Knowledge
Inclusive Education: Tackling Inequalities and Promoting Learning
Mr Mame Omar Diop, Programme Specialist and Chief of Education at UNESCO, New Delhi, and Mr Abhinav Kumar, who works in the education sector at UNESCO, New Delhi, address Inclusive Education in India.
Published
5 years agoon

Education offers the simple ability to read, write, count and calculate which plays a vital role in the process of social progress and development. Access to education has the power to improve the quality of life of an individual by providing economic opportunities; changing public perceptions towards human rights; giving a political voice and understanding legal rights- rights, which an individual might already possess but is not able to utilize because of a lack of knowledge and awareness about what it entails. While access to education is essential, the primary aim of schooling is to transfer knowledge and teach skills to students. In other words, it is important to balance an increase in ‘quantity’ of education with a simultaneous increase in the ‘quality’ of education which is accessible and affordable for each and every individual.
With the vision of “Leaving no one behind”, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG’s) 2030 Agenda by the United Nations has played a pivotal role in drawing attention to the inequalities which restrict access to quality education across the globe. While SDG 4 and SDG 10 specifically talk about ’Quality Education’ and ‘Reduced Inequalities’ respectively, the remaining 15 SDG’s directly or indirectly highlight the emergent need to build an inclusive environment which provides equitable access to quality education for all.
Inequalities do not just exist in societies exclusively but in most cases, different forms of inequality intersect with each other and exacerbate the situation for some individuals. For instance, due to prevailing prejudices, a poor woman from an indigenous community living in a rural area is likely to be more disadvantaged than any other individual in the same locality. This highlights social injustice towards individuals within a community based on their gender, caste, location and cultural habitats. It is extremely important to realise that inclusivity is not restricted to providing access to schools by building infrastructure, ensuring school facilities and increasing enrolment. Geographical location; nutrition; mental health; disabilities are some of the many factors which need to be addressed whilst advocating for inclusivity in education.
Bihar’s case highlighting the importance of inclusivity in education:

Source: World Bank Data, 2016
Figure 1. The graph depicts the disparities in educational attainment (%) among different social groups of Bihar
While there are policy frameworks laid down by the Government of India to reduce and challenge inequalities, they are either not applied correctly or there are multiple forms of inequalities which make these policies redundant. In the education sector, The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009 was passed in an attempt to boost primary level education enrolment rates for children aged between 6 and 14 (Government of India 2009). While this has had a positive impact on the enrolment rates in Bihar with student enrolment rates going above 90% for primary level education (Mukul 2015), figure 1 highlights the large number of disparities among different social groups. Nearly 60% of the Scheduled Caste (historically termed as ‘socially backward communities’ in India) remain to be illiterate while the ‘general’ category seems to have better access to quality education with a 20% figure. Consequently, these differences tend to restrict access to other social protection systems in the long run. This implies the need to amend policies in a way which creates equal opportunities for every individual in the country, regardless of her/his economic status or social identity.
Making foundational learning part of ‘Inclusive Education’
Inclusivity is also to be met with quality learning outcomes. The World Development Report 2018 entirely focused on the urgent need to promote learning to fully utilize the potential of education (World Bank 2018). The report shares a decline in the learning abilities of students mainly from developing countries and has emphasised on the need to prioritize learning and not just schooling. Amongst the developing countries, with a population of over 1.3 billion people spread across the 28 states and 8 union territories, the challenge of providing equal access to quality education is a tremendous one for India. In fact, as per the latest census data, India has a high child population (0-18 years) percentage (39%) highlighting the increased responsibility on the state for providing equitable access to quality education to all age groups (Government of India 2018). While this shows that India has a huge challenge to overcome right now, an optimistic way to look at it is that if an ‘efficient’ education system is put in place at the earliest, the country can reap benefits of its high demographic dividend in the long run.
There are multiple pathways to building an ‘efficient’ education system in India. There is substantial evidence at both, international and national level to prove that one of the most effective ways to attain quality education for all is an investment in Early Childhood Education (ECE) (OECD 2019). The India Early Childhood Education Impact (IECEI) study, conducted by the ASER Centre and the Centre for Early Childhood Education and Development (CECED), shows that children who have access to high-quality ECE are more ‘school ready’ than those who do not (Kaul et al. 2017). Over and above ECE’s potential to improve linguistic, cognitive and socio-emotional skills of the child, ECE is also extremely beneficial for the mother, the family and the national economy in the long run (OECD 2017).
Despite increasing evidence that ECE contributes towards better education, social, health and economic indicators; universalization of pre-primary education was not given the priority it requires in India until recently. The draft National Education Policy (NEP) 2019 has stated that the learning gaps start even before children attend school. It has identified foundational learning as the root cause of the learning crisis in the country and it is now upon state governments to anticipate and simultaneously react to the challenges ahead in providing foundational literacy and numeracy skills to make all young children ‘school ready’.
In order to make sure a holistic approach towards inclusivity in education, UNESCO defines inclusive education as- “Inclusion is seen as a process of addressing and responding to the diversity of needs of all learners through increasing participation in learning, cultures and communities, and reducing exclusion within and from education. It involves changes and modifications in content, approaches, structures and strategies, with a common vision which covers all children of the appropriate age range and a conviction that it is the responsibility of the regular system to educate all children” (UNESCO 2005).
In its efforts to address inclusivity, the Government of India passed the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016 which identified the types of disabilities have been increased from 7 to 21 and that the Central Government will have the power to add more types of disabilities. This was a great step taken in addressing inclusive education as it went beyond the physical aspects of disability and included mental aspects. Inclusive Education had to be rethought and implications of disabilities on learning had to be considered and addressed.
UNESCO New Delhi is committed in promoting and ensuring the need to provide equitable access to quality education for all. Inclusive education comes out of a vision of the world based on equity, justice and fairness. In this regard, UNESCO New Delhi office launched, ‘N FOR NOSE – State of the Education Report for India 2019: Children with Disabilities’, in July 2019. It aims to articulate a vision of education for children with disabilities for 2030 as set out in national and international policy documents and legislative frameworks. Similarly, an annual report on Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) will be released in 2020. As we step up our efforts in the countdown towards achieving the 2030 agenda, we reaffirm the need to form an education system which is inclusive by tackling social, cultural, economic and spatial inequalities within countries. Concerted and multi-sectoral efforts are the need of the hour to ensure the fulfilment of the SDGs’ pledge of ‘leaving no one behind’.
In 2020 and during a period where almost all countries are going through a crisis situation due to Covid19, it is our duty to reflect on the difficulties of those people who cannot switch to e-learning methods due to their inability to access the internet, computers and laptops or even lack of knowledge about online learning courses. As we advocate for education for all in such testing times, we need to ensure that individual from all backgrounds is made part of the education ecosystem which can further empower them to fight situations like these in the future.
To face the COVID-19 crisis, UNESCO has provided immediate support to countries by updating the distance learning guides for more than 1.47 billion children who are out of school because of school closures across the globe (UNESCO 2020).
As a right, learning must continue and the efforts should go more to those who are the most disadvantaged. There is an urgent need to emphasize the role of education in responding to such crises. UNESCO New Delhi Education team will continue to think and reflect on:
- How to ensure the continuity of learning for all even in times of crisis/emergency
- How to train teachers for their preparedness and what to include in the content of their education
- How to organize distance education, homeschooling and personalized pathways

