Education
Heatwaves Disrupt School Education Across India

The scorching heatwaves sweeping across India have significantly impacted school education, prompting several states to take precautionary measures. Many educational institutions have either adjusted their timings or announced early summer vacations to safeguard students from the extreme weather conditions.
In Chandigarh, authorities have decided to close schools by noon, responding to a severe heatwave alert. This decision aims to protect students from the peak afternoon heat, which poses severe health risks. Similarly, Ghaziabad has closed schools for classes up to 8th grade until May 25th due to the scorching heatwave conditions.
Haryana’s Education Department issued a notice to the Deputy Commissioner concerning the closure of schools amid rising temperatures. The department’s proactive approach highlights the seriousness of the situation and the importance of ensuring student safety during such extreme weather events.
Moreover, several states have preponed their summer vacations. This decision, although disruptive to the academic calendar, is necessary to protect the well-being of students. Schools in regions like Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Delhi have all adjusted their schedules to accommodate the unforeseen weather challenges. The Financial Express reports that these changes are a direct response to the ongoing heatwave, which has made regular school hours untenable.
In a notable instance, the Chandigarh administration’s move to close schools by noon is a commendable example of swift action in the face of environmental challenges. Similarly, Ghaziabad’s early closure for younger students is a preventive measure to avoid heat-related illnesses.
These disruptions have brought to light the urgent need for long-term solutions to deal with extreme weather conditions. While short-term measures like adjusting school hours and early vacations are necessary, there is a pressing need to incorporate climate resilience into educational planning. This could include infrastructural changes to schools, such as better ventilation, air conditioning, and green spaces to combat the heat. Additionally, education on climate change and its impacts should be integrated into school curriculums to raise awareness among students.
These heatwaves impacting India have led to significant changes in school operations, reflecting the need for adaptive measures in the face of climatic challenges. And this is just the beginning. So these adjustments, while disruptive, are not permanent solutions for ensuring the safety and well-being of students during extreme weather events. As India continues to face such climatic adversities, a holistic approach to climate resilience in education is imperative.
Education
The Man Who Called His Students Gods: Dwijendranath Ghosh
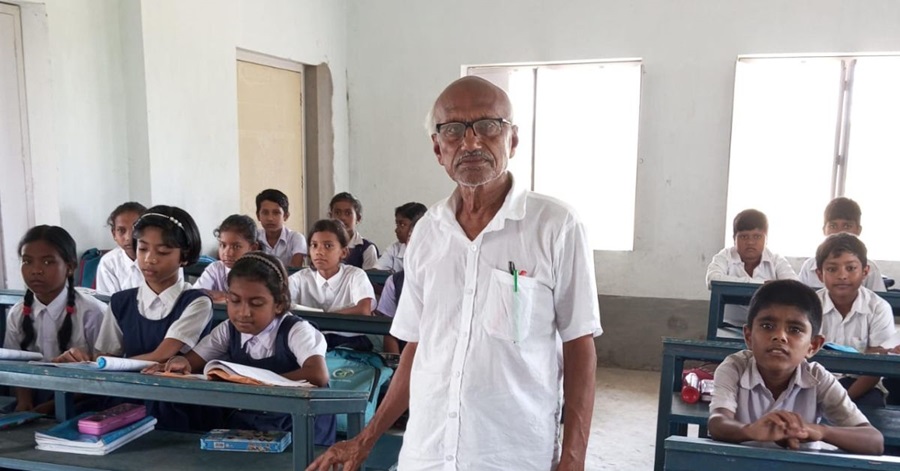

