Inspiration
Teacher Warriors 2022: Ranjitsinh Disale – The Accidental Teacher
When he was appointed for his first post as a teacher, he found himself in a remote village, looking for a school that did not exist. This is the story of Ranjitsinh Disale, the accidental teacher.
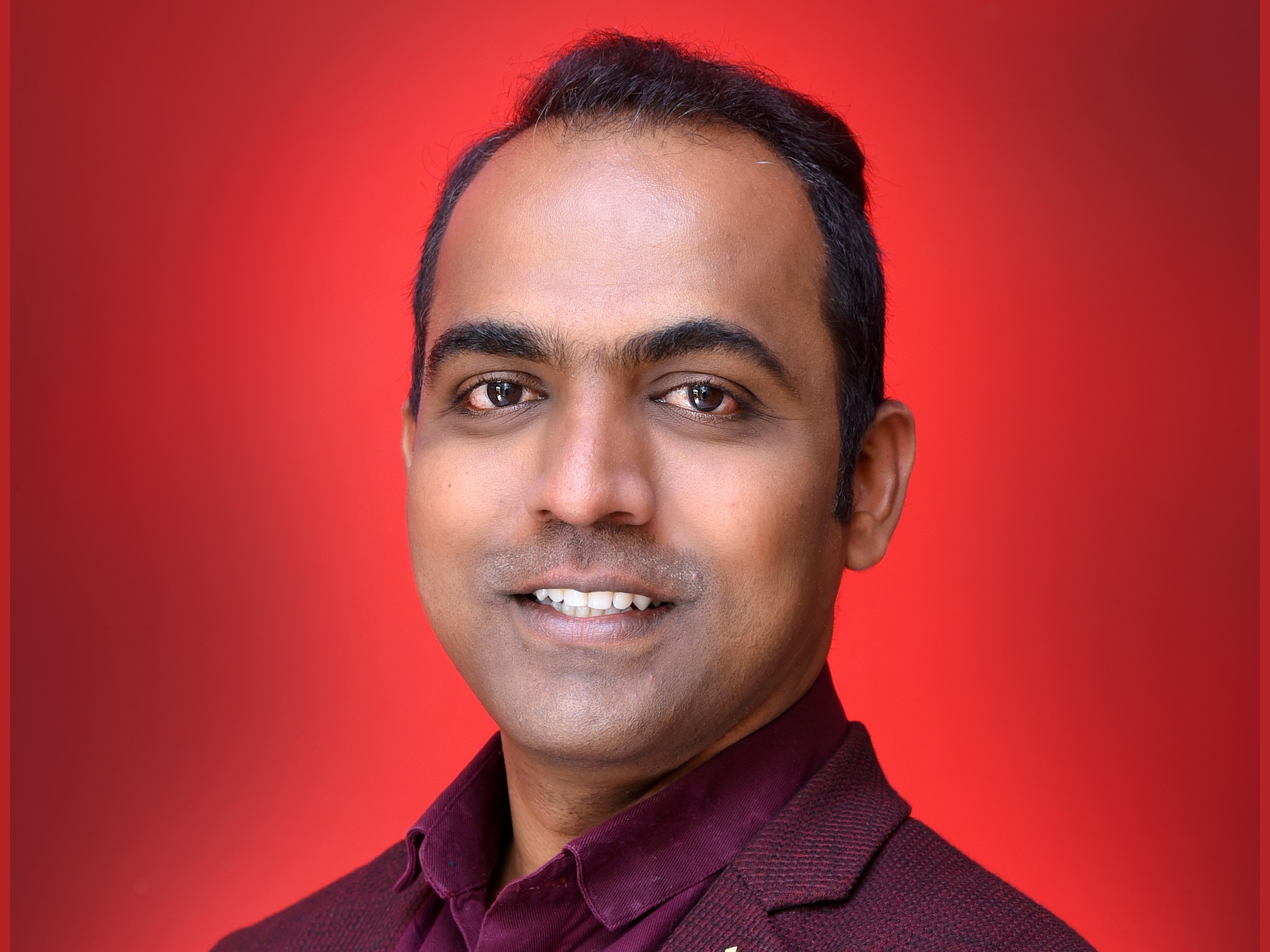

