Education
A Joyful Journey To Positive Parenting
Dr Kamini Prakash Rege pens down a joyful journey to positive parenting; how it can be inculcated by all of us.
Published
6 years agoon

A garden with different flowers becomes beautiful when it blossoms. Similarly, if parents learn how to be a ‘gardener’ and are able to recognise their child’s personality and nourish it, then their ‘garden’ will become fragrant! This is what positive parenting is all about! Parenting children can be enormously rewarding and fulfilling – but also exhausting and challenging. It is truly the best and the worst of times. Yet you are the role model for your child, and most parents, when asked what they really want for their children, respond with ‘I want them to be happy’. Your parenting choices really can help – and the love and support you give your children is critical to their future well-being. When it comes to family life, everyone strives to figure out how the relationship between parents and children can become ideal. Positive parenting techniques work well for raising children with discipline and good moral values, and are every parent’s dream. However, it is not an easy feat. And it is important to know that the parent child relationship is a two-way street, in other words, it is actually a partnership between a parent and their child.
When parents develop effective parenting skills, they are able to take the initiative in filling the generation gap. When parents start to understand the balance of where to place boundaries, where to encourage, and where to discourage, then their children will not get spoiled. In this way they become good parents. When people do not know how to be a good parent, distance between the two develops.
Positive parenting involves emphasising the positive and planning ahead to prevent problems. It also involves using everyday situations and creating opportunities to help children learn and to motivate them to do their best. Children who grow up with positive parenting are likely to develop the skills they need to do well at schoolwork, build friendships, and feel good about them. They are also much less likely to develop behavioural or emotional problems when they get older. Parents who learn to use positive parenting skills typically feel more confident and competent in managing daily parenting tasks, are less depressed, less stressed, and have less conflict with their partners over parenting issues.
NEED FOR POSITIVE PARENTING
Being a positive parent doesn't only mean better outcomes for your child, but it also has benefits for relationships with other important adults in the child's life, and for you as a parent. As babies and children develop, they go through natural stages of development and attachment to their parent. Positive parents recognise these stages and respond accordingly, teaching the child that his or her own actions matter, and that loving relationships are stable and secure, no matter what the circumstances may be.
Positive parenting with a partner also means open and honest communication – and teaching your children – by your own actions – about how to find positive solutions to conflicts. Of course, all parents argue, and sometimes it's in front of the children. Yet what is essential for the children is to also see the resolution – to witness how two adults who love each other can solve their differences and return to a stable, caring, supportive relationship, despite the fractious emotion.
For you as a parent, recognising that there will be ups and downs and taking care of self goes a long way. If you are stressed or upset, your children will naturally pick up on this and feel those emotions intensely as well. If you are more relaxed and joyful, your children also mirror those sentiments, and the entire household is more harmonious. We all feel those negative emotions at times – and by watching how we deal with them, our children learn models for their own behaviour in future.
APPROPRIATE TIME TO INITIATE PARENTING
In recent years there have been some startling discoveries about how the love and support we receive in our earliest years affects our lives. It turns out that love is essential to brain development in the early years of life, particularly to the development of our social and emotional brain systems. As babies, our nervous systems are profoundly shaped by our earliest relationships and this has lasting consequences for our adult life, despite our inability to remember babyhood. Research shows that the way our brain develops as a baby can affect the way we respond to stress and our future emotional wellbeing. A lack of love and support during the crucial early years can increase the likelihood of future mental health issues and conditions such as anorexia, addiction, and anti-social behaviour. As parents we often think about the early years of our children's lives as a time to be struggled through, where getting our child "into a good routine" and helping them develop their basic skills in eating, walking and speaking are the most important things. But the research suggests that what matters most is providing unconditional love for our children and helping them feel understood, valued and secure.
BE THERE FOR YOUR CHILD.
No matter the age of your child, he or she wants and needs your full attention.
With young babies, this means getting closer to their faces and making noises and imitating their own actions.
With toddlers and pre-schoolers, this means getting on the floor with them and playing at their level, reading books, zooming cars, dressing dolls and doing it over and over and over again.
As your child starts attending school being present with them means sharing stories about your day as he or she shares stories about what happened at school. Asking open questions with a sense of humour can help draw out interesting anecdotes.
With teenagers, some parents tend to draw back and give more room. However, teenagers still need to know that you are there, loving and supportive. Ask questions, and respect their desire for privacy. Be prepared for the unexpected – the most interesting stories come out when you least anticipate it, driving in the car or late at night.
And above all, dedicate time to your child – put away the technology and play.