Authors: Mame Omar Diop and Abhinav Kumar
Mr. Mame Omar Diop is Programme Specialist and Chief of Education at UNESCO New Delhi Cluster Office for India, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Maldives, and Mr. Abhinav Kumar works in the education sector at UNESCO New Delhi.
References:
- Government of India (2009) The right of children to free and compulsory education act, 2009. No. 35 of 2009. New Delhi http://mhrd.gov.in/rte
- Government of India (2018), “Children in India 2018- A Statistical Appraisal”, page 68. By Social Statistics Division Central Statistics Office Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Retrieved from: http://www.mospi.gov.in/sites/default/files/publication_reports/Children%20in%20India%202018%20%E2%80%93%20A%20Statistical%20Appraisal_26oct18.pdf
- Kaul, V., Bhattacharjea, S., Chaudhary, A. B., Ramanujan, P., Banerji, M., & Nanda, M. (2017),” The India Early Childhood Education Impact Study”, New Delhi: UNICEF, Retrieved from https://www.academia.edu/34458607/The_India_Early_Childhood_Education_Impact_Study,
- OECD (2017), “Improve early education and care to help more children get ahead and boost social mobility” Retrieved from http://www.oecd.org/newsroom/improve-early-education-and-care-to-help-more-children-get-ahead-and-boost-social-mobility.htm,
- OECD (2019), “Providing Quality Early Childhood Education and Care Results from the Starting Strong Survey 2018”, TALIS, OECD Publishing, page19-21, Paris, Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1787/301005d1-en,
- UNESCO (2005), ‘Guidelines for Inclusion: Ensuring Access to Education for All’ available at http://www.ibe.unesco.org/sites/default/files/Guidelines_for_Inclusion_UNESCO_2006.pdf
- UNESCO (2020), ‘COVID-19 Educational Disruption and Response’ available at https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/coronavirus-school-closures
- World Bank (2016) ‘Bihar Poverty, Growth & Inequality’ last accessed on 12th January 2019 http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/781181467989480762/pdf/105842-BRI-P157572-PUBLIC-Bihar-Proverty.pdf
- World Bank (2018), ‘World Development Report 2018: Learning to Realize Education’s Promise’. Washington, DC: World Bank. DOI:10.1596/978-1-4648-1096-1. License: Creative Commons Attribution CC BY 3.0 IGO https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2018
You may like
-


“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space
-


A Structural Proposal to Transform School Education in Bihar
-


National Conference Pushes for Common Standards Across School Boards
-


Maharashtra: Over 8,000 Villages Lack Schools, CCTV Compliance Still Patchy
-


Haryana to Offer Free After-School Coaching for JEE, NDA Aspirants
-


Telangana CM Calls for Overhaul of Intermediate Education in Telangana
-


Indian Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla to Connect with School Students Live from Space
-


Are 4-Year Degrees Dead? Nikhil Kamath and the WEF Say Lifelong Learning Is Here to Stay
-


UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures
-


Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead
Education
Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead
Published
1 week agoon
June 26, 2025
In a decisive step toward reforming India’s fragmented senior secondary education system, the Ministry of Education has constituted an 11-member high-level committee to address the mushrooming of dummy schools and the unchecked influence of coaching centres. Chaired by Higher Education Secretary Vineet Joshi, the committee includes representatives from CBSE, NCERT, and faculty from IITs in Madras, Kanpur, and Trichy.
The move is seen as part of a growing policy consensus across central and state governments to reclaim the authority of schools, following recent crackdowns and reforms aimed at regulating coaching institutions and curbing the dummy school culture that sidelines holistic education.
Dummy schools — where students are officially enrolled but rarely attend — have emerged as a by-product of India’s competitive entrance exam culture. These institutions prioritise JEE, NEET, and CUET preparation through coaching classes, while students disengage from formal schooling. The CBSE’s March 2025 advisory warning that students from dummy schools could be barred from board exams marked a serious turning point in policy enforcement.
Earlier this year, the Delhi Government carried out inspections in over 600 private schools, issuing notices to at least 10 for running dummy setups. The move followed media reports and parental complaints about students being denied regular schooling in favour of coaching arrangements.
Meanwhile, the Rajasthan Cabinet approved a bill in April 2025 to regulate coaching centres operating in Kota and other education hubs. The legislation aims to curb exploitative practices, mandate mental health counsellors, and prevent coaching centres from operating without a minimum infrastructure standard—prompted by rising student suicides in the state.
Central Framework and Industry Oversight
In February 2025, the Central Government announced a new framework for coaching centres, proposing registration, transparency in fee structures, and guidelines on advertising to prevent misleading claims. Together with the current committee’s formation, these reforms indicate a systematic tightening of oversight at all levels.
The new panel’s mandate is broad. It will investigate:
- The socio-academic reasons behind the rise of dummy schools
- The misalignment between school curricula and competitive exams
- The impact of coaching on student well-being and critical thinking
- The need to promote alternate career pathways beyond engineering and medicine
- Regulations around coaching advertisements and contract practices
A National Rethink on the Purpose of Schooling
Education experts like Dr Ameeta Mulla Wattal have welcomed the initiative, calling it “a vital opportunity to restore the sanctity of school education.” The rise of coaching centres as parallel systems, she noted, has come at the cost of creativity, values, and even mental health in adolescents.
As India contemplates the future of its learners, the Ministry’s recent actions suggest a serious intent to bridge the gap between boardrooms and classrooms. Whether the new committee’s recommendations lead to tangible change remains to be seen, but the signals are clear: education in India must prepare children for life, not just for an entrance exam.
Education
How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 24, 2025By
Renu Sharma
The dopamine-rich scrolling in late mornings with amorphous freedom has made our zealous students so comfortable that they are re-entering their classrooms with minds tuned to instant gratification, not delayed rewards. Now the challenge isn’t just academics but to re-engage our bud’s attention and curiosity. Neuroscience backed motivation strategies and intentional school design could prove to be a catalyst as it will bring a positive change and enable the students to learn at a better pace.
1. Rewiring the Dopamine rush with 2 Ps, Purpose and Productivity:
Neuroscience says: Where our brains are functional to seek novelty and purpose on their own, during summer break, the buds often lean into adding the activities to their routine which are unpredictable, quick, and rewarding referring back to instant gratification, these activities may include social media, gaming, and chatting anonymously and grateful to internet and inventions, there are plethora of platforms enabling students to be distracted. And then joining back the school with a gradual drip of delayed academic rewards may seem to be a let-down for students.
Actionable tip: We as facilitators have to be the mystery-solvers channeling their energy into productivity, enlightening them with real-world challenges, interdisciplinary projects, or a mystery to solve that taps into their intrinsic curiosity. Novelty may allow us to reset their attention-even primitive changes in surrounding like rearranged desks, learning outdoors, and using the BALA method to utilize infrastructure, can signal a shift in engagement and productivity.
2. Design for Autonomy and Flow
Neuroscience says:
Neuroscience tells us that motivation really flourishes when students feel they have some control over their learning. The brain’s reward system kicks in when choices are part of the equation, especially regarding how tasks are structured or what content is covered.
Here’s a practical tip: give students structured choices, like deciding which book to dive into, which problem to tackle first, or how they want to present their findings. A design that promotes flow—complete with clear goals, manageable challenges, and instant feedback—helps keep students in that ideal zone, avoiding both boredom and anxiety.
3. Rebuild Social Motivation Through Spaces That Connect
Neuroscience tells us that connecting with peers is a huge motivator, especially after the pandemic. Our brains are wired for social interaction, which plays a key role in how we learn and engage emotionally.
Actionable tip: Create flexible seating arrangements or common areas that encourage group work and casual collaboration. Try incorporating daily activities like “curiosity circles” or peer-led problem-solving sessions to foster a sense of belonging and shared learning objectives.
4. Leverage Routines to Rewire Attention
Neuroscience shows that our habits influence our attention. After a summer of scattered focus, students thrive on rhythmic and consistent routines that help retrain their executive functions.
Actionable tip: Kick off classes with familiar “mind-on” rituals — whether it’s a thought-provoking question, a brief reflection, or a quiet sketch — to help anchor their attention. Consistency breeds comfort, and that comfort boosts confidence.
5. Make Joy a Design Priority
Neuroscience indicates that positive emotions can enhance learning by boosting neuroplasticity. When students (and teachers) experience joy, they’re more likely to engage deeply and retain what they learn.
Actionable tip: Infuse joyful moments into the day — through fun challenges, movement breaks, or a bit of humor. Allow time for students to share what excites them. A joyful classroom isn’t just a nicer place to be; it’s also more effective for learning.
Conclusion: To capture wandering minds, we need to understand how motivation truly works and design both our curriculum and learning spaces to support it. When we ignite curiosity, honor autonomy, and weave joy into the experience, even the sleepiest summer brain can come alive again.
This article is written by:

Renu Sharma
Assistant Director – Systems – Indirapuram Group of Schools
Principal – Indirapuram Public School – Crossings Republik
Education
Assam Brings Sign Language to Senior Secondary Classrooms in Landmark Move
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 24, 2025
The Assam State School Education Board (ASSEB) has announced the introduction of Sign Language as an elective subject for Higher Secondary (Classes XI–XII) from the current academic year.
Education Minister Dr. Ranoj Pegu made the announcement during the inauguration of a residential AI training programme for teachers at IIT Guwahati. While Artificial Intelligence and Financial Literacy were also introduced as new electives, Sign Language stood out as a critical stride towards making classrooms more accessible to the deaf and hard-of-hearing community.
“This is not just about a subject; it’s about acknowledging communication rights,” said Dr. Pegu, who also unveiled a specially designed AI textbook at the event. The textbook was developed in collaboration with experts from IIT Guwahati and Dibrugarh University. He added that the curriculum reforms are aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s vision of equity, inclusion, and skill readiness.
According to education officials, the rollout of Sign Language will begin in institutions where qualified educators or resource personnel are available. Training for teachers is expected to be scaled up across the coming months. The subject aims to raise awareness about Indian Sign Language (ISL), improve communication access for students with hearing impairments, and sensitise peers to inclusive practices from a young age.
Later in the day, Dr. Pegu chaired a review meeting with officials from the Department of School Education to discuss budget allocations and planning for the 2025–26 academic year. While schemes like the Chief Minister’s Nijut Moina initiative, distribution of bicycles for Class IX girls, and the upgradation of Bodo-medium schools were discussed, the emphasis remained on delivering structural reforms that bridge equity gaps in access and opportunity.
The addition of Sign Language, AI, and Financial Literacy as electives reflects a broader shift in how Assam is reimagining school education — one where life skills, digital literacy, and inclusive values are no longer optional, but integral.
Education
History, Identity, and Pride: Books That Make Sense of Being You
Published
3 weeks agoon
June 11, 2025
Every June, rainbow flags go up, corporate logos get a splash of colour, and the words Pride Month fill our timelines. But behind this month-long celebration lies something far deeper — an entire universe of history, identity, and stories that often remain outside the margins of our textbooks, especially here in India.
When we talk about queer histories, most people quickly say: Pride is an American concept. And yes, the Stonewall Riots of 1969 are often marked as the start of the modern LGBTQIA+ rights movement. But to believe that queer identities only exist where the parades happen is both lazy and inaccurate. Because if you look carefully — at temple walls, ancient texts, and folklore — you’ll find that India, too, has always had queer stories. We’ve just failed to write them down as part of our “official” history.
Take Mahabharat — where Shikhandi, a warrior born as a woman but raised as a man, plays a crucial role in Bhishma’s death. Or Brihannala, Arjuna’s year-long identity as a eunuch. Look at Khajuraho or Konark temples — where fluid sexual depictions exist without judgement. Even Mughal records speak softly of same-sex companionship. Yet none of these ever made it to our history chapters. Why? Because of historiography — the selective way in which history gets written, where lived experiences are often filtered through political, cultural or moral lenses. What we’re left with is history that’s comfortable — not always complete.
But while adults debate culture wars, there’s a rising generation of Indian teens who are quietly asking braver questions. More kids today — some as young as 12 or 13 — are exploring their gender identities, sexual orientations, or even just the vocabulary to describe what they feel. And many of them don’t know who to turn to. Some are scared of being mocked by peers. Others fear judgement from family. Teachers, too, often don’t have the training or language to guide them. The result? Stories like Aarvey Malhotra’s — a young boy who couldn’t bear the bullying he faced for his gender expression — remind us how deadly this silence can be.

Arvey Malhotra with his mother Aarti Malhotra
So where can these kids turn? Sometimes, the safest place to meet yourself is inside a book.
Here’s a small, carefully chosen list of books (curated with the help of AI) that may help teens (13+) begin that journey of understanding — about themselves or others:
1. Beyond the Gender Binary by Alok Vaid-Menon

Written by a gender non-conforming writer of Indian origin, this is a short, deeply accessible introduction to gender fluidity.
2. The Boy & The Bindi by Vivek Shraya (Illustrated by Rajni Perera)

While more suitable for slightly younger kids, this beautifully illustrated book helps children embrace non-conformity and Indian culture together.
3. Pride: The Story of Harvey Milk and the Rainbow Flag by Rob Sanders
An excellent way to understand where the modern pride movement began, told through the story of the Pride flag’s creation.
4. Gender Identity: Beyond Pronouns and Bathrooms by Maria Cook

Written for teens, this breaks down gender identity, expression, dysphoria and non-binary identities in simple, compassionate language.
5. The Queer Hindu: A Spiritual Perspective by Devdutt Pattanaik (Selected Essays)
While not strictly a children’s book, certain essays by Pattanaik can open doors for older teens who wish to explore how queerness exists within Indic traditions.
6.Pet by Akwaeke Emezi

A young-adult novel that tackles identity, family, and justice in a tender, imaginative way by a non-binary author.
7. When Aidan Became a Brother by Kyle Lukoff