A young student pursuing an IT engineering degree was starting to lose interest in it. Perplexed, he went to his father for advice. The retired headmaster did not convince his son, he asked him to enroll in a teacher-training college. Teaching was never his interest but, he respectfully followed his father’s advice and joined the college. He was taught to empathize with children, understand their questions and solve their problems. He wasn’t very sure at the beginning about this profession. Especially, because when he was appointed for his first post as a teacher, he found himself in a remote village, and the school did not exist. This is the story of Ranjitsinh Disale, the accidental teacher.
In 2009, he was sent to Paritewadi Zilla Parishad Primary School in Solapur, Maharashtra for his first teaching experience. When he entered the quiet village, he realized neither the children nor the parents were interested in the concept of school. Not even a handful of students were going to the school and there were no female students enrolled. So, for the first six months, Disale did not even mention textbooks to them. He would have conversations and share facts and stories on his laptop and mobile phone. This started having a magical effect on the local children of the village. They wanted to spend more time around him, learning without having the fear to be scolded or punished. He would teach the students through their observations and with the help of videos, audio, and sometimes field trips.
In 2014, Disale came up with an innovative idea that enabled easy access to learning resources. He knew that the children enjoyed audio-visual aid to study. So, he created QR code-enabled textbooks that were embedded with audio poems, video lectures, stories, and assignments. He curated the content for each of the children he was teaching so that they could learn at their own pace.
The word spread fast and in 2015, the Maharashtra government adopted Disale’s idea and made QR codes available in Balbharti textbooks. As a result of these efforts, the school was awarded Best School for the district in 2016, and 98 percent of students achieved their expected learning outcomes before completing the school year. The Ministry of Human Resource & Development (MHRD) encouraged the use of QR codes and in 2017, launched the project ‘Diksha’, which used an open-source platform called Sunbird to produce the content. Subsequently in 2018, the then Union Human Resource Development Minister Prakash Javadekar announced that all National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) textbooks will have embedded QR codes. Even with schools closed, 20 lakh students in Maharashtra used QR-code learning to continue with their studies.
Innovative method of teaching
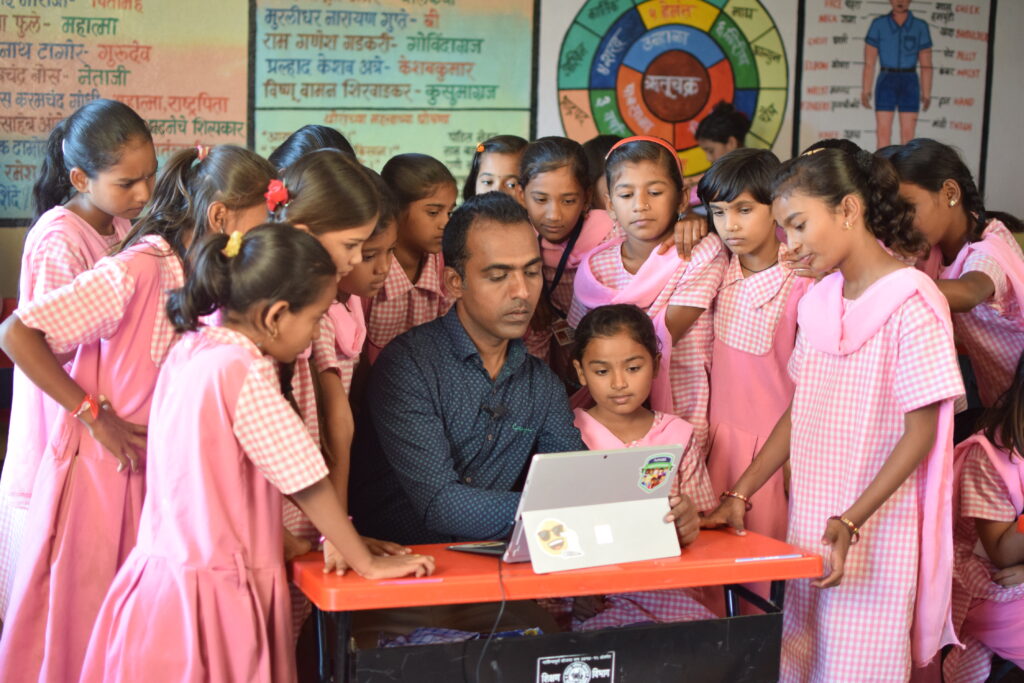
The students of the Zilla Parshad school in Solapur’s Paritewadi study with Disale where he teaches grades 3 and 4. The school is only until grade 4 but, there is a possibility of introducing higher grades in the school. They follow Marathi as their medium of teaching. The students often study with the help of visual aid. “I don’t have a single method of teaching. I try to use multiple methods for the same topic. We also have guest lecturers and expert teachers for different subjects so the children don’t lose interest by studying all subjects from just one teacher,” he said.
Disale made the transition from entertainment to edutainment very smooth for the children. He understood the learning style of each student, whether it was visual media, face-to-face explanations, or others, and grouped the children accordingly. He would modify his teaching methods according to each group. Within a year and a half, the school had achieved 100 percent attendance and the children were performing excellently in their academics.
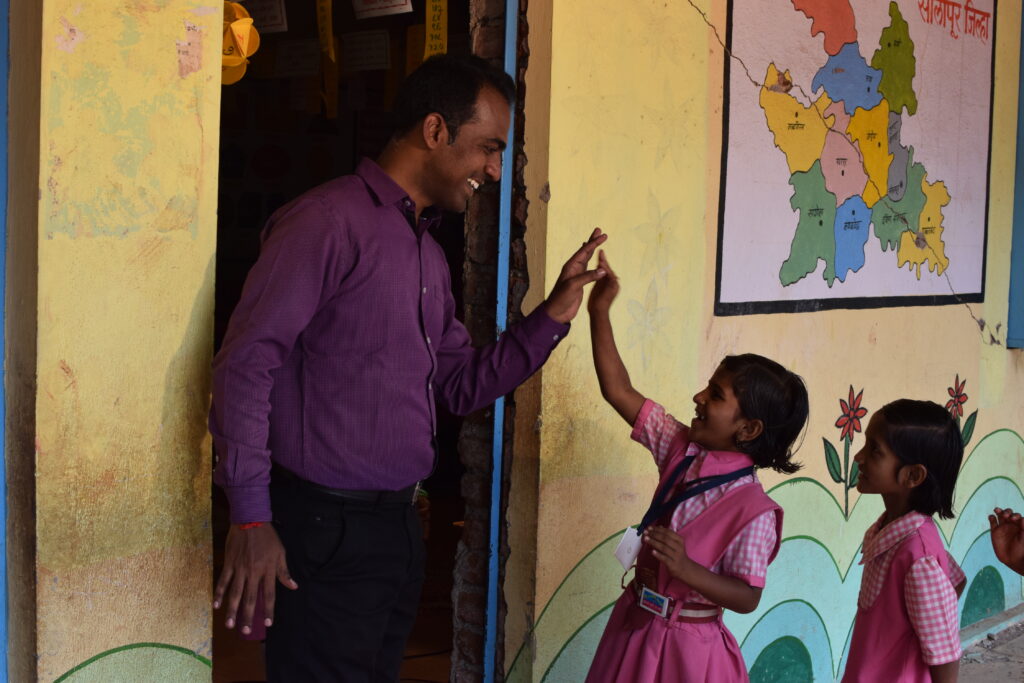

Challenges on the way
The tribal people of the village were the local inhabitants. Due to poor economic conditions, and backward thinking, not many children were sent to school. Attendance was as low as two percent. The parents did not seem to mind that too much. This also led to the conversion of the school rooms into cowsheds and storerooms. However, this did not break the spirit of this teacher who was determined to make a change.
His first step involved visiting the families of the village. He would initiate informal dialogue with them and spend time trying to understand their perspective on education. Gradually, he established polite friendships with the people. To persuade them, he would share the achievements of the children living in the nearby villages and ask a simple question – wouldn’t you want to see your child reach great heights? It took about six months for Disale to gain their trust and convince them.
His second step was to be friends with the children and come up with an idea to make the classroom interesting. So, for the first semester, he did not even mention textbooks. Disale borrowed money from his father and bought a laptop for the class where children would watch movies, interesting videos, and presentations. With this technique, he was sending a message to the children – a school is a place of fun and enjoyment, just as much as it is a place of education. The remaining few students who were yet to start school were soon sitting amongst the rest of the children. His method had worked.
School closures had devastating consequences on children’s learning during the covid-19 pandemic. In these, most vulnerable children come from remote areas which have do not have access to learning and are at risk of never returning to classrooms and even being forced into child marriage or child labor. According to a report by UNESCO, the education of more than 888 million children worldwide faced disruptions due to full or partial school closures. In India, most government and rural students rely on schools for peers, support, access to a safe environment, and a nutritious meal. The shutdown of schools affected these children the most.
For Disale, the biggest challenge during the pandemic was to stay connected with the students. He appealed to people through social media and requested to donate old mobile phones. He collected 67 devices and distributed them amongst his students, convincing their parents to buy an internet pack to ensure effective learning. However, in the post-pandemic era, the effect of the intense two years can be seen in the progress of the students. While some have been able to maintain their level of learning, many students have to struggle because the online method of teaching wasn’t the easiest to adapt.
NEP 2020
This National Education Policy 2020 is the first education coverage of the 21st century and aims to increase the growth and development of the education sector. The new policy proposes the revision and revamping of all aspects including regulation and governance, to create a brand new system that is aligned with the aspirational goals of 21st-century education including SDG4 while building upon India’s traditions and value system. Along with appreciation, there is also criticism that focuses on the drawbacks of this new education policy.
In an article written by Disale on the recruitment, training, and assessment of teachers, he highlighted challenges that teachers face and said, “considering the diversity and different socio-economic strata in the society, there is a need for tailored teachers training. The training should be customized/need-based, continuous, practical, and more focused.”
“The NEP looks promising as it rightly highlights the changes necessary in the 21st century. With the addition of some more alterations to teachers’ training program and their implementation, the system will achieve greater goals, assist teachers to think out of the box to attain great heights,” he added.