MAINTAIN A POSITIVE RELATIONSHIP WITH YOUR PARTNER
Really listen to what people are saying
Understand each other’s needs
Enhance your relationship with your partner
Look for the good
Ask about the things that have gone well
HELP YOUR CHILDREN DEVELOP EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE
Accept all emotions and work with your child to name them – both the positive and negative.
Share in the joyous moments with your child, letting him or her experience the full pleasure of pride, love, excitement, anticipation, surprise and the like.
Accept that your child will have difficult moments. These are the times that build resilience. Instead of trying to take the sad away from a disappointed child, share in the disappointment with him or her and acknowledge the emotion.
For example, say "I understand that you're disappointed. It must be very disappointing to have a play date all scheduled and then your friend is sick and can't come over."
Give your child a safe and supportive space to share and feel all emotions.
DON'T BE TOO HARD ON YOURSELF
There will be times when you didn't do something the way that you wanted. Don't kick yourself. Learn and move on. Everyone has bad days.
Be realistic in your reasoning
Detox your negative thinking patterns
FIND OPTIMISTIC WAYS TO EXPLAIN THINGS
When negative things happen, resist the urge to see them as permanent. A child who is being defiant may be having a bad day, or may be tired, or may be frustrated from an earlier event. That defiance is temporary, and not a permanent character trait.
When negative things happen, resist the urge to generalise them across time and space. A child who behaves one way at home may not behave the same way at school, or on the sports team.
When good things happen, enjoy them and savour them. Actively share with your child when you see them doing or saying positive things.
Catch your child doing things right. For example, say "I saw you helping that younger child up when she fell down off the see-saw. That was a very kind thing to do."
FIVE PRINCIPLES OF POSITIVE PARENTING
The principles go hand in hand to help you build a strong bond with your children and to position you as the effective leader your child needs throughout childhood.
Principle #1: Attachment: Attachment is a deep, secure emotional bond. Children are hardwired to connect with their caregivers emotionally, and without it, their development is hindered. The bond between primary caregivers and infants is responsible for shaping all our future relationships! It strengthens or damages our ability to focus, be conscious of our feelings and calm ourselves. It can even affect our resilience. If a secure attachment is made, children will rest in our love and security. They feel safe with us, and this safety provides them room to grow and learn appropriately. If a secure attachment is not made, research tells us that behavioural problems and relationship troubles later in life are likely. Not only do we want to create a secure bond so that our children can grow and develop properly, but this attachment also makes it easier to guide and correct them. A strong attachment gives us genuine influence, which is far better than forced compliance. Children want to please those they feel connected to. They listen to us and accept our boundaries much more readily when the bond is secure and strong. To develop a strong attachment, trust is essential. They must feel felt by us. When they feel we are for them, not against them; when they feel we are safe to run to; and when they feel that they are loved and valued, we will have their hearts. Only when we have their hearts do we have real, lasting influence in their lives.
Principle #2: Respect: Respect regarding children is often a one-sided topic. We expect them to show it to adults. The idea of showing respect to children is usually tied to permissiveness or being too “soft,” but this isn’t so. Children learn how to show respect best by living it. We respect a child’s mind when we develop a secure attachment and when we are positive and affirming. We respect a child’s body and dignity when we choose not to use shame or physical punishment. We respect their personhood by allowing space to explore and develop at their own pace, and we respect their spirit by honouring them just the way they are.
Principle #3: Proactive Parenting: I think parents will often wait until a problem arises before teaching the boundaries and skills needed to deal with that particular behavioural issue, but being proactive means putting in the time up front, before a problem arises. It means teaching children how anger feels in the body and giving them ways to deal with it (dinosaur breaths or shake-itout, for example) before they ever hit or bite a friend. Proactive parenting means building the relationship and allotting sufficient time for play and connection each day to thwart any behaviour problems that could arise from disconnection. It requires us to be watchful at play dates and around babies and pets so that we can intervene at the first sign of a problem. Proactive parenting also means responding rather than reacting to our children’s behaviours. This requires forethought into how we will handle certain situations. Responsive parents are in control of their emotions and able to respond thoughtfully when a problem arises.
Principle #4: Empathetic Leadership: Too often, Positive Parenting is confused with permissiveness. This is unfortunate because they are completely opposite. Positive parents are very much in a leadership role with their children. It just doesn’t look like the dictatorship we have come to recognize as typical. Empathy is an important part of leadership because it draws us closer and provides that important attachment. When children feel understood and know that we are on their side, they accept our leadership.
Principle #5: Positive Discipline: Positive discipline moves beyond punishment and toward problem-solving. Children don’t learn life lessons with their noses in a corner. Positive discipline holds them accountable by teaching them how to own up to and fix their mistakes. It gives them the skills and tools necessary to do better in the future and focuses on their capabilities, not their mistakes.
You may like
-


UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures
-


Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead
-


CBSE To Conduct Board Exams Twice for Class 10 from 2026
-


How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
-


Tripura Becomes Third Indian State to Achieve Full Literacy
-


Assam Brings Sign Language to Senior Secondary Classrooms in Landmark Move
-


Delhi Schools to Implement Age 6 Rule for Class 1 Admissions from 2026
-


Tripura Adds Sex Education & HIV Awareness to Their Curriculum
-


Four Indian Schools Shine on the Global Stage at World’s Best School Prizes 2024
-


Centre Urges 7 States to Consider Common Board Amid Alarming Student Failure Rates
Education
UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures
Published
16 hours agoon
June 30, 2025
In a firm push for accountability, the University Grants Commission (UGC) has issued show-cause notices to 89 higher education institutions for failing to comply with mandatory anti-ragging regulations. The defaulters include some of India’s most prestigious institutions—17 of which are Institutes of National Importance—including IIT Bombay, IIT Kharagpur, IIT Hyderabad, and IIM Bangalore.
These institutions, despite repeated advisories, failed to submit the required anti-ragging undertakings from students and institutional compliance reports. The lapses have been termed a “significant violation of regulatory norms” by the UGC, raising serious concerns over student safety and campus climate in India’s top educational spaces.
A notice dated June 9, signed by UGC Secretary Prof. Manish R Joshi, has directed all 89 institutions to respond within 30 days by submitting comprehensive compliance reports, securing online anti-ragging affidavits from all students, and detailing both current and planned anti-ragging mechanisms.
If the institutions fail to act within the deadline, consequences may include withdrawal of UGC grants, public disclosure of non-compliance status, and potential derecognition or withdrawal of affiliation.
Among the list of defaulters are the Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata, AIIMS Raebareli, Aligarh Muslim University, RGIPT Basar, and several National Institutes of Design. The issue becomes even more urgent in light of recent ragging-related incidents and an increasing perception of campus hostility. “Institutions must treat this as a matter of utmost urgency. Your prompt compliance will be essential in upholding institutional responsibility towards student welfare,” reads the UGC’s statement.
Ragging has no place in modern education, especially not in a country positioning itself as a global knowledge leader.
In 2025, with India’s education sector expanding in reach, recognition, and responsibility, compliance with anti-ragging norms shouldn’t require reminders. It should be a given.
As the world watches Indian institutions climb global rankings, student safety and well-being must remain central, not as compliance checkboxes, but as part of the educational culture we aspire to build.
Education
Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead
Published
5 days agoon
June 26, 2025
In a decisive step toward reforming India’s fragmented senior secondary education system, the Ministry of Education has constituted an 11-member high-level committee to address the mushrooming of dummy schools and the unchecked influence of coaching centres. Chaired by Higher Education Secretary Vineet Joshi, the committee includes representatives from CBSE, NCERT, and faculty from IITs in Madras, Kanpur, and Trichy.
The move is seen as part of a growing policy consensus across central and state governments to reclaim the authority of schools, following recent crackdowns and reforms aimed at regulating coaching institutions and curbing the dummy school culture that sidelines holistic education.
Dummy schools — where students are officially enrolled but rarely attend — have emerged as a by-product of India’s competitive entrance exam culture. These institutions prioritise JEE, NEET, and CUET preparation through coaching classes, while students disengage from formal schooling. The CBSE’s March 2025 advisory warning that students from dummy schools could be barred from board exams marked a serious turning point in policy enforcement.
Earlier this year, the Delhi Government carried out inspections in over 600 private schools, issuing notices to at least 10 for running dummy setups. The move followed media reports and parental complaints about students being denied regular schooling in favour of coaching arrangements.
Meanwhile, the Rajasthan Cabinet approved a bill in April 2025 to regulate coaching centres operating in Kota and other education hubs. The legislation aims to curb exploitative practices, mandate mental health counsellors, and prevent coaching centres from operating without a minimum infrastructure standard—prompted by rising student suicides in the state.
Central Framework and Industry Oversight
In February 2025, the Central Government announced a new framework for coaching centres, proposing registration, transparency in fee structures, and guidelines on advertising to prevent misleading claims. Together with the current committee’s formation, these reforms indicate a systematic tightening of oversight at all levels.
The new panel’s mandate is broad. It will investigate:
- The socio-academic reasons behind the rise of dummy schools
- The misalignment between school curricula and competitive exams
- The impact of coaching on student well-being and critical thinking
- The need to promote alternate career pathways beyond engineering and medicine
- Regulations around coaching advertisements and contract practices
A National Rethink on the Purpose of Schooling
Education experts like Dr Ameeta Mulla Wattal have welcomed the initiative, calling it “a vital opportunity to restore the sanctity of school education.” The rise of coaching centres as parallel systems, she noted, has come at the cost of creativity, values, and even mental health in adolescents.
As India contemplates the future of its learners, the Ministry’s recent actions suggest a serious intent to bridge the gap between boardrooms and classrooms. Whether the new committee’s recommendations lead to tangible change remains to be seen, but the signals are clear: education in India must prepare children for life, not just for an entrance exam.