For kids exploring trans experiences, this picture book offers a gentle, positive portrayal of gender transition.
(Book covers- Amazon.in, Goodreads)
So why does Pride matter in schools?
This isn’t about imposing ideologies — it’s about offering answers to kids who are already asking. And if we want fewer kids like Aarvey to feel alone, confused, or ashamed, we need to stop treating gender and sexuality like topics too complicated for them to understand. They’re not. What they need are trusted spaces, the right words, and adults who listen without first judging.
After all, education was always meant to make us more human — and queerness, in all its forms, is part of that humanity.
Edutainment
Of Formulas and Frames: Why India Must Stop Dividing Science and Art
Published
4 weeks agoon
June 10, 2025
In a recent interview with Lallantop, Varun Grover—acclaimed writer, lyricist, comedian, and filmmaker—hit upon a truth so striking, it should’ve been plastered across school walls: India has lost its plot in nurturing innovators. And the reason? We’ve boxed our subjects—and our students—into separate lanes. Science on one side, art on the other. One wears lab coats, the other paints canvases. They rarely, if ever, meet.
Grover put it sharply: in India, we’ve created a caste-like hierarchy between subjects. Science students often carry the burden of “doing real work,” while arts students claim the higher ground of exploring life and meaning. The result? A deep-rooted disconnect. And it begins early—often in Class 11, when students are forced to pick a stream and silently abandon the rest of their interests.
But must a physicist give up poetry? Must a musician ignore algorithms?
It doesn’t have to be this way. At MIT, one of the world’s top science and tech universities, PhD students in Physics can take courses in music, design, or history—and earn credits for them. Why? Because innovation thrives where disciplines intersect. Because understanding how a flute works can teach you more about frequencies than a textbook diagram ever will.
Consider Steve Jobs, who credited a college calligraphy class for inspiring the Mac’s typography. Or Indian innovator Sonam Wangchuk, whose work in Ladakh seamlessly blends engineering with local art, architecture, and sustainability. His Himalayan Institute of Alternatives (HIAL) teaches future engineers and designers side-by-side, breaking the very silos our system has normalised.
Even Nobel laureate Richard Feynman once said, “I have a friend who’s an artist… He’ll hold up a flower and say, ‘Look how beautiful it is,’ and I’ll agree. But I can also see beauty in how the flower works—its structure, its physics. Science only adds to the beauty.”
And yet, in India, we continue to teach these as separate things. We train students to clear tests, not to create. We push them into IIT-JEE coaching at 13 and expect them to build world-changing ideas at 25.
This isn’t just an academic issue—it’s cultural. Our textbooks rarely reference architecture as both engineering and aesthetic legacy. Our school plays and science exhibitions are held in different corners of the building. Our awards are either for “Best Innovation” or “Best Performance”—never both.
The irony is painful. A land of classical music rooted in maths. A civilisation that built temples with astronomical precision. A country that once integrated dance, sculpture, and geometry with everyday life. And yet, we’ve chosen to modernise by compartmentalising.
It’s time we remember what Varun Grover reminded us of: the pyramid is both an engineering feat and an artistic marvel. And so is the human mind.
Let’s build an education system that stops asking children to choose between knowing and feeling, between numbers and narratives.
Let’s stop making them pick a lane—when the real magic happens at the crossroads.
Education
Beyond the Buzz: Investors Call for Grounded AI Innovation in Indian Classrooms
Published
1 month agoon
June 5, 2025
At a time when Artificial Intelligence (AI) headlines dominate global discourse, a quieter but more consequential conversation is unfolding in India’s education sector—one that cuts through the hype to explore whether AI is genuinely improving learning outcomes or just riding a wave of fascination.
In its latest article titled “Not Just Hype: What Investors Really Think About AI in Indian Education”, Entrepreneur India reported on insights shared by Ganapathy Venugopal, Co-founder & CEO of Axilor Ventures, at the IGIS 2025 forum. Offering a candid investor’s lens, Venugopal remarked, “We’ve seen plenty of hype around AI. But for us, it’s about where the real value lies—can it solve something fundamental, like India’s teacher-student gap?” According to him, the most investable AI tools are not the flashiest but the most functional—those that support teachers, amplify their effectiveness, and reach where human resources fall short.
Echoing this, Kobi Gal from Ben-Gurion University pointed out that while AI has democratised access to learning, it hasn’t yet changed the core of how we learn. “The education system remains rigid. AI can increase reach, yes, but transformation is still elusive,” he said.
India’s edtech sector is poised for growth with its vast K–12 student base and rapidly expanding internet access. However, a major challenge remains—only 24% of households have internet, per NSSO data. This makes Tier II–IV cities a key battleground for AI-powered learning tools. Investors are now shifting focus from “edtech” as a label to learning outcomes, engagement, and job-readiness, with AI viewed as an enabler rather than a product category.
Venugopal pointedly questioned current trends: “Are we building tools to complete homework, or to change how we learn?” His statement taps into the broader tension—between consumer-friendly shortcuts and pedagogically sound, scalable solutions.
At ScooNews Global Educators Fest (SGEF) 2023, this theme of AI with a conscience was also central. Held in Jaipur, the festival brought together educators, artists, and changemakers to discuss how artificial intelligence can serve—not replace—human values in education. Noted speakers like Lakshyaraj Singh Mewar, Rama Datt, and Padma Shri Anand Kumar reinforced the idea that technology must remain grounded in empathy, inclusivity, and purpose. A memorable moment was Anand Kumar’s speech on whether AI could ever truly replace a teacher’s role—a thought-provoking precursor to the investor sentiments voiced at IGIS 2025.
The conversation today is no longer about AI replacing the classroom, but enhancing it. With investor confidence growing in tools that support hybrid delivery models, regional customisation, and lifelong learning, the sector appears headed toward a more sustainable future.
Yet, Venugopal issued a final word of caution: “We look at sectors where demand is unquestionable and the cost of not solving the problem is high. Education in India fits that bill. But we must build with humility—and rigour.”
As India’s AI-powered education future unfolds, investors, educators, and innovators alike seem to agree: the goal is not disruption for disruption’s sake, but designing systems that serve learners in meaningful, measurable ways.
📌 Stay tuned for SGEF 2025 — This year, we gather under the theme: “Purpose-Driven Education: Designing for Future Realities.” Explore how we can reimagine school curricula to align with the evolving needs of our society and the professional world. Register here
Education
Government School Enrolment Drops Across States, Centre Flags ‘Disturbing Trend’
Published
1 month agoon
June 2, 2025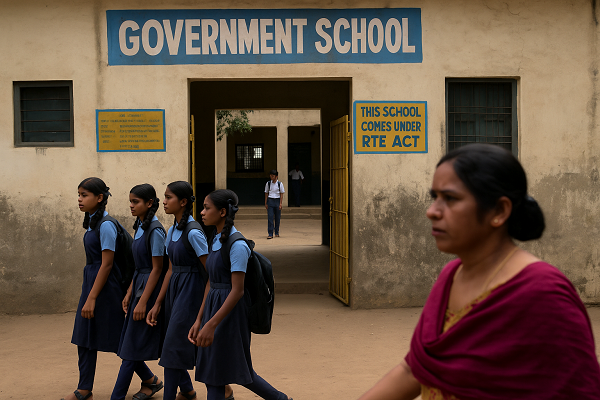