Pat on the back
Ranjitsinh Disale was the first Indian teacher to win the Global Teacher Prize 2020. He was among 12,000 educators from 140 countries, who were nominated for the prize, which was set up to recognize teachers making outstanding contributions to the profession as well as to shine a spotlight on the important role teachers play in society. He promptly shared half of his $1 million win with the nine other finalists.
With his share of the prize, he has been able to provide scholarships of Rs 1 lakh each to 10 girls who are completing their graduation. Currently, he is particularly focused on the teachers of the country. “The country needs to invest more in its teachers. We are not respecting their work and status in society. There is also no system to support teachers for their innovative teaching projects. So, I am trying to give incentives to teachers and support their initiatives towards education and especially for rural education,” he said. He has also invested in his ‘Let’s Cross the Borders’ project, which connects young people from India and Pakistan, Palestine and Israel, Iraq and Iran, and other conflict zones.
The CEO of Microsoft (Satya Nadella) has recognized Ranjitsinh’s work as one of three stories from India in his book Hit Refresh. The central government named Ranjitsinh 2016 Innovative Researcher of the Year, and he also won the National Innovation Foundation’s Innovator of the Year award in 2018. He has communicated his methods by writing more than 500 newspaper articles and blogs, as well as participating in television discussions on educational topics.
Disale spends a lot of time with fellow teachers to keep himself motivated. He believes in sharing his methods of teaching and also appreciates critical feedback on them to improve every day.
Call for action
From sharing knowledge and skills to contributing to the school’s infrastructure, and contributing to children’s resources like bicycles, mobile devices, or stationary, Disale’s school accepts donations in both, cash and kind. Whether you would like to support them or become a volunteer, we would urge the readers to visit their website and reach out to the members to contribute and engage in this cause for change.
Inspiration
Before the Nobel, There Was a Teacher
Before Albert Camus was the voice of a generation, he was an invisible child in a house without books. He was a boy whose future was already written by the harsh ink of illiteracy and loss. Then came the intervention that changed everything. Decades later, at the pinnacle of human achievement, Camus would look back at his Nobel Prize and realize it was built upon a foundation laid by a single elementary school teacher. “I remain your grateful pupil,” Camus wrote to his mentor—a phrase that serves as a timeless anthem for every educator who has ever looked at a struggling student and said: You matter.
The Day Everything Changed
Paris, October 1957
Albert Camus was 43 years old when the telegram arrived.
He unfolded the message and read the words that would secure his place in literary history: he had been awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.
He was one of the youngest recipients ever. The world saw him as the conscience of his generation — the author of The Stranger, The Plague, The Myth of Sisyphus — a writer who had captured the absurdity and alienation of modern life.
The celebrations would soon follow: journalists, interviews, speeches, congratulations.
But Camus’ mind went somewhere else entirely.
After thinking of his mother, he thought of a man in a quiet classroom many years earlier — the teacher who had once looked at a poor, silent boy and seen a future no one else imagined.
That night, Camus sat down to write a letter.
A Childhood on the Margin
Born Into Poverty — French Algeria, 1913
To understand the letter, you must understand where Camus began.
Albert Camus was born in Mondovi, French Algeria, on November 7, 1913.
His father, Lucien, was killed in World War I before Albert turned one. His mother, Catherine, was partially deaf, nearly illiterate, and worked as a cleaner so her children could eat.
The family lived in a cramped apartment in the working-class Belcourt district of Algiers — no electricity, no running water, no books. Poverty wasn’t merely a condition; it was an entire world with sharply defined limits.
In such neighborhoods, school was a holding place. Working-class children learned the basics, then quit to earn wages. No one expected one of them to become a writer.
Camus sat in class: thin, watchful, quiet. A child easy to overlook.
Except one person didn’t overlook him.
The Teacher Who Refused to Let Him Disappear
Louis Germain’s Quiet Intervention
Louis Germain, Camus’ elementary school teacher, noticed something unusual about the boy:
- the intensity in his eyes
- the way he listened
- the unresolved questions beneath his silence
Germain decided that poverty would not define this child’s future.
He gave Albert extra help.
He handed him books — more than the boy had ever seen at home.
He stayed after school to explain ideas, encourage curiosity, and open windows Camus never knew existed.
Then came the decisive moment: the competitive exam for admission to lycée, the gateway to higher education — a path almost never offered to children of Camus’ background.
Germain tutored him personally.
He convinced administrators to let Albert sit for the exam.
He prepared him, defended him, believed in him.
Camus passed.
From that moment, his life opened: secondary school, university, journalism, Resistance work during World War II, philosophy, novels, essays — and eventually, worldwide recognition.
But beneath every achievement was that first act of belief.
Camus never forgot it.
The Letter of Gratitude
November 19, 1957
After the Nobel Prize announcement, Camus waited for the noise to fade.
Then he wrote to “Monsieur Germain.”
He thanked his teacher for the kindness and patience shown to a poor child who needed someone to see him. He confessed that when the Nobel news arrived, after his mother, his first thought was of Germain.
He wrote that without his teacher’s influence, none of his success would have existed. He wanted Germain to know that the time, the generosity, and the belief he had invested in that quiet boy lived on in the man the world now celebrated.
Camus ended with a line that has echoed through generations:
“I remain your grateful pupil.”
The Teacher’s Reply
A Humble Answer From Across the Years
Louis Germain, now an older man, wrote back.
He did not take credit for shaping a great writer.
Instead, he expressed the simple joy of having helped a student use his education well — that, he said, was the true reward of teaching.
Across decades and continents, they met again — not in a classroom, but in a pair of letters that captured the enduring connection between a teacher and a child who needed one.