Education
CBSE To Conduct Board Exams Twice for Class 10 from 2026
Published
5 days agoon
June 26, 2025
In a move aimed at reducing academic pressure and offering students a second shot within the same academic year, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has announced a revised board examination structure for Class 10. Starting from the 2025–26 session, students will appear for two board exams: the first in February and the second in May.
While the February exam will be the ‘main’ board, students who wish to improve their scores in up to three subjects can take the second board exam. Those who fail in one or two subjects may also attempt the May exam under the compartment category. However, those who miss three or more subjects will be marked ‘Essential Repeat’ and have to retake the exam the following year.
Importantly, this is not a semester system. Students must appear for the first exam. The second is optional—meant only for improvement or compartment cases. No additional or new subjects can be added between the two exams.
CBSE has clarified that the structure, syllabus, and pattern of questions will remain unchanged. The results of the first exam will be declared in April, enabling provisional Class 11 admissions. However, the final marksheets and certificates will be issued only after the second exam results are announced in June.
This dual-exam model was opened for public feedback earlier this year and will initially apply only to Class 10. A similar system for Class 12 is being considered but has not yet been confirmed.
For schools, this change will require rethinking academic calendars, counselling processes, and internal assessments, especially for students who may be at risk of needing a second attempt. The move aligns with CBSE’s broader goals of offering students more flexibility and reducing the high stakes of a single board exam.
Education
How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
Published
7 days agoon
June 24, 2025By
Renu Sharma
The dopamine-rich scrolling in late mornings with amorphous freedom has made our zealous students so comfortable that they are re-entering their classrooms with minds tuned to instant gratification, not delayed rewards. Now the challenge isn’t just academics but to re-engage our bud’s attention and curiosity. Neuroscience backed motivation strategies and intentional school design could prove to be a catalyst as it will bring a positive change and enable the students to learn at a better pace.
1. Rewiring the Dopamine rush with 2 Ps, Purpose and Productivity:
Neuroscience says: Where our brains are functional to seek novelty and purpose on their own, during summer break, the buds often lean into adding the activities to their routine which are unpredictable, quick, and rewarding referring back to instant gratification, these activities may include social media, gaming, and chatting anonymously and grateful to internet and inventions, there are plethora of platforms enabling students to be distracted. And then joining back the school with a gradual drip of delayed academic rewards may seem to be a let-down for students.
Actionable tip: We as facilitators have to be the mystery-solvers channeling their energy into productivity, enlightening them with real-world challenges, interdisciplinary projects, or a mystery to solve that taps into their intrinsic curiosity. Novelty may allow us to reset their attention-even primitive changes in surrounding like rearranged desks, learning outdoors, and using the BALA method to utilize infrastructure, can signal a shift in engagement and productivity.
2. Design for Autonomy and Flow
Neuroscience says:
Neuroscience tells us that motivation really flourishes when students feel they have some control over their learning. The brain’s reward system kicks in when choices are part of the equation, especially regarding how tasks are structured or what content is covered.
Here’s a practical tip: give students structured choices, like deciding which book to dive into, which problem to tackle first, or how they want to present their findings. A design that promotes flow—complete with clear goals, manageable challenges, and instant feedback—helps keep students in that ideal zone, avoiding both boredom and anxiety.
3. Rebuild Social Motivation Through Spaces That Connect
Neuroscience tells us that connecting with peers is a huge motivator, especially after the pandemic. Our brains are wired for social interaction, which plays a key role in how we learn and engage emotionally.
Actionable tip: Create flexible seating arrangements or common areas that encourage group work and casual collaboration. Try incorporating daily activities like “curiosity circles” or peer-led problem-solving sessions to foster a sense of belonging and shared learning objectives.
4. Leverage Routines to Rewire Attention
Neuroscience shows that our habits influence our attention. After a summer of scattered focus, students thrive on rhythmic and consistent routines that help retrain their executive functions.
Actionable tip: Kick off classes with familiar “mind-on” rituals — whether it’s a thought-provoking question, a brief reflection, or a quiet sketch — to help anchor their attention. Consistency breeds comfort, and that comfort boosts confidence.
5. Make Joy a Design Priority
Neuroscience indicates that positive emotions can enhance learning by boosting neuroplasticity. When students (and teachers) experience joy, they’re more likely to engage deeply and retain what they learn.
Actionable tip: Infuse joyful moments into the day — through fun challenges, movement breaks, or a bit of humor. Allow time for students to share what excites them. A joyful classroom isn’t just a nicer place to be; it’s also more effective for learning.
Conclusion: To capture wandering minds, we need to understand how motivation truly works and design both our curriculum and learning spaces to support it. When we ignite curiosity, honor autonomy, and weave joy into the experience, even the sleepiest summer brain can come alive again.
This article is written by:

Renu Sharma
Assistant Director – Systems – Indirapuram Group of Schools
Principal – Indirapuram Public School – Crossings Republik
Education
Tripura Becomes Third Indian State to Achieve Full Literacy
Published
7 days agoon
June 24, 2025
Tripura has been declared a fully literate state, becoming the third in the country to cross the 95% literacy threshold after Goa and Mizoram.
The announcement was made by Chief Minister Dr. Manik Saha, citing data from the Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society (ULLAS) programme — a flagship literacy and life skills initiative aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. The declaration marks not just an administrative achievement, but a generational leap in educational access and community participation.
Tripura’s current literacy rate stands at 95.6%, as per the latest Periodic Labour Force Survey, a remarkable rise from 87.22% in the 2011 Census, and a far cry from 20.24% in 1961.
“This is a historic moment for Tripura. From a 20% literacy rate six decades ago to 95.6% today, we have rewritten our narrative,” said Dr. Saha in a public post. “Through the successful implementation of ULLAS, we have ensured that literacy is not limited to signing one’s name, but includes the confidence to participate meaningfully in society.”
ULLAS, launched under the New India Literacy Programme, targets adult learners aged 15 and above who have missed out on formal schooling. It goes beyond basic literacy to include numeracy, digital and financial literacy, legal awareness, and other essential life skills — all aligned with NEP 2020’s commitment to equitable lifelong learning.
The shift from traditional signature-based literacy drives to functional literacy has allowed Tripura to reach new learners with practical, future-ready tools. The model also offers a compelling template for other states striving to raise literacy rates beyond conventional benchmarks.
Education
Assam Brings Sign Language to Senior Secondary Classrooms in Landmark Move
Published
7 days agoon
June 24, 2025
The Assam State School Education Board (ASSEB) has announced the introduction of Sign Language as an elective subject for Higher Secondary (Classes XI–XII) from the current academic year.
Education Minister Dr. Ranoj Pegu made the announcement during the inauguration of a residential AI training programme for teachers at IIT Guwahati. While Artificial Intelligence and Financial Literacy were also introduced as new electives, Sign Language stood out as a critical stride towards making classrooms more accessible to the deaf and hard-of-hearing community.
“This is not just about a subject; it’s about acknowledging communication rights,” said Dr. Pegu, who also unveiled a specially designed AI textbook at the event. The textbook was developed in collaboration with experts from IIT Guwahati and Dibrugarh University. He added that the curriculum reforms are aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s vision of equity, inclusion, and skill readiness.
According to education officials, the rollout of Sign Language will begin in institutions where qualified educators or resource personnel are available. Training for teachers is expected to be scaled up across the coming months. The subject aims to raise awareness about Indian Sign Language (ISL), improve communication access for students with hearing impairments, and sensitise peers to inclusive practices from a young age.
Later in the day, Dr. Pegu chaired a review meeting with officials from the Department of School Education to discuss budget allocations and planning for the 2025–26 academic year. While schemes like the Chief Minister’s Nijut Moina initiative, distribution of bicycles for Class IX girls, and the upgradation of Bodo-medium schools were discussed, the emphasis remained on delivering structural reforms that bridge equity gaps in access and opportunity.
The addition of Sign Language, AI, and Financial Literacy as electives reflects a broader shift in how Assam is reimagining school education — one where life skills, digital literacy, and inclusive values are no longer optional, but integral.
Education
Delhi Schools to Implement Age 6 Rule for Class 1 Admissions from 2026
Published
1 week agoon
June 23, 2025
In line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the Right to Education Act (RTE) 2009, the Directorate of Education (DoE), Government of NCT of Delhi, has issued a directive mandating that children must be 6 years old to gain admission into Class 1 starting from the academic session 2026–27.