Dwijendranath Ghosh calls himself ordinary.
But how many “ordinary” people spend their retirement building a school from scratch — with no funding, no government salary, and no promise of support? How many choose to teach every day, without compensation, well into their 70s? And how many refer to their students — many from the most marginalised sections of rural Bengal — as gods?
At 78, Ghosh is the heart and soul of Basantapur Junior High School in West Bengal’s Hooghly district. He opens the gate each morning. He teaches children for free. He never left his village — but his impact now reaches far beyond it.
From Barefoot Dreams to Blackboards
Ghosh’s journey is rooted in personal struggle. Growing up in deep poverty, he had no books, no uniforms, and no certainty. His childhood was spent walking barefoot to school, borrowing textbooks, and studying by the glow of kerosene lamps. And yet, he rose. A master’s degree from Burdwan University followed in 1973.
“The pain of those days still haunts me,” he says. “But it also shaped me.”
That pain turned into purpose. Soon after graduating, he and a few friends began running an informal high school in their village—unrecognised, unpaid, but unstoppable. For nine years, they taught with nothing but commitment. When the government finally recognised the school in 1982, Ghosh had already left to take a government job elsewhere, forced by financial needs.
The Second School
He retired in 2008. But instead of resting, he returned to his village and found that little had changed. Girls were still dropping out after primary school. Child marriage was common. A generation was fading into invisibility. So he began again. With no funding, no building, and no staff, he worked for five years to create Basantapur Junior High School.
In 2014, the school was officially recognised. But the journey was never about the paperwork — it was about presence. Every morning, Ghosh arrives before the first bell. He teaches, supports, and uplifts — without compensation. Because for him, teaching is service.
A Volunteer Army — Running on Faith
He’s not alone. A team of young, educated, but unemployed volunteer teachers stands beside him. They could have chosen easier paths, but chose this one out of belief, not benefit. They are unpaid. At times, local donors offer small stipends, but it’s inconsistent. Most are struggling, yet they return every day. “They have given the most valuable years of their lives,” Ghosh says.
The school receives only ₹25,000 a year as a government grant. For three years, even that was inaccessible. What kept it alive? Former students, now grown, are donating what they can. The community is pitching in. Alumni returning to teach. When a government teacher recently disrespected the volunteers, the team almost walked out. But students and parents wouldn’t let them. Ghosh stepped in to calm tensions.
“We can’t let one bad moment undo decades of good,” he told them.

A Temple Against Child Marriage
One of the school’s biggest challenges is child marriage. In villages like Basantapur, girls are often married by 14—seen as burdens, not futures. By offering local access to education, the school has become a shield. Many girls have completed higher education here. But the battle continues. “This trend,” Ghosh says, “is like an infection. It keeps coming back.”
At Basantapur Junior High School, learning is about more than grades. Students perform in cultural shows, play football and cricket, and take part in morning assemblies. They learn to speak, to lead, to dream. There’s no structured life skills module—because the school itself is the life lesson. Students know they are seen, heard, and cared for. Teachers know their work matters. And visitors walk away knowing this is not just a school—it’s a movement.
His empathy, his daily discipline, and his belief in every child form the blueprint that his students follow. And his impact lives in their dreams.
The Final Lesson
What does his family think?
“They worry about my health,” he laughs. “Not about the money.”
His pension is enough for his needs. What he seeks is not comfort — but recognition for his team. “These teachers have earned the right to be made permanent. A hundred times over,” he says.
When asked what keeps him going, he simply says:
“So long as I am in the school, I am alive.”
In an education system obsessed with metrics, Ghosh offers something rare: meaning.
He didn’t build a career.
He built a sanctuary.
He didn’t earn a salary.
He earned generations of gratitude.
And in every child who enters Basantapur Junior High, the final lesson is quietly imprinted:
Service is not sacrifice. It’s grace.
Education
NCERT Launches New Class 5 & 8 Textbooks, Makes Art Education Mandatory

