now had to work on projects on their own, and could only come to the teacher for guidance and help. The teachers noted that they helped their students ask the right questions, find credible sources, and evaluate their work, instead of completely placing the burden of learning on the teacher themselves.
This change isn’t always easy. It requires a shift in mindset and in many cases, rethinking how time is used in class. But most teachers agree: the shift is worth it. PBL has encouraged interdisciplinary approaches, made space for collaborative learning, and created more meaningful student-teacher interactions.
Unlocking Student Potential: What PBL Offers Beyond Academics
Academic performance remains important, but a lot of teachers repeatedly pointed out that PBL nurtures a broader set of skills, like critical thinking, collaboration, communication, and creativity. One teacher particularly noted on how their quietest students became ‘leaders’, and became outspoken when it came to presenting their ideas and projects. While not directly, PBL helped these students find their voices, and find confidence in their effort and abilities.
Students learn to manage time, negotiate roles, and solve problems, skills that aren’t always reflected in exam scores but are vital for life beyond school. For many teachers, the most rewarding aspect of PBL was watching students take initiative, work through failure, and reflect on their learning.
Widening the Circle: Strategies for Scaling PBL in More Classrooms
While the benefits are clear, teachers acknowledged that implementing PBL at a large scale comes with challenges, like limited time, rigid curriculum structures, and unfamiliarity among teachers.
They offered a few practical suggestions for schools and educators considering wider adoption:
- Start Small and Build Confidence: Starting with short projects aligned to the unit you are already teaching introduces PBL in an easy manner. This way, teachers do not have to worry about overhauling their curriculum, or for making huge changes to their current teaching methods.
- Encourage Collaboration Among Teachers: Joint planning across subjects makes projects richer and more integrated. This also promotes interdisciplinary skills among students, and allows them to craft solutions using different subjects and skillsets.
- Make Time for Reflection: Embedding opportunities for students to present, critique, and reflect helps solidify learning. By reflecting on their projects and mistakes, they can understand how they can improve their approach to PBL.
- Support Professional Development: Teachers emphasized the need for ongoing training, not just one-off workshops but long-term spaces for peer sharing and mentorship. This continuous development would cement and solidify the methods and outcomes that will maximise using PBL for student benefits
Looking Ahead: Redefining Success in Education
PBL challenges traditional ideas of what learning looks like. It pushes students to move beyond memorization, and it challenges teachers to rethink their methods. But more than anything, it opens up the classroom to ideas, to communities, and to possibilities. No longer are students just preparing for exams, but also for the complex world outside school.
As educators continue to navigate the changing landscape of education, the insights from teachers point us toward a hopeful future, where learning is meaningful, relevant, and rooted in real-world experience.
This article is authored by Mrs. Padmashini M Patro, Principal, Air Force School Bamrauli
Education
Over 1 Lakh Single-Teacher Schools Educate 33 Lakh Students Across India: MoE Data
Education
Over 3 Lakh Schools Join Hands for India’s Largest-Ever Innovation Challenge: Viksit Bharat Buildathon 2025

In a historic moment for Indian education, more than 3 lakh schools across the country came together to participate in the Viksit Bharat Buildathon (VBB) 2025, the largest live school innovation challenge ever organised in India. The nationwide event was inaugurated in New Delhi by Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, marking a significant milestone in the Government’s efforts to embed creativity, innovation, and problem-solving into the school ecosystem.
The Viksit Bharat Buildathon, organised by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL) in collaboration with Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog, and AICTE, saw over one crore students from Classes 6 to 12 working simultaneously during a 120-minute live innovation session. Students teamed up in groups of three to five to design prototypes and propose solutions under four themes — Atmanirbhar Bharat, Swadeshi, Vocal for Local, and Samriddhi.
While inaugurating the event, Minister Pradhan interacted virtually with students of PM SHRI Government High School, Khorda, Odisha, and later visited Delhi Public School, Mathura Road, and Kendriya Vidyalaya No. 2, Delhi Cantt. Commending students for their creativity, he said, “The vision of Viksit Bharat will be realised through the innovative spirit of our young learners. These ideas will not only address domestic challenges but also create global models for change.”
The event drew widespread participation, with Uttar Pradesh leading the numbers (78,206 schools), followed by Maharashtra (41,198), Gujarat (20,017), and Madhya Pradesh (18,129). Other states like Tamil Nadu (16,370), Bihar (15,732), Odisha (12,344), and Haryana (11,567) also recorded impressive engagement, showing the growing momentum for grassroots innovation across regions. Even smaller territories like Ladakh (358), Puducherry (149), and Andaman & Nicobar Islands (171) participated actively, reflecting the nationwide reach of the initiative.
According to Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, DoSEL, this unprecedented participation signals a transformation in how Indian students approach learning. “This one-of-a-kind movement strengthens innovative thinking and enhances the problem-solving capabilities of students across India,” he said. Deepak Bagla, Mission Director of AIM, called the initiative a “mass movement connecting schools in remote villages with those in metropolitan cities through innovation.”
A New Chapter for Indian Education
The Viksit Bharat Buildathon signifies more than just a hackathon — it reflects a systemic shift in Indian education towards experiential and innovation-led learning. As schools across the country engage in design thinking, tinkering, and collaboration, students are being equipped not just with knowledge, but with the mindset and skills needed to build a self-reliant India.
By nurturing creativity from an early age and fostering partnerships between schools, government bodies, and industry, the Buildathon is shaping a generation ready to contribute to the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047 — a developed, empowered, and innovation-driven India.
Education
17-year-old Innovator Designs Learning Tools for the Visually Impaired

At just 17, Singapore-based student Ameya Meattle is proving that age is no barrier to impact. What began as a small idea to make education more accessible has evolved into a mission that is transforming how visually impaired learners experience learning and skill development.
Ameya founded Earth First at the age of 14 — a social enterprise that helps visually impaired individuals “earn and learn” by creating sustainable, eco-friendly products. Working with eight NGOs across India and Singapore, the initiative has trained more than 100 visually impaired students and launched over 23 sustainable product lines, from tote bags and jute placemats to macramé planters. Each design is adapted to provide hands-on learning opportunities and help trainees gain confidence in both craft and enterprise.
Beyond social entrepreneurship, Ameya has focused deeply on education and technology. He led a Python programming course for 50 visually impaired students, designing custom training modules that made coding accessible through screen readers and tactile tools. By introducing technology as a viable career pathway, Ameya hopes to help students move from manual tasks to high-skill, digital opportunities.
His work also extends into assistive technology research. Under the mentorship of Dr. Pawan Sinha at MIT, Ameya developed a VR-based diagnostic game to assess visual acuity in children — turning the process into an interactive experience rather than a clinical test. The tool is being piloted at MIT’s Sinha Lab and with Project Prakash in India, helping doctors evaluate and track visual development before and after eye surgeries.
In addition, during his internship at the Assistech Lab at IIT Delhi, Ameya worked on designing tactile STEM teaching aids, such as accessible periodic tables and coding tutorials for visually impaired learners. His goal, he says, is not just to innovate but to make scientific learning inclusive and joyful for all.
Ameya’s work highlights how education, empathy, and innovation can intersect to create a more equitable future — one where technology serves not just progress, but people.
Education
Ministry of Education Urges Schools to Adopt UPI for Digital Fee Payments, Promoting Ease of Schooling

-

 Inspiration3 months ago
Inspiration3 months agoUmeed: A Ray of Hope for Better Tomorrow
-

 Knowledge1 month ago
Knowledge1 month agoBuilding a Healthier India: Why School Health Programs Are Essential
-

 Inspiration1 month ago
Inspiration1 month agoBefore the Nobel, There Was a Teacher
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoWhat the Indian Army Teaches Our Children Beyond Textbooks
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoInclusive Education Summit 2026: Designing the Future of “Learner-Centric” Education
-

 Education4 weeks ago
Education4 weeks agoBeyond the First Bell: 5 Key Takeaways for School Leaders from Economic Survey 2025–26
-

 Education4 weeks ago
Education4 weeks agoSupreme Court’s Landmark Judgment for Schools: Menstrual Health is a Fundamental Right
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoTapas Project Shaala 2026 to Spark National Dialogue on Autonomy, Curiosity and Community in Education
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoJudicial Guardrails: How the J&K High Court’s Fee Regulation Verdict Redraws the Rules for Private Schools
-

 Education3 days ago
Education3 days agoDaring to Dream: Six Years in the Heart of Rural Rajasthan