The Final Pages of a Short Life
January 4, 1960 — The Last Journey
Just over two years after receiving the Nobel Prize, Camus died in a car accident on January 4, 1960. He was 46.
In his briefcase, investigators found the unfinished manuscript of The First Man, a novel in which he began exploring his childhood and the two figures who shaped him most deeply: his mother and his teacher.
Among his belongings were the letters from Louis Germain — carefully preserved, carried with him always.
Even at the height of fame, he kept tangible proof of who opened the door for him.
The Quiet Heroes Behind Every Success
The Camus–Germain Story Is Not Just Theirs
This isn’t only a story about Albert Camus and one extraordinary teacher.
It’s about the invisible army of Louis Germains everywhere:
- the teacher who gave you books because you were hungry for more
- the professor who took your questions seriously
- the mentor who wrote a recommendation letter that changed your life
- the adult who said: You matter. Keep going.
Most will never receive thank-you letters from Nobel laureates.
Many will retire never knowing which seeds they planted grew into forests.
Yet somewhere, a child they believed in is building a life once thought impossible.
What Camus Teaches Us
Success Is Never Self-Made
Camus’ letter cuts through the myth of self-made genius:
Look back.
Remember who saw you when you were invisible.
Say thank you while you can.
Albert Camus won the Nobel Prize at 43.
His first instinct wasn’t I earned this.
It was I owe this.
In a universe he believed lacked inherent meaning, Camus chose gratitude — a meaning built from memory, humility, and human connection.
He remembered the woman who cleaned houses so he could attend school.
He remembered the teacher who stayed late to explain how the world worked.
He remembered the moment someone reached across poverty and said:
You matter. You can go further.
And he said thank you.
Inspiration
Umeed: A Ray of Hope for Better Tomorrow
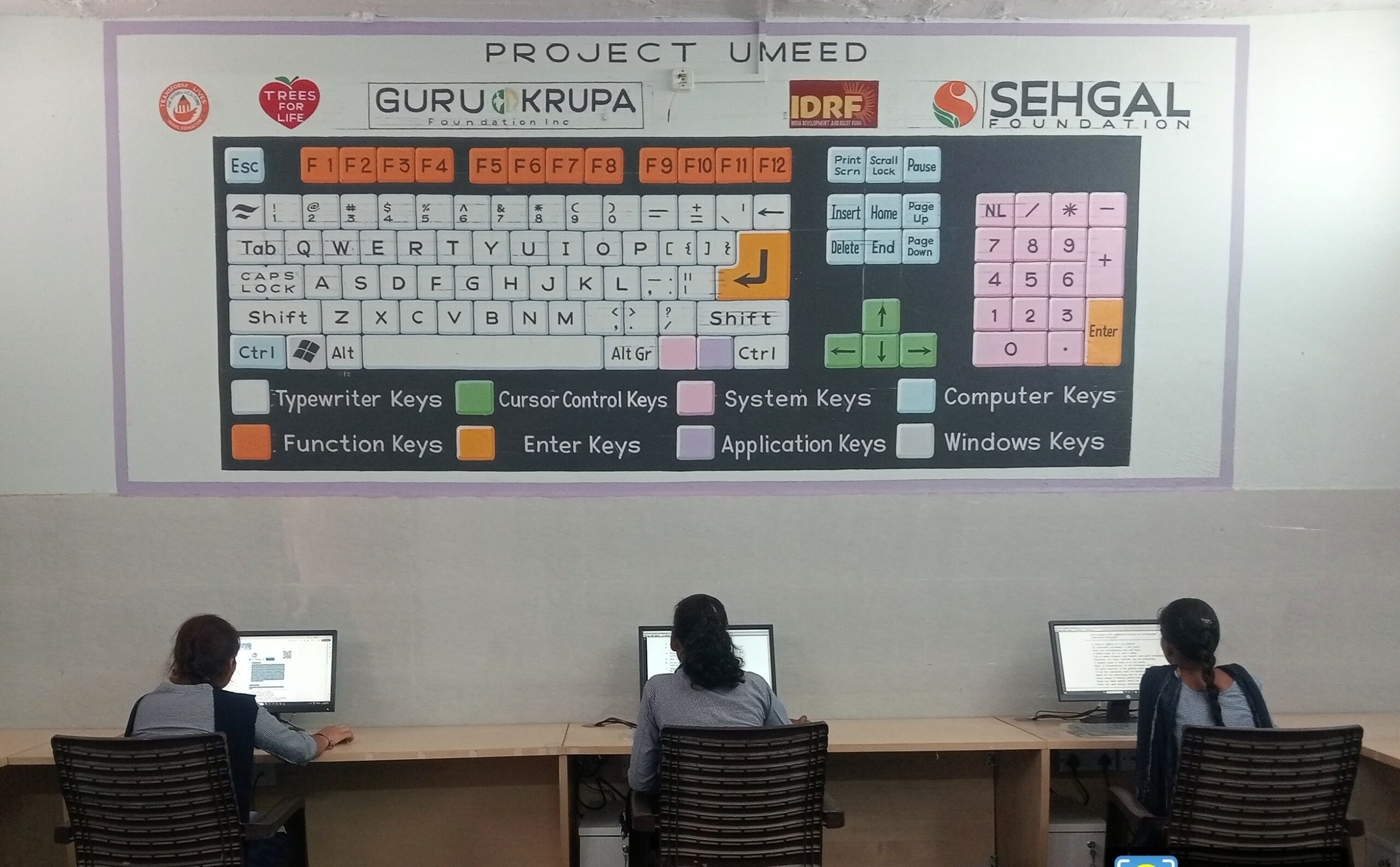
“I used to be hesitant to speak on stage, but after participating in the life skills sessions, I gained confidence. Thanks to Project Umeed,” shared Sanjana, student of Government Senior Secondary School, Kurthala, Nuh, Haryana.
The project Umeed creates equitable learning opportunities for rural schoolchildren by providing enhanced Digital and Life Skills Awareness (DLSA), leading to their overall learning and empowerment. The project is a partnership with Teach for Life supported by Trees for Life, India Development, and S M Sehgal Foundation, which is implementing the project on the ground.
The DLSA course has been operational at Government Senior Secondary School, located in village Kurthala, block Nuh, Haryana, since March 2025. Sixty students are enrolled in this course that is led and facilitated by a dedicated instructor.
The course covers essential topics related to learning about computers, technology, and cyber safety; developing important social and emotional abilities in children; building self–confidence, providing career guidance for goal setting; gaining knowledge about local participation for village development, familiarity with key government programs, and becoming informed, engaged citizens.
Topics such as “Me and My Self” and “Communication Skills” boost children’s confidence strengthen their thinking abilities and communication aptitudes.
Students Shine at the Youth Parliament
With this new learning and enthusiasm, two girl’s students, Sanjana and Renu from Govt. Sr. Sec. School, Kurthala, Nuh, who attend the DLSA classes, were selected for the Youth Parliament program. They were both excited and a little hesitant. They diligently prepared and practiced their skills on effective communication, brainstorming and role playing for over a month. Finally, on the day of the event, the entire auditorium erupted in applause as the girls confidently shared their thoughts on the Youth Parliament. Sanjana moderated the event as speaker, and Renu presented her views as finance minister. Other students participated as members of Parliament. The whole process further strengthened the students’ understanding of social issues and the democratic process. The event showcased the students’ development of confidence and leadership skills.
“I realized how important it is to present your thoughts clearly. This experience helped me hone my life skills, especially the topics of communication skills and ‘Me and Myself’ had a deep impact on me.” – Renu, student, Govt. Sr. Sec. School, Kurthala, Nuh, Haryana
The same course is being conducted at Government Senior Secondary School, Badarpur village, bock Nagina, district Nuh, with another sixty students. As part of their digital awareness sessions, students learned how to use computers and online platforms to access government programs and services. They were taught the importance of the Aadhaar card and guided through the process of downloading or updating their Aadhaar credentials. Students were made aware that their Aadhaar card serves to establish and safeguard their identity, enabling them to access government services and avail different benefits.
Earlier, the students had to depend on the Common Service Centre or Aadhaar Seva Kendras, located 2–3 km away from the village, to download or update government documents such as the Aadhaar card, ration card, or other certificates. Each time they had to update their documents, they had to pay a fee of as much as Rs 100, plus a transportation cost of Rs20. Even then, issues often remained unresolved, forcing them to make repeated trips.
With their newfound confidence in using technology, students no longer need to visit CSC centres and Aadhaar service centres repeatedly, thus saving both time and money. This experience has proven to be a significant step toward achieving autonomy.
The students’ parents and the village council were deeply impressed by this initiative. They expressed their gratitude to S M Sehgal Foundation and urged that more such digital awareness courses should run in the future, so that other people of the village can also become digitally empowered.
About the Authors: Indu Verma, Sr. Program Lead, Transform Lives one school at a time, S M Sehgal Foundation
Mahesh Sharan and Mosim Khan, Instructors, Transform Lives one school at a time, S M Sehgal Foundation
Education
17-year-old Innovator Designs Learning Tools for the Visually Impaired