The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has launched a new set of textbooks for Classes 5 and 8 for the 2025–26 academic session, designed in accordance with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) 2023. This marks a significant shift in India’s school education approach, with a renewed focus on creativity, scientific temper, skill development, and values rooted in Indian heritage.
The new Class 8 textbooks include Curiosity (Science), Kaushal Bodh (Vocational Education), Poorvi (English), Malhaar (Hindi), and Kriti (Art Education). For Class 5, the newly introduced books are Santoor (English) and Veena (Hindi). Designed with simple language and rich visuals, these books aim to spark curiosity while enhancing concept clarity.
Among the highlights is Curiosity, the Class 8 science book that covers topics across physics, chemistry, and biology through real-life examples and activity-based modules. It includes dedicated chapters on COVID-19 vaccine development, India’s space missions like Chandrayaan, Ayurveda, and the Make in India initiative—positioning science education within the context of India’s modern achievements.
Kaushal Bodh introduces students to skill-based learning, preparing them for real-world employment and entrepreneurship. Poorvi, the Class 8 English book, presents stories based on the lives of national icons such as Major Somnath Sharma, Verghese Kurien, and physicist Bibha Choudhary to inspire values like courage and innovation.
In a landmark move, art education has been made compulsory. Kriti brings music, drama, and theatre into the mainstream classroom, as recommended by NEP 2020. This initiative aims to nurture creativity across disciplines, allowing children to express themselves beyond textbooks and tests.
For younger learners, the new Class 5 books Santoor and Veena adopt an activity-based learning model that promotes language acquisition through stories, songs, and play—departing from rote methods to make early education more engaging.
Despite enthusiasm from schools and parents, distribution has seen some hurdles. Reports indicate limited stock availability on platforms like Amazon and in local stores. Many parents and educators are urging NCERT to make digital versions of the books available in PDF format. NCERT has acknowledged the demand and plans to print over 15 crore copies to meet nationwide needs. Partnerships with e-commerce platforms are also being explored to streamline delivery.
This new textbook rollout is part of a broader national effort to reimagine the Indian classroom—rooted in local knowledge, focused on real-world skills, and responsive to 21st-century learning needs.
Education
US Embassy Tightens Social Media Checks for Student Visas

The U.S. Embassy in New Delhi has intensified its vetting process for applicants of F, M, and J non-immigrant visas by requiring disclosure of and public access to social media accounts used over the past five years. Under the updated rules, all social media handles—including Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, TikTok, Reddit, and others—must be listed on the DS‑160 form, and profiles must be set to public during the visa screening process.
Consular officers are explicitly authorised to review candidates’ public posts, comments, and shares—and may even check private messages—to assess “hostility toward the United States” or support for extremist or anti‑U.S. content. Failure to comply, misrepresent information, or omit an account can result in visa denial and bar future visa eligibility.
This update forms part of a broader expansion of screening procedures initiated in June. Diplomatic posts worldwide paused student visa interviews to implement the new protocol, which treats every visa decision as a “national security decision”. The U.S. Embassy in India also recently issued a reminder via X, stating continuous monitoring of visa holders is in effect and violations of U.S. laws—even after visa issuance—can result in revocation and deportation.
These changes reflect the U.S. administration’s emphasis on enhanced national security and combating visa fraud. While some students and immigration advocates have raised concerns about privacy and freedom of expression, the Embassy stresses that visa screening is an ongoing process. Indian students and other applicants are advised to review their online activity and ensure transparency with their DS‑160 submissions.
Education
A School Without Walls: The Pehchaan Story, Led by Akash Tandon

Sometimes the biggest change begins with the smallest act — a few mats on the ground, five curious children, and a group of young volunteers refusing to look away.
In the heart of Delhi, just steps away from the WHO headquarters and the grandeur of Lutyens’ Delhi, an open drain separates two vastly different worlds. On one side: embassies, privilege, policy. On the other: a slum of over 10,000 people, where childhood is often lost to labour, illness, and invisibility.
It’s here that Pehchaan — The Street School — took root.
“We knew we couldn’t change the world. But we could change someone’s world.”
For co-founder Akash Tandon, Pehchaan wasn’t part of a five-year plan. It was a response. A moment of reckoning, watching children play in a toxic drain, unaware of the danger. “This isn’t water,” they told the kids. “It’s poison.” The kids laughed.
That laugh stayed with them.