A recent report by The Indian Express reveals a worrisome shift in India’s school enrolment patterns—more students are opting for private institutions, even in states with a robust network of government schools. During meetings held by the Ministry of Education with state officials in March–April 2025 to discuss projects under the Samagra Shiksha scheme, the Centre flagged this as a “disturbing trend.”
In states like Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Uttarakhand, the enrolment in unaided private schools has consistently risen despite government schools forming the majority in number. For instance, in Andhra Pradesh, 73% of schools are government-run, yet they account for just 46% of total student enrolment. Similarly, Telangana’s government schools form 70% of total schools but educate only 38% of students, compared to nearly 61% in private schools.
This trend isn’t isolated. Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, and several northeastern states have also reported declining numbers in government school enrolment. The Union Ministry has urged states to reverse this decline, citing the need for introspection and reform. In Tamil Nadu, for example, government schools make up 64% of the total but serve just 37% of the student population.
Interestingly, some states have responded by conducting Aadhaar-based “data cleansing” to explain the drops. Still, the Centre believes deeper, systemic issues—such as rising aspirations and perceptions of quality—are driving families towards private schooling.
The concern goes beyond statistics. According to UDISE+ 2023–24 data, 36% of total school enrolment in India (over 9 crore students) is now in private schools. In 2022–23, it was 33%. Pre-pandemic figures already indicated this steady rise.
Where Do Government Schools Go From Here?
The falling trust in government schools paints a grim picture—especially when education budgets face cuts and systemic reform remains slow. However, all is not lost. States like Madhya Pradesh are setting examples through initiatives like the CM Rise Schools, which aim to rejuvenate public education with upgraded infrastructure, teacher training, and modern pedagogy.
But such success stories remain scattered. Without strong policy backing, increased funding, and public support, the future of government schooling appears uncertain. In an era of aggressive privatisation—be it formal schooling or the booming coaching industry—government schools risk being sidelined unless urgently revitalised.
Why must they survive? Because they remain the only accessible option for millions, especially in rural and marginalised communities. They are not just institutions—they’re vehicles of social equity, offering a shot at mobility to those who may otherwise be left behind.
Education
Banu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature
Published
1 month agoon
May 22, 2025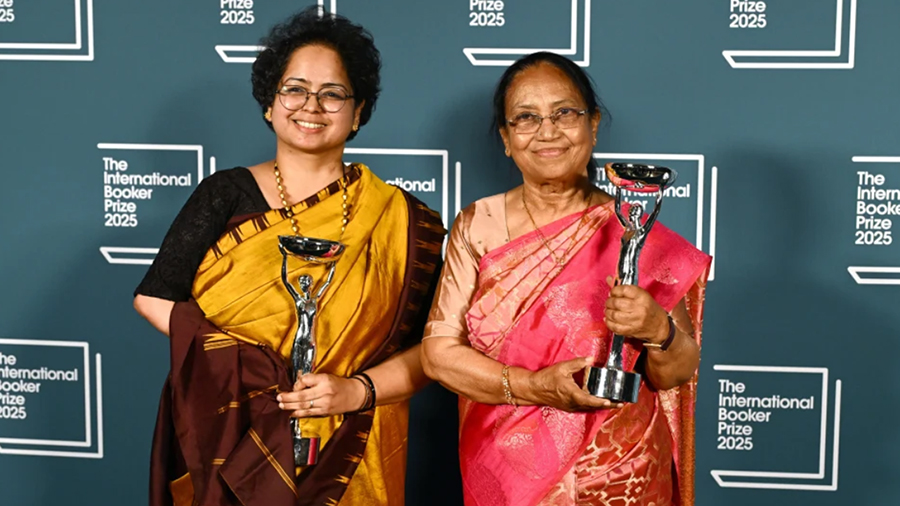
When Banu Mushtaq became the first Kannada author to win the prestigious International Booker Prize for her short story collection Heart Lamp, she didn’t just make literary history—she reignited a conversation about the role of literature in shaping society, and the way schools can nurture future writers not just as hobbyists, but as cultural forces.
Mushtaq, along with translator Deepa Bhasthi, was honoured for Heart Lamp, a collection of stories chronicling the lives of Muslim women in Karnataka across three decades. The stories are rooted in resistance, critique of religious and patriarchal structures, and everyday courage. The recognition was not just for the literary craft, but for the emotional and moral clarity the stories offer—a kind of truth that is rarely rewarded in global spaces. But the International Booker did just that.
And yet, how many students in Indian classrooms today know what the Booker Prize even is? While the Grammys, Oscars and even YouTube Play Buttons are common cultural currency among young people, literary awards often pass under the radar. This needs to change.
The International Booker Prize is one of the most prestigious literary honours in the world, recognising the finest works of fiction translated into English. It opens up space for voices that often remain local to reach a global stage. For students in India, this is an opportunity to understand that writing, especially in regional languages, is not a dead-end path. Yes, it may not offer the instant gratification of a viral video or influencer deal—but as Mushtaq’s life proves, it can shape public discourse, win global accolades, and leave behind a legacy that matters.
For educators, this is a teaching moment. Banu Mushtaq’s story is as much about literary merit as it is about resilience. She wrote in Kannada, a language she adopted over her native Urdu. She survived deep personal trauma, including a suicide attempt, and faced social backlash for her activism. She was a councillor, a journalist, and a lifelong advocate for women’s rights. These are the kinds of role models classrooms should be spotlighting—especially for young girls who need to see that stories, quite literally, can change lives.
Heart Lamp may not be appropriate for every age group, but its themes—identity, voice, justice—can be introduced in many ways. Schools should consider book discussions, literary circles, or even creative writing prompts inspired by such works to encourage students to find their voice, in whatever language or form it may come.
This win is also a reminder that educators need to broaden the definition of success they present to students. STEM, coding, and commerce continue to dominate career conversations, but it’s equally crucial to show that the arts—especially literature—have their own path to impact and influence. We hope for a time when young writers are not asked “what else do you do?” but are valued for what their words bring to the world.
Banu Mushtaq’s Booker Prize win is not just an individual triumph—it’s a collective opportunity. For schools, for students, and for all of us who believe that a powerful story can change minds, communities, and someday, the world.
Education
Human (Soft) Skills: The Missing Piece in School Curriculums
Published
2 months agoon
May 19, 2025
As the future of work continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, one thing is becoming increasingly clear: the ability to be human is our greatest advantage. In an age where automation and AI are reshaping industries, it’s no longer technical proficiency that sets students apart, it’s human skills.
And yet, our schools aren’t keeping up.
Globally, education systems remain heavily weighted towards academic and technical achievement. While these are certainly important, they no longer tell the whole story. Employers across sectors are united in their call for graduates who can communicate effectively, manage stress, work in diverse teams, and adapt to constant change.
Deloitte’s 2019 report The path to prosperity: Why the future of work is human found that by 2030, two-thirds of all jobs created will be reliant on human capabilities. These include empathy, creativity, collaboration, emotional intelligence, and the ability to learn continuously. All of which are underdeveloped in our current school structures.
This is not a theoretical problem. The impact is already being felt. Research consistently shows that up to 68% of high school students report feeling anxious, underprepared, and lacking the confidence to take the next step into work or further education. The transition from school to career requires more than ‘knowledge acquisition,’ it requires self awareness.