This move aligns Delhi’s education system with the restructured 5+3+3+4 school framework introduced in the NEP 2020. Under the revised structure, the foundational stage will now include three years of pre-primary education before Class 1: Nursery (Bal Vatika/Preschool 1) at age 3, Lower KG (Preschool 2) at age 4, and Upper KG (Preschool 3) at age 5. Class 1 will be open to children only upon completion of 6 years of age.
All Heads of Government, Government-Aided, and Recognized Unaided Private Schools have been instructed to adopt this change beginning in the 2026–27 academic session.
By standardising entry age norms, the move aims to promote uniformity and developmentally appropriate learning, ensuring children enter Grade 1 equipped with foundational skills from three years of early childhood education.
Education
Tripura Adds Sex Education & HIV Awareness to Their Curriculum
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 20, 2025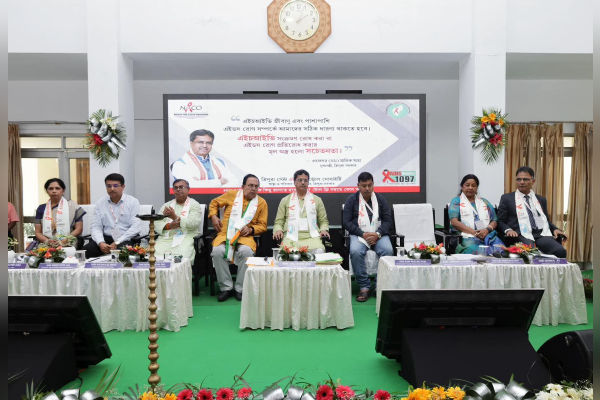
In a progressive step towards comprehensive health education, the Tripura government has announced plans to integrate sex education and HIV/AIDS awareness into its school curriculum, Chief Minister Manik Saha confirmed.
According to officials, the curriculum update aims to equip students with accurate knowledge about sexual health, disease prevention, and safe practices—key factors in curbing the prevalence of HIV/AIDS in the state. With around 5,000 active cases reported by late 2024, including a notable infection rate of 0.33% among adults and over 800 student cases, the move is seen as a timely measure.
The new content will be deployed through age-appropriate lessons, Red Ribbon Club activities, and sensitisation drives led by health and education officials. This initiative builds upon previous efforts, such as school- and college-level awareness programs, the involvement of key stakeholders, and information, education, and communication (IEC) campaigns across rural and urban centers.
Chief Minister Saha emphasised the role of educators and community leaders in delivering accurate information and fostering a supportive environment: “Students from school to college level should be made aware of the dangers of this disease,” he remarked earlier.
The curriculum integration aligns with state-level action under the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP). It resonates with India’s broader public health mandate to move HIV/AIDS education from stigma to mainstream schooling. By addressing misconceptions and promoting prevention early, Tripura hopes to protect its youth and reduce dropout rates among vulnerable groups.
Education
Four Indian Schools Shine on the Global Stage at World’s Best School Prizes 2024
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 20, 2025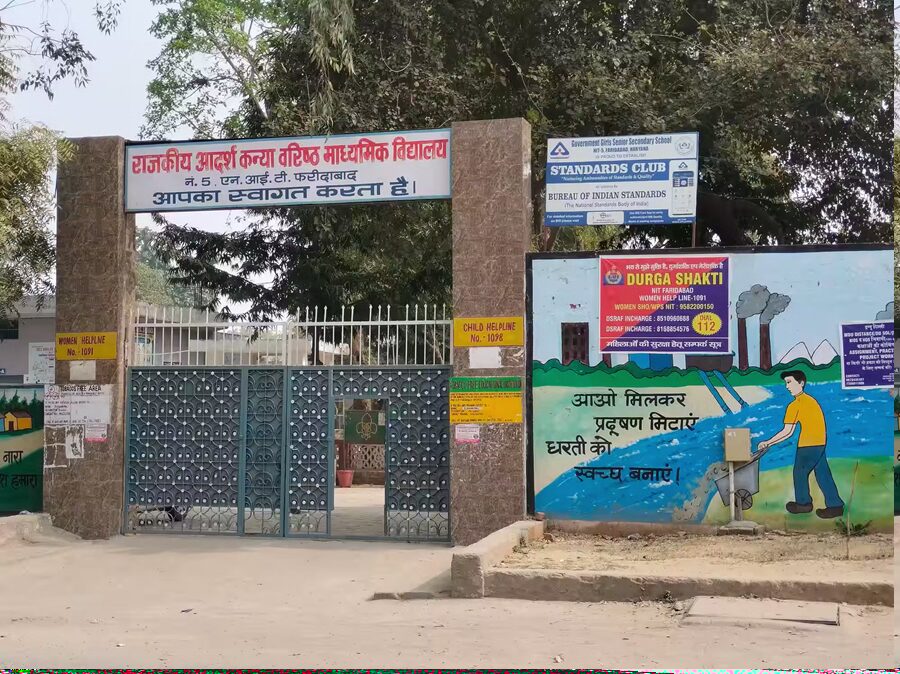
In a proud moment for Indian education, four schools from across the country have been named among the top 10 global finalists in the prestigious World’s Best School Prizes 2024, organised by UK-based T4 Education. These awards honour schools that are pushing the boundaries of innovation, inclusion, and community impact — and this year, India has made its presence felt in four out of five categories.
A Snapshot of India’s Global Finalists
From government to private, rural to urban — the diversity of India’s representation this year is striking.
-
Government Girls Senior Secondary School, NIT 5, Faridabad (Haryana) – Supporting Healthy Lives
A government-run school is redefining what public education can achieve. By interweaving nutrition, mental health, and physical well-being into its core ethos, the school is transforming the lives of at-risk girls, ensuring that no student is left behind. -
Ekya School, JP Nagar, Bengaluru (Karnataka) – Innovation
Recognised for reimagining learning through a design-thinking framework, Ekya encourages student agency, interdisciplinary inquiry, and real-world problem-solving — a blueprint for future-ready schooling. -
ZP School, Jalindar Nagar, near Pune (Maharashtra) – Community Collaboration
A rural government school that has placed local communities at the heart of education. By building trust and ownership at the grassroots, it has created a model of sustainable, community-driven transformation. -