So Akash and his friends returned. Not with speeches or slogans — but with notebooks, mats, and the stubborn belief that every child, no matter their address, deserves to learn.
What started as a weekend effort with five students has now grown into a network of 10 centres, reaching over 1,600 children. And yet, Pehchaan remains fiercely grassroots — no paid staff, no office, no formal backing. Just a living, breathing movement powered entirely by volunteers.
Education That Heals
Pehchaan doesn’t just teach. It listens. It adapts. It believes that the first step to learning is dignity — and that means personalised mentorship, trust, and a curriculum that sees the child beyond the textbook.
Children are grouped into three learning tracks: those already in school who need support, dropouts looking to rejoin, and first-time learners who’ve never stepped inside a classroom. The model is lean but layered — with low student-volunteer ratios, personalised goals, and modules that blend academics with life skills.
There’s dance, storytelling, debate, and painting. There’s coding and digital literacy. And there’s space to be seen.
“My school encouraged me to sing, speak, perform,” says Preeti Adhikari, a longtime Pehchaan volunteer. “These children deserve that too. Because it’s not just about marks — it’s about confidence.”

From Drain to Degree
One story stays close to Akash’s heart.
A boy joined Pehchaan in Class 3. He faced pressure to drop out and start working. But he stayed. Pehchaan gave him academic support, counselling, and community. He completed Class 12 with 86%. Then cracked the Delhi University entrance exam.
But the resistance didn’t stop. “What will you earn from books?” neighbours asked. Still, Pehchaan raised the funds, got him into college — and today, that boy teaches at the same centre where he once sat as a student.
“He’s the proof,” Akash says. “That this works. That this matters.”
A System That Runs Without a System
Despite being volunteer-run, Pehchaan operates with the discipline of a corporate team. Every 10 teaching assistants report to a centre head. Weekly reports are filed. Interns handle HR, design, digital media, and curriculum — all without salaries.
In 2024 alone, 8,000+ interns from 75+ colleges joined hands with Pehchaan. Many now lead verticals, train others, or launch their own community learning spaces.

“Earlier I taught five kids,” one intern said. “Now I’m hiring 30 volunteers who each teach five. That’s impact at scale.”
The community, too, is beginning to notice. Blanket drives, nutrition partnerships, and the newly launched Digital Literacy Lab — built with scrap funding and donated laptops — have brought a sense of permanence to the pop-up classrooms.
But the hardest barrier? Still parents.
“You show up for 10 years — then they believe you.”
Convincing slum families to send their children — especially girls — to informal schools was a long battle. Many children still get married by 14. Others are pushed into work.
But when the same group of volunteers keeps returning, year after year, in sun, rain, or smog — trust begins to grow. “We’ve moved beyond convincing now,” Akash reflects. “We’re building the next layer. It’s about dignity.”
Girls who once never stepped outside now give public speeches. Boys once caught in addiction now mentor others.
Akash is clear about the goal: “We don’t want to go pan-India. We want 50 other Pehchaans to emerge. That’s how you scale — by letting go.”

Read the full story in our latest issue, Teacher Warriors 2025.
Education
CBSE Requests Affiliated Schools to Host NIOS Public Exams in October–November 2025