Human skills are the gateway to that self-awareness. They help students identify their strengths, regulate their emotions, communicate effectively, and develop resilience. These are the foundational competencies that allow young people to navigate uncertainty and thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Importantly, these skills are not innate. They are learned, practised, and refined over time — just like maths, science, or coding. When introduced early, human skill development empowers students with confidence and clarity. They learn how to navigate social complexity, resolve conflicts, deal with failure, and see growth as a lifelong journey rather than a fixed destination.
So, why aren’t we teaching these skills in schools as deliberately as we teach literacy or numeracy?
Perhaps it’s because human skills feel harder to measure. But we must shift our mindset. What we value, we measure — and what we measure, we teach. Forward-thinking educators and school leaders across the globe are beginning to incorporate social-emotional learning, strengths-based development, and mental wellbeing into their curriculums, recognising that these are not “nice-to-haves” — they are must-haves.
Imagine a student graduating from high school with not just academic marks, but a toolkit of emotional and interpersonal strengths: an understanding of who they are, what drives them, and how to manage themselves under pressure. Imagine a generation that sees learning as a lifelong pursuit and failure as a stepping stone rather than a setback.
This is the future we must design for.
It starts by giving human skills a seat at the table – not as a supplement to education, but as a core component of it. We need to empower educators with the tools and frameworks to deliver this kind of learning and where necessary provide expert facilitators to avoid adding more to the workload of educators. We need to engage students in real, reflective experiences that help them connect their inner world with the outer demands of life and work.
The most meaningful educational innovation doesn’t just teach students to do more. It teaches them to be more – to be self-aware, to be empathetic, to be adaptable. That’s how we create work-ready individuals and life-ready citizens.
The world doesn’t need more rote learners. It needs more critical thinkers, resilient leaders, and emotionally intelligent problem solvers. And the time to cultivate them is now – in our classrooms, through our curriculums, and with intention.
This article is authored by Renata Sguario
Renata Sguario is the founder and CEO of Maxme and the current chairman of the board of Future First Technology (formerly known as PS+C Limited), listed on the ASX (FFT), one of Australia’s leading end-to-end ICT and digital consulting organisations.
Education
CBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
Published
2 months agoon
May 19, 2025
In an effort to combat rising sugar consumption among students, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has directed all affiliated schools to establish “Sugar Boards”—a dedicated awareness initiative designed to monitor and educate students about the dangers of excessive sugar intake. This decision follows a sharp increase in Type 2 diabetes among children, a condition once primarily seen in adults, but now a growing concern in school-aged populations.
Why Sugar is Becoming a Silent Crisis
The CBSE has observed a troubling rise in Type 2 diabetes among students over the past decade. Health experts attribute this trend to the easy availability of sugary snacks, soft drinks, and processed foods within school environments. Studies indicate that sugar constitutes 13% of daily calorie intake for children aged 4 to 10 years and 15% for those aged 11 to 18 years—far exceeding the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended limit of 5%.
These Sugar Boards, mandated by CBSE, will serve as educational displays within schools, informing students about the risks of excessive sugar consumption. They will display critical information, such as:
-
Recommended daily sugar intake
-
Sugar content in commonly consumed foods (sweets, sodas, chocolates)
-
Health risks associated with high sugar intake, including obesity, diabetes, and dental problems
-
Healthier dietary alternatives
The directive also encourages schools to conduct awareness seminars and workshops, helping students make informed food choices. Schools are required to submit reports and photographs of their Sugar Boards by July 15.
The Real Enemy is Advertising
But while the CBSE is focusing on sugar consumption within schools, global research highlights a much larger problem—junk food advertising. As reported by The South First in a recent story, a study presented at the 2024 European Congress on Obesity in Malaga found that even five minutes of exposure to junk food advertisements could cause children to consume an extra 130 kilocalories per day. Professor Emma Boyland from the University of Liverpool explained, “Our results show that unhealthy food marketing leads to sustained increases in caloric intake among young people—enough to promote weight gain over time.”
This research highlights that children’s sugar consumption is not just influenced by what they eat in school but also by what they see on their screens. Junk food marketing—whether through TV, online ads, or even brand-only advertisements—significantly impacts children’s eating habits.
Nithin Kamath, Founder & CEO of Zerodha & Rainmatter Foundation, and a popular LinkedIn thought leader, recently highlighted the Sugar Boards initiative on social media, thanking Food Pharmer (Revant Himatsingka) for contributing to this change with his content.
Revant Himatsingka, popularly known as Food Pharmer, has been a vocal advocate for healthier eating habits among children. His digital content, which breaks down the sugar content of everyday foods—from malted drinks to packaged juices—has gained widespread attention and spurred conversations on healthy eating among parents, schools, and policymakers.
Kamath’s post acknowledged that while the CBSE’s initiative is a step in the right direction, true change requires parental awareness and action. “Now to figure out how to get parents to care about it. How to reduce sodas, coffee/tea (majority of it is mostly sugar), malted drinks, chocolates, sweets, etc.,” he wrote.
Will ‘Sugar Boards’ Be Enough?
While the Sugar Boards are a commendable initiative, many may argue that they are only part of the solution. Schools can monitor students’ sugar intake on campus, but the problem extends beyond the school gates. Children are exposed to junk food advertising on social media, in video games, and even through influencer endorsements.
Professor Boyland’s research shows that even brand-only food ads—advertisements that showcase brand logos without directly promoting food—can significantly increase children’s calorie intake. This means that without stricter advertising regulations, schools may find it difficult to counter the impact of sugar marketing.
CBSE’s Sugar Boards are a commendable initiative, but their success will depend on consistent awareness efforts, parental involvement, and broader policy changes. Experts recommend a multi-pronged approach:
-
Stricter regulations on junk food marketing aimed at children
-
Mandatory nutrition education as part of the curriculum
-
Collaboration with parents to reduce sugary foods at home
-
Regular health check-ups and BMI monitoring in schools
With diabetes and obesity on the rise among young Indians, addressing the sugar crisis is no longer just a dietary choice—it is a public health necessity.
Newsletter