At just 17, Singapore-based student Ameya Meattle is proving that age is no barrier to impact. What began as a small idea to make education more accessible has evolved into a mission that is transforming how visually impaired learners experience learning and skill development.
Ameya founded Earth First at the age of 14 — a social enterprise that helps visually impaired individuals “earn and learn” by creating sustainable, eco-friendly products. Working with eight NGOs across India and Singapore, the initiative has trained more than 100 visually impaired students and launched over 23 sustainable product lines, from tote bags and jute placemats to macramé planters. Each design is adapted to provide hands-on learning opportunities and help trainees gain confidence in both craft and enterprise.
Beyond social entrepreneurship, Ameya has focused deeply on education and technology. He led a Python programming course for 50 visually impaired students, designing custom training modules that made coding accessible through screen readers and tactile tools. By introducing technology as a viable career pathway, Ameya hopes to help students move from manual tasks to high-skill, digital opportunities.
His work also extends into assistive technology research. Under the mentorship of Dr. Pawan Sinha at MIT, Ameya developed a VR-based diagnostic game to assess visual acuity in children — turning the process into an interactive experience rather than a clinical test. The tool is being piloted at MIT’s Sinha Lab and with Project Prakash in India, helping doctors evaluate and track visual development before and after eye surgeries.
In addition, during his internship at the Assistech Lab at IIT Delhi, Ameya worked on designing tactile STEM teaching aids, such as accessible periodic tables and coding tutorials for visually impaired learners. His goal, he says, is not just to innovate but to make scientific learning inclusive and joyful for all.
Ameya’s work highlights how education, empathy, and innovation can intersect to create a more equitable future — one where technology serves not just progress, but people.
Education
Class 11 Student Navya Mrig on a Mission to Bust Myths About Organ Donation

Saahas, a Delhi-based non-profit organisation founded by Class 11 student Navya Mrig of The Ram School, Moulsari, Gurugram, is creating awareness about organ donation and working to counter myths that prevent families from giving timely consent.
Established in 2024, Saahas focuses on every aspect of organ donation, particularly deceased organ donation where family approval must be granted quickly. The organisation highlights that hesitation and misinformation often stop families from making decisions that could save lives.

To address this, Saahas conducts workshops, myth-busting talks, and seminars in schools, resident welfare associations, hospitals, and workplaces. These sessions explain processes such as brain-stem death certification and the role of family consent in simple, clear terms. Each session concludes with practical guidance, ensuring participants leave with both knowledge and actionable steps.
The initiative has also developed resource kits with slide decks, facilitator notes, QR-linked checklists, and referral contacts to make it easier for schools and institutions to host repeatable sessions. Saahas partners with community groups and healthcare institutions to co-host Q&A sessions with clinicians and transplant coordinators, and also honours donor and recipient families through small ceremonies that highlight the impact of organ donation.
At its core, Saahas is designed to bring organ donation discussions into everyday spaces rather than waiting for the urgency of hospital decisions. By focusing on conversations in classrooms, community meetings, and staff rooms, the organisation aims to gradually build a culture where organ donation is better understood and more widely accepted.
Navya’s initiative reflects how young people are increasingly taking up important social causes and contributing to public awareness campaigns with structured, replicable models.
(News Source- ANI)
Education
Educate Girls Becomes First Indian NGO to Win the Ramon Magsaysay Award
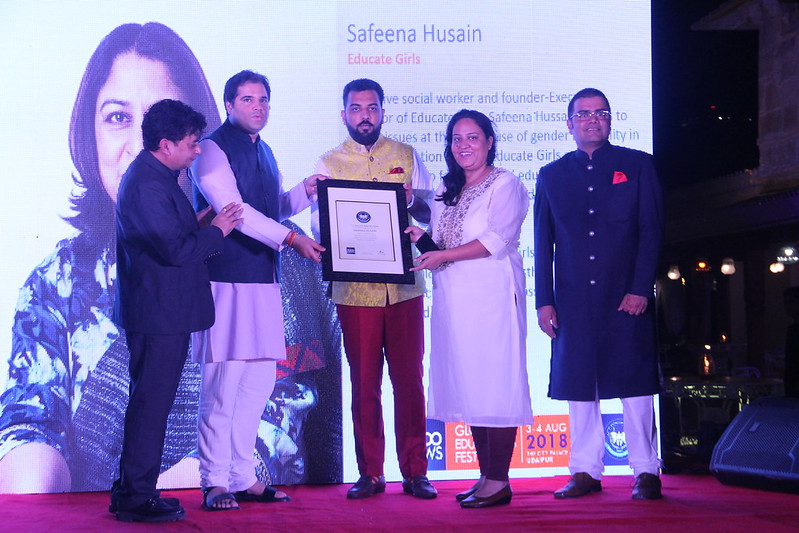

In a landmark recognition for Indian education and grassroots activism, Educate Girls, founded by Safeena Husain, has been named one of the recipients of the 2025 Ramon Magsaysay Award. Often referred to as Asia’s Nobel Prize, this honour highlights the organisation’s transformative work in enrolling and empowering out-of-school girls across some of India’s most remote and underserved regions.
The announcement marks a historic moment — Educate Girls is the first Indian organisation to ever receive this award, underscoring the global importance of its mission. Alongside Educate Girls, the other awardees include Shaahina Ali from the Maldives for her environmental work and Flaviano Antonio L. Villanueva from the Philippines. The formal ceremony will take place on November 7 at the Metropolitan Theatre in Manila.
Safeena Husain: From Teacher Warrior to Global Recognition
For ScooNews, this moment carries a special resonance. In 2018, Safeena Husain was celebrated as a Teacher Warrior, honoured for her vision of tackling gender inequality at the root by ensuring that every girl receives access to education. What started as a 50-school test project in Rajasthan has since scaled into an expansive movement spanning 21,000 schools across 15 districts, supported by a network of 11,000+ community volunteers known as Team Balika.
Her journey, as she has often recalled, was shaped by both personal and professional turning points. After studying at the London School of Economics and working in grassroots projects across Latin America, Africa, and Asia, Safeena returned to India, deeply aware of the entrenched discrimination girls faced. A family encounter in a village, where her father was pitied for not having a son, crystallised her resolve to fight for gender equity through education.