The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has called on its affiliated schools to assist with the conduct of the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) public examinations scheduled for October–November 2025.
In a recent official communication addressed to principals and heads of schools, CBSE emphasised that NIOS requires infrastructural and logistical support to conduct its biannual board examinations, which include assessments for Class 10, Class 12, and various vocational courses.
“The next Public Examinations of NIOS are scheduled to be held in October–November 2025,” the notice stated, adding that CBSE-affiliated institutions have historically played a key role in enabling NIOS to run its exams smoothly.
Schools willing to extend support have been asked to register their intent on the official NIOS website at https://exams.nios.ac.in under the section: Examination Centre > Register Now.
NIOS operates under the Ministry of Education and is the country’s largest open schooling body. It caters to learners from diverse backgrounds, offering flexibility in learning and examination schedules, especially for students who may be outside the traditional school system.
“Your assistance will help NIOS in holding Public Examinations of its learners,” the CBSE notice concluded, underlining the collaborative nature of this effort.
By participating in this initiative, CBSE schools are not only supporting a national mandate for inclusive education but also contributing to educational equity by helping millions of NIOS learners access fair and organised exam environments.
Education
When AI Reaches the Top of Bloom’s—and Our Students Are Left Behind

We often talk about how AI is transforming education, but are we talking enough about what it’s quietly taking away?
CREATIVITY
As Sir Ken Robinson often reminded us,“Creativity is as important as literacy.”
And yet, in a system so focused on marks, rubrics, and outcomes,creativity is often the first thing we sacrifice.
Bloom’s Taxonomy places Creating right at the top,but in many classrooms today, it feels like AI has reached that level faster than our students have.While children are still figuring out sentence structure and grammar, AI is already generating poems, paintings, and polished presentations with a single click.
Which brings us to a deeply uncomfortable question:
What happens when AI starts to “create”?
And more importantly—what happens when our students stop?
Today’s AI isn’t truly creative.It mimics. It reuses. It draws from patterns and reproduces what’s already been done.And if we don’t pause now to protect what’s uniquely human,we risk raising a generation of students who know how to use tools,but don’t know how to think.
Everything’s Starting to Look the Same
I’ve seen it. You’ve probably seen it too.
Creative writing tasks that sound strangely uniform.Artwork that feels formulaic.Presentations that are polished, yes, but empty.AI has democratised access to intelligence,but in doing so, it has started to flatten creativity.We’re now at a point where students are outsourcing not just answers,but imagination.
But true creativity cannot be prompted.It’s messy. It’s emotional. It’s born out of thinking, feeling, failing, and trying again. It lives in how we interpret the world. In how we care. In how we connect.
How Can We Bring Creativity Back?
We need to bring back the building blocks of creativity.
READ
Let students read more deeply,not just skim or summarise.Let them feel what’s in the pages, get lost in ideas, debate their favourite character in a book or movie, and form their own emotional connections.
EXPERIENTIAL LEARNING
Let’s re-focus on learning through doing,projects, fieldwork, play, nature, making mistakes, working with hands, collaborating, and reflecting.It’s in these non-linear, real-world experiences that creativity quietly blooms.
FINDING THE PURPOSE
We need to pause and ask: What is this child truly passionate about?
It could be animals, gardening, football, art—anything that sparks joy and curiosity.
Once we discover that passion, we can connect learning to it.
Let’s not just ask what they’re reading, but why they’re reading it.
What inspires them? How can that interest help them solve real-world problems?
That’s when learning becomes meaningful,and creativity starts to flow with purpose.
Because by the time they grow up,the world won’t just need people who can use AI – It will need people who can imagine what AI cannot.
Education
No More Backbenchers: How a Simple Seating Shift Is Reimagining Learning