“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space

A Structural Proposal to Transform School Education in Bihar

NIIT Foundation and YuWaah, UNICEF Launch Free Online Digital Marketing Course for Youth

National Conference Pushes for Common Standards Across School Boards

Maharashtra: Over 8,000 Villages Lack Schools, CCTV Compliance Still Patchy

Haryana to Offer Free After-School Coaching for JEE, NDA Aspirants

Telangana CM Calls for Overhaul of Intermediate Education in Telangana

Indian Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla to Connect with School Students Live from Space

Are 4-Year Degrees Dead? Nikhil Kamath and the WEF Say Lifelong Learning Is Here to Stay

UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures

Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead

CBSE To Conduct Board Exams Twice for Class 10 from 2026

How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
Tripura Becomes Third Indian State to Achieve Full Literacy

Assam Brings Sign Language to Senior Secondary Classrooms in Landmark Move

Delhi Schools to Implement Age 6 Rule for Class 1 Admissions from 2026

Tripura Adds Sex Education & HIV Awareness to Their Curriculum

Four Indian Schools Shine on the Global Stage at World’s Best School Prizes 2024

Centre Urges 7 States to Consider Common Board Amid Alarming Student Failure Rates

IIT Delhi Leads India in the QS Rankings 2026; MIT Tops Globally

Chandigarh, Punjab Lead in School Education Rankings; Meghalaya Trails Behind

Maharashtra Revises Policy on Third Language in Schools, Hindi No Longer Mandatory

From Academics to Empathy: Redefining Academic Success

India Sends 20 Students to Japan Under Sakura Science Programme 2025

Delhi Schools to Observe June as Anti-Malaria Month, Says DoE

Is Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?

CBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
CBSE Warns Dummy School Students May Be Barred from Board Exams

Maharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020

MAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
China Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035

John King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education

CBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020

Rewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution

CBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme

India Bids Farewell to NEP Architect Dr K. Kasturirangan

Banu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature

Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar 2025: Nominations Now Open for India’s Young Achievers

NCERT Class 7 Textbooks Updated: Mughals Removed, Focus on Indian Ethos and Pilgrimage

Delhi Government Cracks Down on Dummy Schooling; Over 600 Schools Inspected, 10 Issued Notices

Delhi Approves Landmark Bill to Regulate School Fees Across 1,677 Institutions

The Ethics of AI Art in Education & Nostalgia: The Ghibli Effect

Operation Sindoor and Operation Abhyaas: Navigating School Safety and Student Well-being Amid Rising Tensions

Harvard Stands Its Ground: Harvard Faces ₹18,400 Crore Funding Freeze After Rejecting Trump Administration’s Demands
CBSE Revises Class 10, 12 Curriculum: Biannual Exams, New Subjects and Flexible Passing Criteria Introduced

CUET-UG 2025 Likely to be Postponed, Fresh Dates Expected Soon

Aalamaram 2025: Where Indian Educators Came Together to Grow, Reflect, and Lead

Trump Signs Executive Order to Promote AI Integration in U.S. K-12 Education

Mizoram Declared First Fully Literate State in India

Indian Students Flock to Singapore, Ireland, and Dubai for Higher Studies: 38% Surge Recorded
SGEF2023 | Special Address by Rama Datt, Trustee, Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II Trust, Jaipur

ScooNews | After Movie | ScooNews Global Educators Fest 2023

Aftermovie | NIES2 UP Chapter | 21 Jan 2023

WEBINAR | Gamification in Education: How Digital Badges Can Boost Student Motivation and Engagement

ScooNews | WEBINAR| Importance of Physical Activity for Children at School | Plaeto

SCOONEWS | WEBINAR | WHY DIGITIZING YOUR SCHOOL IS A MUST | TEACHMINT

Keynote Address | Lakshyaraj Singh Mewar

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, CBSE at SGEF2022

How schools can nurture every student’s genius

Aftermovie | SGEF2022 | Jaipur

Li Andersson | Minister of Education | Finland

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) discusses NEP2020

ScooNews | Early Ed Asia 2019 | Aftermovie
#PodarECEconf : Pursuing quality ECE

#CBSE Class XII #Results #Highlights

The interesting story of India’s educational system | Adhitya Iyer

A young scientist’s quest for clean water

The Danger of Silence: Clint Smith

National Digital Library of India is an initiative by HRD Ministry

Remembering Kalpana Chawla on her birthday!

Message from Sadhguru for Students!
Message from Sadhguru for Students!

The Untapped Genius That Could Change Science for the Better

Eddy Zhong: How school makes kids less intelligent TEDxYouth@Beacon

#TEDxCanberra : What if every child had access to music education…
Trending
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCBSE Warns Dummy School Students May Be Barred from Board Exams
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme







