Education
India’s Education Conundrum: Envisioning 2025 Amid Ground Realities

Education
“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space

Education
A Structural Proposal to Transform School Education in Bihar
Education
NIIT Foundation and YuWaah, UNICEF Launch Free Online Digital Marketing Course for Youth

Education
National Conference Pushes for Common Standards Across School Boards

Education
Maharashtra: Over 8,000 Villages Lack Schools, CCTV Compliance Still Patchy
Education
Haryana to Offer Free After-School Coaching for JEE, NDA Aspirants
Education
Telangana CM Calls for Overhaul of Intermediate Education in Telangana

Education
Indian Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla to Connect with School Students Live from Space

Education
UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures
Education
Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead

-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 News3 months ago
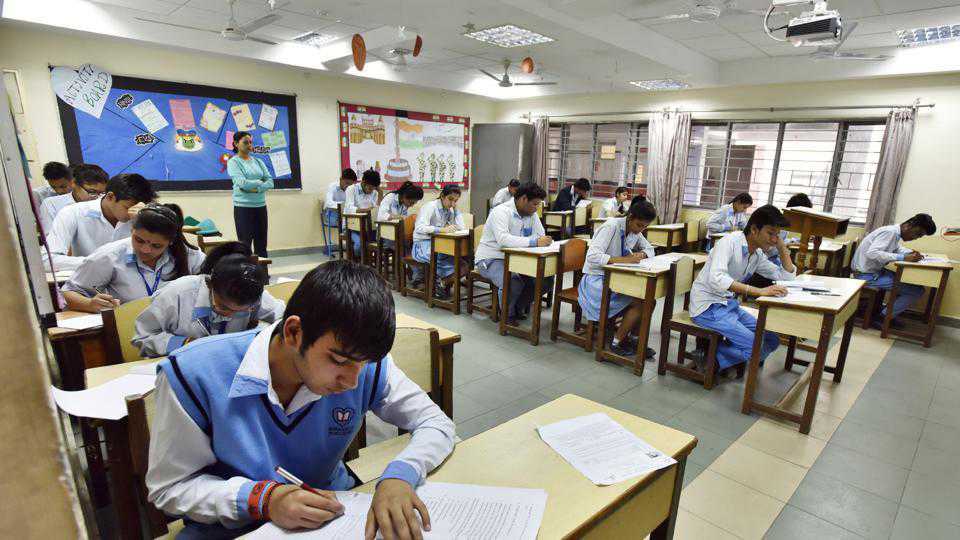
News3 months agoCBSE Warns Dummy School Students May Be Barred from Board Exams
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme












































