When was the last time you thought about where your students sit? If you think a seat is just a seat — think again.
A simple shift in seating arrangements, sparked by the Malayalam film Sthanarthi Sreekuttan, is inspiring schools in Kerala to break the age-old divide of “frontbenchers” and “backbenchers”. The Times of India recently reported how some schools have begun rethinking how rows of benches shape mindsets — often turning bright learners into passive listeners by default.
Preethi Vickram, Founder of Tapas Progressive Learning, applauded this unique approach online:
The truth is, classroom seating is more than furniture. It’s a mirror of our teaching philosophies. For decades, rigid rows have told students to sit down, face forward, and stay quiet while the teacher talks. One person speaks, everyone else absorbs. But learning doesn’t work in a straight line — it happens in loops, debates, disagreements, and those random questions that make everyone think.
It’s not just an emotional idea — there’s solid science behind it. A 2020 review in Frontiers in Psychology found that classroom layouts directly affect interaction and motivation. The Classroom Direct blog points out that flexible layouts foster collaboration, peer learning, and inclusivity. And a 2022 ESI Conference study noted that traditional seating can create power hierarchies where only frontbenchers thrive.
In India, we know this divide well. Backbenchers are often seen as mischievous or disinterested — but what if they were simply disengaged by design? Many schools still enforce outdated seating rules: girls must sit separately from boys; ‘weak’ students banished to the back; bright ones pushed to the front like prized trophies. But what are we telling children when we make them sit apart based on gender, marks or silence? That some voices matter more than others.
Architects and education designers have long championed a different approach. Rosan Bosch’s designs for Sweden’s Vittra School are modular and playful, showing that space itself can be a teacher. Danish Kurani, an expert in reimagining learning spaces, writes that the biggest mistake schools make is assuming they can modernise teaching methods without changing the physical space: “You can’t have collaborative, project-based learning in a classroom still set up for rows of passive listening.”
Kerala’s small but significant shift is a reminder that big change often starts with small, visible actions. When students sit in circles, clusters, or flexible pods, they are more likely to speak up, listen actively, and learn from one another. It helps break the silent stigma that ‘the back’ means you don’t matter.
Designers like Kurani argue that students should have a voice in how their classrooms look and feel — because when the space reflects curiosity and movement, it encourages the same in young minds. The Studio Schools Trust in the UK, the Reggio Emilia approach in Italy, and Big Picture Learning schools in the US all prove that flexible, student-centred learning environments are not “alternative” anymore — they’re the future.
And this shift doesn’t need fancy gadgets or big budgets. It’s the lowest-cost ‘edtech’ upgrade schools can make: moving a few benches, opening up a circle, creating nooks for quiet work and spaces for loud debate. It tells children: “Your voice matters, wherever you sit.”
In a world that needs more curiosity, connection, and creativity — we cannot afford to let seating stifle learning.
So let’s not just remove the backbenchers — let’s remove the very idea of front and back.
Because when every child feels seen and heard, there are no bad seats in the house.
References: * Classroom Direct Blog, 2021 * Frontiers in Psychology, 2020 * ESI Conference Proceedings, 2022 * Danish Kurani on Common Classroom Design Mistakes
Education
NEP 2020’s Panch Sankalpa to Guide Central Universities: Dharmendra Pradhan