Breaking Barriers in Education
Educate Girls has gone beyond enrolling girls into schools. Its programmes aim at:
-
Increasing enrolment and retention of out-of-school girls
-
Improving learning outcomes for all children in rural districts
-
Shifting community mindsets through participation and ownership
The organisation has also pioneered innovative financing models such as the world’s first Development Impact Bond (DIB) in education, tying funding directly to learning outcomes.
Safeena has often spoken about the transformative power of education citing stories of girls who once had no aspirations simply because nobody asked them what they wanted to be, and who today, thanks to education, dream of becoming doctors, teachers, or even police officers.
Global Platforms, Indian Roots
Safeena’s vision has found resonance globally. In her TED Talk titled “A Bold Plan to Empower 1.6 Million Out-of-School Girls in India”, she emphasised that girls’ education is the closest thing we have to a silver bullet for solving some of the world’s toughest problems from poverty to health to gender inequality. In 2023, she was also awarded the WISE Prize for Education, cementing her reputation as one of the leading voices in education worldwide.
But even as Educate Girls receives international acclaim, its deepest impact continues to be felt in the dusty lanes of rural Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, where every single enrolment represents a victory against entrenched social barriers.
Why This Award Matters
The Ramon Magsaysay Award not only recognises Safeena Husain’s leadership but also places Indian NGOs on the global stage. It sends a powerful message: education is both the foundation of equity and the key to transformation. For India, a country with one of the world’s largest populations of out-of-school girls, this award validates years of struggle, innovation, and community-driven action.
For ScooNews, which first honoured Safeena as a Teacher Warrior in 2018, this moment is both proud and historic. It shows that when educators and changemakers stay rooted in their vision, their work can resonate far beyond borders.
Education
In Every Smile, a Victory – Sandhya Ukkalkar’s Journey with Jai Vakeel’s Autism Centre
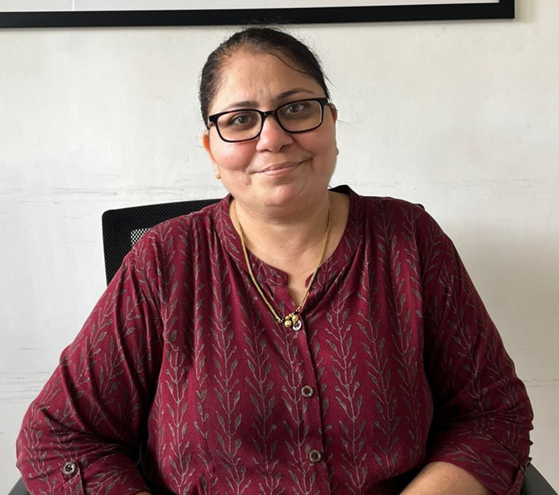

For Sandhya Ukkalkar, the path to becoming an educator in the field of special education was never just a professional decision — it was deeply personal. It began in the quiet, determined moments of motherhood, as she searched for a school that could truly understand her son’s unique needs. Diagnosed with Autism and Intellectual Disability, he required more than care — he needed acceptance, structure, and a nurturing environment.
In 1996, a compassionate doctor guided her to Jai Vakeel School. From the moment her son was enrolled, Sandhya witnessed a transformation that brought not only relief, but hope. Encouraged by the school’s doctor, she enrolled in a special education course, and by June 2000, she returned to the same institution — this time as a teacher. Over the years, she grew into the role of Principal of the Autism Centre at Jai Vakeel, dedicating her life to children who, like her son, simply needed to be seen, understood, and supported.

What sets the Autism Centre apart is not just its experience or legacy, but its guiding philosophy: a child-led, strengths-based approach that celebrates neurodiversity. Here, each learner follows an Individualised Education Plan (IEP), supported through small groups, one-on-one sessions, and methodologies that include Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA), Sensory Integration, and Visual Supports. The goal isn’t to fit children into a mould but to honour their unique ways of engaging with the world.
Serving children aged 3 to 18, the centre focuses on early intervention, functional academics, and pre-vocational training — all grounded in a multisensory curriculum aligned with NCF and NCERT. For the 31 students with Autism and Intellectual Disability who currently attend, the emphasis lies on building communication and sensory skills that can translate into real-world independence.

Sandhya believes collaboration is the cornerstone of success. At the centre, therapists, educators, parents, and healthcare professionals work as a unified team. Over 75% of the children served come from low-income families, and many receive free or subsidised education and therapy through rural camps and outreach programs.
“These aren’t luxuries,” Sandhya insists, referring to tools like sensory rooms and assistive tech. “They’re essentials.”
And the results are deeply moving. Children who once struggled with attention now engage joyfully in sessions. Some who were non-verbal begin to use gestures, visuals, and eventually words. Others transition into mainstream schools. One student, now preparing for CA exams, once needed foundational classroom readiness support. These are not isolated cases — they are the product of consistent, individualised attention and belief.
For Sandhya, the real victories come in the smallest moments: a child pointing to a picture to communicate, another who finally sits through a full session, or a parent whispering “thank you” with tears in their eyes. These everyday breakthroughs are everything.
Her personal experience as a parent gives Sandhya a unique lens. She understands the fears, hopes, and quiet triumphs families carry. That’s why parental involvement is not optional at the centre — it’s essential. Families regularly participate in progress meetings, classroom observations, and hands-on training. Home goals — practical and doable — are shared, and customised visual aids help ensure continuity beyond school hours. Emotional support is offered just as readily as academic strategies.
Still, the challenges are real. There is a pressing shortage of professionals trained in autism-specific interventions, especially for students with high support needs. Assistive communication tools are expensive and often out of reach. Space is limited, even as demand grows. Sandhya dreams of expanding — with dedicated sensory rooms, inclusive playgrounds, and classrooms designed for neurodivergent learners. “These help children feel safe, calm, and ready to learn,” she says.

Her vision for the future is clear: inclusion that goes beyond tokenism. She dreams of classrooms where neurodivergent children aren’t merely accommodated, but genuinely valued — where belonging is a given, not a gift. To get there, she believes we must build on three pillars: Mindset (a shift from awareness to true acceptance), Capacity (training educators, therapists, and families), and Belonging (where every child is emotionally safe and socially included).
As she looks ahead, Sandhya hopes to increase enrolment, offer structured training for parents and teachers, partner with inclusive schools for smooth transitions, and support students well into adulthood — through vocational training, community participation, and self-advocacy.
Her journey is a reminder that special education isn’t just about what children need — it’s about what they deserve.
Because, as Sandhya says,
“In every smile, there’s a victory. And every child deserves to smile.”
Read the full story in our issue of Teacher Warriors 2025 here.
Education
Indian Army to Sponsor Education of 10-Year-Old Who Aided Troops During Operation Sindoor

In a heartwarming gesture of gratitude, the Indian Army has pledged to fully sponsor the education of 10-year-old Shvan Singh, a young boy from Punjab’s Ferozepur district who supported troops with food and water during the intense gunfire of Operation Sindoor.
During the cross-border conflict in early May, Shvan—then mistakenly reported as ‘Svarn’ Singh—fearlessly stepped up to help soldiers stationed near Tara Wali village, just 2 km from the international border. With lassi, tea, milk, and ice in hand, the Class 4 student made repeated trips, delivering supplies to the troops amid ongoing shelling and sniper fire.
Moved by his courage, the Golden Arrow Division of the Indian Army has now taken full responsibility for Shvan’s educational expenses. In a formal ceremony held at Ferozepur Cantonment, Lt Gen Manoj Kumar Katiyar, General Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the Western Command, felicitated the boy and applauded his spirit of service.
“I want to become a ‘fauji’ when I grow up. I want to serve the country,” Shvan had told media in May. His father added, “We are proud of him. Even the soldiers loved him.”
Shvan’s actions during Operation Sindoor—India’s strategic missile strike on nine terror camps across the border in retaliation to the Pahalgam attack—have now turned him into a symbol of quiet heroism and youthful patriotism.
In a world where headlines are often dominated by despair, Shvan’s story reminds us that bravery has no age—and that the seeds of service can bloom early.
Education
Lighting the Way, One Beam at a Time – Monika Banga
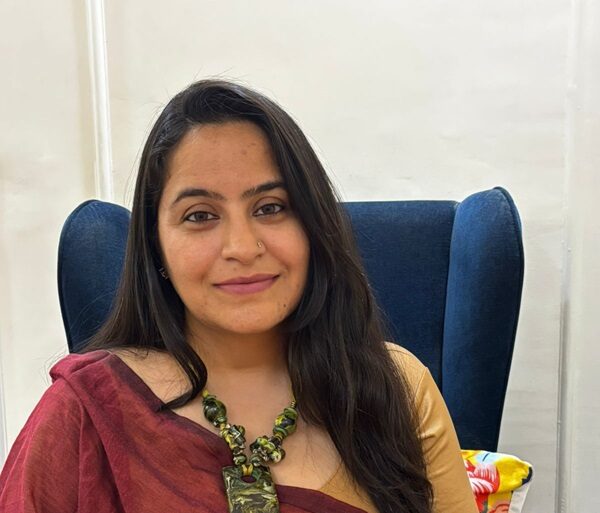

In the stillness of the COVID-19 lockdown—when the world hit pause and uncertainty gripped communities—Monika Banga quietly sparked something radical. Not radical in funding or scale, but in spirit. Born out of a moment of global stillness, The LightBeam Project wasn’t launched with loud declarations or big grants. It began as something far more intimate: a bridge between continents, classrooms, and possibilities.
But Ms. Monika’s journey didn’t start there. It began over a decade earlier, in under-resourced classrooms where she worked with children who had never known structured learning, or imagined speaking with someone from another country. With over 12 years of experience, she didn’t just teach—she listened. And what she heard, again and again, was a hunger not for food, but for discovery, belonging, and expression.

When the Granny Cloud initiative—a volunteer-driven project that connected retired educators with children—came to a close, Monika felt the silence it left behind. Along with her friend and fellow educationist Lesley Keast from Spain, she wondered: What if that spark of connection could be reignited? That one idea gave birth to The LightBeam Project. It began modestly: a handful of volunteers, one school, a few curious children, and shaky internet. But it carried a powerful belief: every child has the right to dream, and someone, somewhere, will listen.
Unlike traditional education interventions, LightBeam didn’t come with a manual. It came with open-ended conversations. Sessions inspired by SOLE (Self-Organised Learning Environments) nudged children toward self-discovery. Initially, the children were hesitant.
“They were used to answers, not questions,” Monika recalls.
But soon, wonder took over. They began asking: Why do we age? What if all insects disappeared? These weren’t sessions—they became rituals of curiosity.
As their questions deepened, so did their digital skills. Devices once used for distraction turned into tools of creation. Children began making digital presentations, recording videos, and sharing local traditions with volunteers across the globe. One girl proudly made a Canva slideshow introducing her Beamer to her village’s customs. These weren’t just projects. They were windows into identity.

Lesley Keast, one of LightBeam’s earliest volunteers, reflects on the transformation she’s seen. “The children now have SOLE sessions in their learning DNA. They own the enquiry. They direct the wonder.” For her, the project isn’t just about teaching—it’s about being part of a global community stitched together by purpose. “Our WhatsApp and Facebook groups are more than admin tools. They’re our digital campfires,” she smiles.
Sometimes, it’s the smallest moments that leave the biggest marks. In one session disrupted by technical issues, Lesley recorded a video and sent it to the students with a few questions. They responded with videos of their own. One came from Ruby, a student who had never spoken during any session. With support from her peers, she sent a video back—radiant with confidence. “That’s when the ice cracked,” Lesley said.
In another session, students chose their own topics and returned with insights on dark matter and Freud. “We thought those were far beyond them,” Lesley said. “But with no ceilings, they soared.”
The LightBeam Project has no classrooms. And that’s its strength. By embedding itself into existing schools—like DIKSHA in Gurgaon—it stays grounded. DIKSHA, Monika shares, has been a pillar, ensuring support, space, and safety for these sessions. The absence of fixed walls creates a flexibility rare in educational systems. Sessions can happen anywhere children and curiosity meet.

The project’s growth depends on sustained partnerships—with schools, funders, and storytellers. “Support in storytelling,” Monika says, “goes a long way. Stories beam us into places we’ve never been.”
For teachers who feel trapped by rigid systems, Monika’s advice is gentle: Start small. Ask students what they’re curious about. Let them explore. Joy isn’t the enemy of rigour—it fuels it. And agency doesn’t create chaos. It creates connection.
Through The LightBeam Project, Monika Banga has redefined what education looks like in a post-pandemic world. Not transmission, but transformation. Not instruction, but invitation. Each call is a candle lit. Each question, a door opened. Each child, a beam of light—brighter than the last.
Education
Dancing Beyond Boundaries – The Story of Krithiga Ravichandran

In the heart of Puducherry, where colonial buildings wear salt stains and stories, lives a woman quietly orchestrating a revolution — barefoot, graceful, and defiant. Krithiga Ravichandran, a Bharatanatyam dancer and Assistant Professor of Computer Science, moves between two seemingly different worlds. But look closer, and both are bound by the same rhythm — teaching, nurturing, and transforming.
Born into a family where the arts were heritage, not hobby, Krithiga was raised by the sounds of mridangam, violin, and Carnatic ragas. Her earliest memories? Her grandmother reciting jathis while tapping on a steel plate. “That was my first dance class,” she recalls. “No stage. Just the veranda and a heart full of movement.” By five, she was training formally in Bharatanatyam. And yet, even then, she saw how exclusionary the classical arts could be. The costs — of costumes, jewellery, music recordings — kept so many young girls out.
In 2014, on her birthday, Krithiga founded the Veer Foundation of Arts and Culture Trust, inspired by her father’s values of service. With it, she began offering free Bharatanatyam classes to underprivileged girls. These weren’t just lessons in movement, but in identity. Under temple porticos, community halls, and now small studios, these girls train rigorously — not to perform for others, but to discover themselves.

When she’s not dancing, Krithiga teaches Computer Science at Indira Gandhi Arts and Science College.
“Whether I’m breaking down a loop or a mudra, it’s the same joy — watching a student’s eyes light up.”
Her days begin with code and end in abhinaya. Yet, this rhythm energizes her — it’s how she lives her purpose.
Over the years, shy girls who once hesitated to speak now take the stage with confidence. Dance has offered them more than grace — it has given them resilience. “They come unsure,” Krithiga says. “But they bloom. They plan rehearsals, mentor juniors, manage logistics. They lead.” What begins as dance becomes training in leadership, storytelling, budgeting, and cultural memory.
Dancers in the Making, Leaders in the Wings
In a pioneering move, Krithiga introduced Bharatanatyam as a therapeutic tool inside Puducherry’s Central Prison. “It was experimental,” she admits. “But we saw remarkable change — calmness, awareness, even hope.”
Some questioned her decision. “Why offer sacred art to prisoners?” But she insists: “Who better to understand longing and repentance?” To Krithiga, art must include. Art must heal.
Creating safe, inclusive spaces for marginalised girls remains central to her vision. “They don’t just need a guru. They need a safe adult.” She counsels, supports, and makes sure no girl feels alone. From arranging transport to lending jewellery, she builds a circle of trust around them. Much of it runs on her own earnings. “If you believe in something, you fund it — with time, energy, and soul.”