More than 50 Vice Chancellors of India’s central universities gathered in Kevadia, Gujarat for a two-day conference to assess the implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and lay the groundwork for the coming years. Organised by the Ministry of Education in collaboration with the Central University of Gujarat, the conference seeks to align higher education institutions with the broader national vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, addressing the gathering, outlined the Panch Sankalpa of NEP 2020—next-generation education, multidisciplinary learning, innovation, holistic development, and Bharatiya orientation—as the guiding principles for institutional transformation. He emphasised that India’s higher education ecosystem has undergone significant change over the last decade, becoming more flexible, inclusive, and innovation-driven. Student enrolment has increased by 30% since 2014–15 to reach 4.46 crore, with female enrolment growing by 38%. The gross enrolment ratio for female students now exceeds that of males, while enrolment among Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes has also improved. PhD enrolments have nearly doubled, with women registering a 136% increase.
The Minister urged Vice Chancellors to play a transformative role by redesigning curricula, improving digital infrastructure, strengthening faculty training, and promoting multidisciplinary education. He reiterated the goal of raising the gross enrolment ratio in higher education to 50% by 2035, in line with the NEP’s vision. Placing students at the centre of all reform efforts, he called on universities to foster job creators, ethical innovators, and socially responsible graduates.
Pradhan also encouraged institutions to reflect on India’s intellectual heritage while preparing for a global future, invoking the academic “Triveni Sangamam” of celebrating the past, calibrating the present, and creating the future. He recommended that each university prepare a strategy paper to fully implement NEP 2020, incorporating Indian Knowledge Systems, digital skilling initiatives, and campus-led innovations. He proposed that such review conferences be hosted at the campus level to promote decentralised engagement and exchange of ideas.
Dr. Hashmukh Adhia, Chancellor of the Central University of Gujarat, spoke about the six principles of karmayoga and the importance of Indian knowledge systems in shaping individual and collective progress. Dr. Vineet Joshi, Secretary of Higher Education, reflected on the journey since the policy’s launch and reiterated that NEP 2020 imagines universities not as degree-granting institutions, but as ecosystems of innovation, research, and holistic development. Dr. Sunil Barnwal, Additional Secretary, underlined the foundational values of access, equity, quality, affordability, and accountability, and highlighted the importance of stakeholder partnerships in driving reform.
Prof. Rama Shanker Dubey, Vice Chancellor of Central University of Gujarat, reaffirmed that all central universities are committed to advancing the vision of Viksit Bharat through concrete, on-ground measures. The conference, spread over ten thematic sessions, includes discussions on the Four-Year Undergraduate Programme, digital tools like SWAYAM and AAPAR, university governance through SAMARTH, alignment of education with the future of work, and research and innovation frameworks such as ANRF and PMRF. Other themes include equity, internationalisation, faculty development, and the integration of Indian languages and knowledge systems.
Participating universities include Jawaharlal Nehru University, University of Delhi, Tripura University, Central University of Rajasthan, Sikkim University, and many others. The outcomes of the conference are expected to help define the next phase of NEP 2020 implementation, enabling institutions to become more responsive, inclusive, and globally competitive.
Education
Less Than Half of Indian Schools Offer Skill-Based Courses for Senior Students: NCERT Survey

A recent survey conducted by NCERT’s National Assessment Centre has revealed that only 47% of schools across India currently offer any skill-based courses to students in Class 9 and above. This statistic highlights a significant gap in the availability of practical, job-ready education at the secondary level—an area that India’s New Education Policy has been aiming to strengthen.
The survey also found that student enrolment in these courses is even lower. Just 29% of students in Classes 9 and above have opted for skill-based subjects, indicating the need for better awareness, guidance, and integration of these programmes into mainstream learning.
The courses that are being offered include trending and industry-relevant subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics, Digital Marketing, and E-commerce. However, experts believe these numbers are far from adequate in a country with one of the world’s largest youth populations.
At the higher education level, there is a stronger push for integrating skills into curricula. Many skill universities now structure their programmes with a 60% to 70% skill-based component, offering students a blend of theoretical and practical knowledge designed to make them workforce-ready.
The NCERT report recommends that more schools must be brought into the fold of skill education. With the job market rapidly evolving and the demand for digital and emerging technology skills growing, strengthening school-level skill education can bridge the gap between academic learning and real-world employability.
Building robust vocational streams in schools could also help address the challenge of students dropping out after secondary education due to a lack of clear pathways into meaningful careers.
Education
The Woman Who Refused to Disappear – Aditi Sharma’s Quiet Fight for Education

In a quiet corner of Karnal, Haryana, Aditi Sharma runs a small school for underprivileged children. She is the founder, principal, and often, the only teacher. As a transgender woman in North India, her journey has been marked by resistance and isolation — but also by unwavering commitment. Her school may lack formal recognition or resources, but it stands as a space of learning, inclusion, and quiet resilience.
Aditi is not just the founder and principal of Haryana Public School. She is also a transgender woman who dared to imagine a different kind of North India — one where prejudice makes way for possibility, and education belongs to everyone.

But dreams, she learned early on, come at a cost.
Born and raised in Delhi, Aditi was no stranger to the stereotypes that shadow the transgender community.
“Even educated people carry the assumption that all trans people beg or perform ceremonial rituals. That’s the stereotype I grew up seeing around me,” she says.
It disturbed her and lit the fuse of quiet rebellion.
Leaving Delhi behind, she moved to Karnal with one goal: to build a school not just for visibility, but for children who had nowhere else to go. Her father, unaware she had come out, gave her a 1,200-square-yard plot to build on. “At the time, I hadn’t fully come out. Had they known I was transgender, they wouldn’t have named it to me.”
What she built wasn’t just a school — it was a statement.
In the beginning, there were no teachers, no steady funds, and no blueprint. “I doubted whether I could run a school at all. I had no confidence. But slowly, a few children started coming in. Then a few more. At one point, we had 60–70 students.”
That number dropped, not due to a lack of dedication, but constant harassment. Neighbours let their dogs loose outside. Parents were warned, “Why send your child there? This isn’t a real school.” Some believed her identity disqualified her from leadership, from teaching, from existing with dignity.
She persisted anyway.
Aditi never set out to run a school for underprivileged children. It wasn’t a strategic choice or a targeted mission. It was simply what remained when everyone else walked away. Families who could afford higher fees refused to send their children to a school run by a transgender woman. Teachers quit under social pressure. So she opened her doors to those who had nowhere else to go — children whose families could pay ₹100 a month, sometimes just ₹50, and often nothing at all. “If they don’t learn here, they won’t learn anywhere,” she says. And so she teaches — not because it’s easy, but because no one else will.

Her day begins at 4 AM — cleaning, prepping, sourcing supplies. By 8 AM, she’s teaching English, guiding students through computing tasks, or painting with them on borrowed desktops. She buys second-hand books herself. There are no permanent staff members. Most teachers leave within weeks. “They say, ‘My family doesn’t want me working here.’ The social pressure is immense.”
Once, a neighbour handed her a one-day-old baby and walked away. Aditi cared for her. When the child fell ill, she spent 12 days at the hospital with her — and the other children. Alone. “They don’t speak to me anymore,” she says of her family. “I’ve learned to let go. If someone doesn’t want to stay in touch, that’s okay. You still have to be happy.”
Haryana Public School is still not recognised by the state government. Despite its large plot, authorities claim she doesn’t meet the criteria. “Other schools on smaller land get recognised,” she says. “But because I’m transgender, they say no.” Her case is currently being reviewed by the Human Rights Commission. Justice Lalit Batra, in a hearing, reportedly said:
“If she doesn’t meet your current rule, change the rule.”
Meanwhile, the children continue to learn — with donated books, basic tools, and the irrepressible will of one woman. Aditi has even built two giant model airplanes — one stretching 20 feet — from scrap and wood. “They don’t fly, but they spark curiosity. Ten children can sit inside. It makes them dream.”

And dreams are something she insists on, even when the world offers no applause. “One child had developmental issues. No school would take him. People told me I was wasting my time. But he deserved a chance.”
Sometimes, appreciation is scarce. Respect even more so. “When parents don’t respect you, neither do their children,” she admits. “When your own life is a constant struggle, it becomes hard to build emotional bonds.”
But she still shows up every day. Reporters ask why so many people visit her school. “Because we’re doing something that shakes the norms,” she tells the children. “This school is special.”
And they believe her. Because children don’t discriminate. Adults do.
Her message to the transgender community is clear:
“Don’t wait for society to accept you. Build your own path. Even if you’re the only one walking it.”
Aditi Sharma may be the only openly transgender woman in North India running a school. But she’s not asking for sympathy. Just space. Just dignity. Just the right to show up — and not disappear.
“Even if only one child comes,” she says,
“I’ll keep the doors open.”
Read the full story in our latest Teacher Warriors issue: https://scoonews.com/magazines/scoonews-june-july-2025-digital-edition/
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoBanu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature
















































