Though she receives small donations — old costumes, music books — she’s kept the work intimate and rooted. “Every piece of jewellery on stage has a story,” she says. “Someone’s daughter outgrew it, someone remembered their Arangetram. It’s a circle of generosity.”
“Dance Doesn’t Ask Who You Are. It Asks, How Do You Feel?”
Krithiga’s vision is to build a holistic centre for classical arts — with a stage, library, wellness wing, and space for reflection. “I don’t want to just train dancers. I want to raise artists — those who know the pulse of the past and can choreograph the future.”
To her, Bharatanatyam isn’t ornamental. It’s essential. A language of liberation — especially for those the world forgets to watch.
Education
The Man Who Called His Students Gods: Dwijendranath Ghosh
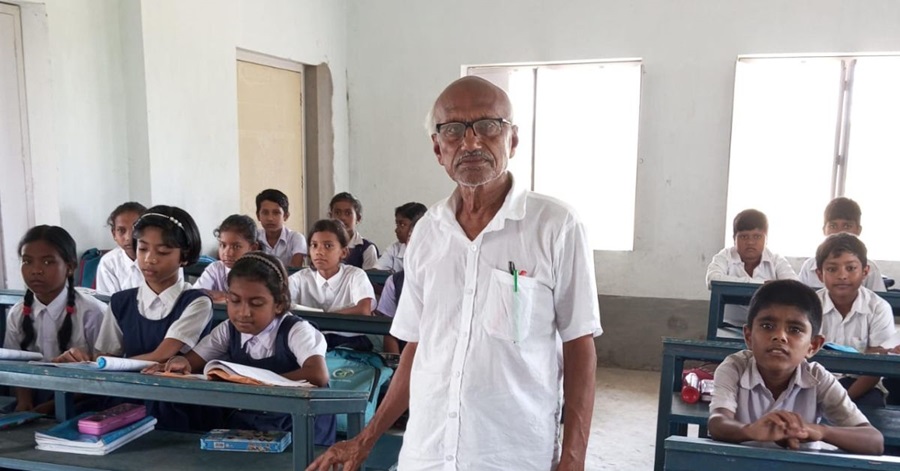

Dwijendranath Ghosh calls himself ordinary.
But how many “ordinary” people spend their retirement building a school from scratch — with no funding, no government salary, and no promise of support? How many choose to teach every day, without compensation, well into their 70s? And how many refer to their students — many from the most marginalised sections of rural Bengal — as gods?
At 78, Ghosh is the heart and soul of Basantapur Junior High School in West Bengal’s Hooghly district. He opens the gate each morning. He teaches children for free. He never left his village — but his impact now reaches far beyond it.
From Barefoot Dreams to Blackboards
Ghosh’s journey is rooted in personal struggle. Growing up in deep poverty, he had no books, no uniforms, and no certainty. His childhood was spent walking barefoot to school, borrowing textbooks, and studying by the glow of kerosene lamps. And yet, he rose. A master’s degree from Burdwan University followed in 1973.
“The pain of those days still haunts me,” he says. “But it also shaped me.”
That pain turned into purpose. Soon after graduating, he and a few friends began running an informal high school in their village—unrecognised, unpaid, but unstoppable. For nine years, they taught with nothing but commitment. When the government finally recognised the school in 1982, Ghosh had already left to take a government job elsewhere, forced by financial needs.
The Second School
He retired in 2008. But instead of resting, he returned to his village and found that little had changed. Girls were still dropping out after primary school. Child marriage was common. A generation was fading into invisibility. So he began again. With no funding, no building, and no staff, he worked for five years to create Basantapur Junior High School.
In 2014, the school was officially recognised. But the journey was never about the paperwork — it was about presence. Every morning, Ghosh arrives before the first bell. He teaches, supports, and uplifts — without compensation. Because for him, teaching is service.
A Volunteer Army — Running on Faith
He’s not alone. A team of young, educated, but unemployed volunteer teachers stands beside him. They could have chosen easier paths, but chose this one out of belief, not benefit. They are unpaid. At times, local donors offer small stipends, but it’s inconsistent. Most are struggling, yet they return every day. “They have given the most valuable years of their lives,” Ghosh says.
The school receives only ₹25,000 a year as a government grant. For three years, even that was inaccessible. What kept it alive? Former students, now grown, are donating what they can. The community is pitching in. Alumni returning to teach. When a government teacher recently disrespected the volunteers, the team almost walked out. But students and parents wouldn’t let them. Ghosh stepped in to calm tensions.
“We can’t let one bad moment undo decades of good,” he told them.

A Temple Against Child Marriage
One of the school’s biggest challenges is child marriage. In villages like Basantapur, girls are often married by 14—seen as burdens, not futures. By offering local access to education, the school has become a shield. Many girls have completed higher education here. But the battle continues. “This trend,” Ghosh says, “is like an infection. It keeps coming back.”
At Basantapur Junior High School, learning is about more than grades. Students perform in cultural shows, play football and cricket, and take part in morning assemblies. They learn to speak, to lead, to dream. There’s no structured life skills module—because the school itself is the life lesson. Students know they are seen, heard, and cared for. Teachers know their work matters. And visitors walk away knowing this is not just a school—it’s a movement.
His empathy, his daily discipline, and his belief in every child form the blueprint that his students follow. And his impact lives in their dreams.
The Final Lesson
What does his family think?
“They worry about my health,” he laughs. “Not about the money.”
His pension is enough for his needs. What he seeks is not comfort — but recognition for his team. “These teachers have earned the right to be made permanent. A hundred times over,” he says.
When asked what keeps him going, he simply says:
“So long as I am in the school, I am alive.”
In an education system obsessed with metrics, Ghosh offers something rare: meaning.
He didn’t build a career.
He built a sanctuary.
He didn’t earn a salary.
He earned generations of gratitude.
And in every child who enters Basantapur Junior High, the final lesson is quietly imprinted:
Service is not sacrifice. It’s grace.
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoDharav Utsav to Celebrate Rajasthan’s Cultural Heritage and Local Talent
-
 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoAI to Become a Core Subject from Class 3: India’s Big Leap Toward a Future-Ready Generation
-

 Inspiration2 months ago
Inspiration2 months agoUmeed: A Ray of Hope for Better Tomorrow
-

 Knowledge3 weeks ago
Knowledge3 weeks agoBuilding a Healthier India: Why School Health Programs Are Essential
-

 Inspiration3 weeks ago
Inspiration3 weeks agoBefore the Nobel, There Was a Teacher
-

 Education3 weeks ago
Education3 weeks agoWhat the Indian Army Teaches Our Children Beyond Textbooks
-

 News2 weeks ago
News2 weeks agoInclusive Education Summit 2026: Designing the Future of “Learner-Centric” Education
-

 Education5 days ago
Education5 days agoSupreme Court’s Landmark Judgment for Schools: Menstrual Health is a Fundamental Right
-

 Education5 days ago
Education5 days agoBeyond the First Bell: 5 Key Takeaways for School Leaders from Economic Survey 2025–26



























