Delhi Public School, Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh) – Environmental Action
Known for its strong environmental initiatives, DPS Varanasi’s students lead from the front — managing waste, conserving energy, and creating a campus-wide culture of sustainability.
These schools are now among 50 global finalists, selected from thousands of applications worldwide. The shortlist highlights institutions not merely chasing academic results but actively shaping well-being, equity, and systemic reform in education.
What Happens Next
All 50 finalist schools are now competing for the Community Choice Award, determined through an open global vote. Winners across each of the five main categories — Supporting Healthy Lives, Environmental Action, Innovation, Community Collaboration, and Overcoming Adversity — will be announced in October 2024.
The celebration will culminate at the World Schools Summit in Abu Dhabi in November, where global education leaders will convene for a high-impact dialogue on best practices and policy influence.
The Broader Picture
Launched in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World’s Best School Prizes have rapidly emerged as one of the most influential accolades in global education. Powered by T4 Education, a platform that connects over 200,000 educators worldwide, the awards are more than just recognition — they are a launchpad for schools to amplify their voice, scale impact, and drive systems-level change.
For India, the presence of four unique schools among global changemakers is both a celebration and a reminder — that bold ideas, no matter where they are born, can shape the future of learning.
Education
Centre Urges 7 States to Consider Common Board Amid Alarming Student Failure Rates
Published
2 weeks agoon
June 19, 2025
In a significant move aimed at streamlining school assessments and improving learning outcomes, the Ministry of Education has recommended that seven states—Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Kerala, Manipur, Odisha, Telangana, and West Bengal—adopt a common board for Class 10 and 12 examinations.
The recommendation follows a detailed analysis by the Department of School Education, which found that these states accounted for a staggering 66% of student failures across India last academic year. In total, over 22 lakh students failed Class 10, and 20 lakh failed Class 12 nationally in 2024, highlighting persistent challenges in retention and transition to higher education.
“Not having a common board leads to poor academic outcomes,” said School Education Secretary Sanjay Kumar, stressing that standardisation in assessment, curriculum, and evaluation is key to reversing this trend. “A common board is the way forward for ease of schooling,” he added.
India currently has 66 examination boards, including three national-level boards and 63 state-level ones. However, only 33 of these boards cater to 97% of enrolled students. The rest, often covering smaller student populations, contribute disproportionately to inconsistent academic performance.
The report also placed a renewed focus on the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), especially in high-failure states. While NIOS currently has a stronger presence in Delhi, Rajasthan, and Haryana, the ministry wants to see its footprint expand in the recommended states to engage unsuccessful students and prevent dropouts.
However, the report didn’t just stop at structural issues. It shed light on regional and linguistic disparities in student performance. For instance, students taking exams in Odia and Malayalam consistently outperformed peers writing in Kannada, Telugu, and Assamese. Interestingly, Kerala, with its integrated board system, recorded an astounding pass rate of 99.96%. Odisha and Manipur also showed success rates above 97%.
Meanwhile, Navodaya Vidyalayas (NVs) and Kendriya Vidyalayas (KVs) continue to set benchmarks in academic excellence. The report found that 72% of NV students cleared NEET-UG, with strong showings also reported in engineering entrance exams. NVs, which cater primarily to rural talent, seem to be reinforcing the case for equity in access to quality education.
As conversations around NEP 2020 continue to push for holistic, inclusive, and standardised learning, the Centre’s recommendation serves as both a wake-up call and a window of opportunity. With the right reforms, these states could be on the brink of a transformative shift in student success.
Newsletter

UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures

Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead

CBSE To Conduct Board Exams Twice for Class 10 from 2026

How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
Tripura Becomes Third Indian State to Achieve Full Literacy

Assam Brings Sign Language to Senior Secondary Classrooms in Landmark Move

Delhi Schools to Implement Age 6 Rule for Class 1 Admissions from 2026

Tripura Adds Sex Education & HIV Awareness to Their Curriculum

Four Indian Schools Shine on the Global Stage at World’s Best School Prizes 2024

Centre Urges 7 States to Consider Common Board Amid Alarming Student Failure Rates

IIT Delhi Leads India in the QS Rankings 2026; MIT Tops Globally

Chandigarh, Punjab Lead in School Education Rankings; Meghalaya Trails Behind

Maharashtra Revises Policy on Third Language in Schools, Hindi No Longer Mandatory

From Academics to Empathy: Redefining Academic Success

India Sends 20 Students to Japan Under Sakura Science Programme 2025

Delhi Schools to Observe June as Anti-Malaria Month, Says DoE

Telangana Govt Ties Up With 6 NGOs to Revolutionise Teaching in Govt Schools

History, Identity, and Pride: Books That Make Sense of Being You

Delhi Government Clears Ordinance to Regulate Private School Fees After Protests

Of Formulas and Frames: Why India Must Stop Dividing Science and Art

43-Day Hunger Strike Ends as Govt Backs Teachers’ Demands

OpenAI Academy Launches in India to Democratise AI Education for Students, Teachers, and Startups

World Environment Day: Why Your School’s Environmental Education Needs a Cleanup

UNESCO Flags Foundational Learning Crisis & Leadership Gaps in India’s Education System

Beyond the Buzz: Investors Call for Grounded AI Innovation in Indian Classrooms

Is Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?

CBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools

“Be the Change in a Changing World”: Anita Karwal and Anju Chazot Reflect on NEP 2020
CBSE Warns Dummy School Students May Be Barred from Board Exams

Maharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
China Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035

MAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET

‘Baalpan ki Kavita’ Initiative Launched to Restore Indian Rhymes for Young Learners

John King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education

Rewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution

CBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020

CBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme

India Bids Farewell to NEP Architect Dr K. Kasturirangan

Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar 2025: Nominations Now Open for India’s Young Achievers

Banu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature

NCERT Class 7 Textbooks Updated: Mughals Removed, Focus on Indian Ethos and Pilgrimage

Delhi Government Cracks Down on Dummy Schooling; Over 600 Schools Inspected, 10 Issued Notices

Delhi Approves Landmark Bill to Regulate School Fees Across 1,677 Institutions

The Ethics of AI Art in Education & Nostalgia: The Ghibli Effect

Operation Sindoor and Operation Abhyaas: Navigating School Safety and Student Well-being Amid Rising Tensions
CBSE Revises Class 10, 12 Curriculum: Biannual Exams, New Subjects and Flexible Passing Criteria Introduced

Harvard Stands Its Ground: Harvard Faces ₹18,400 Crore Funding Freeze After Rejecting Trump Administration’s Demands

CUET-UG 2025 Likely to be Postponed, Fresh Dates Expected Soon

Aalamaram 2025: Where Indian Educators Came Together to Grow, Reflect, and Lead

Trump Signs Executive Order to Promote AI Integration in U.S. K-12 Education
SGEF2023 | Special Address by Rama Datt, Trustee, Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II Trust, Jaipur

ScooNews | After Movie | ScooNews Global Educators Fest 2023

Aftermovie | NIES2 UP Chapter | 21 Jan 2023

WEBINAR | Gamification in Education: How Digital Badges Can Boost Student Motivation and Engagement

ScooNews | WEBINAR| Importance of Physical Activity for Children at School | Plaeto

SCOONEWS | WEBINAR | WHY DIGITIZING YOUR SCHOOL IS A MUST | TEACHMINT

Keynote Address | Lakshyaraj Singh Mewar

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, CBSE at SGEF2022

How schools can nurture every student’s genius

Aftermovie | SGEF2022 | Jaipur

Li Andersson | Minister of Education | Finland

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) discusses NEP2020

ScooNews | Early Ed Asia 2019 | Aftermovie
#PodarECEconf : Pursuing quality ECE

#CBSE Class XII #Results #Highlights

The interesting story of India’s educational system | Adhitya Iyer

A young scientist’s quest for clean water

The Danger of Silence: Clint Smith

National Digital Library of India is an initiative by HRD Ministry

Remembering Kalpana Chawla on her birthday!

Message from Sadhguru for Students!
Message from Sadhguru for Students!

The Untapped Genius That Could Change Science for the Better

Eddy Zhong: How school makes kids less intelligent TEDxYouth@Beacon

#TEDxCanberra : What if every child had access to music education…
Trending
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education1 month ago
Education1 month agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months ago“Be the Change in a Changing World”: Anita Karwal and Anju Chazot Reflect on NEP 2020
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCBSE Warns Dummy School Students May Be Barred from Board Exams
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months ago‘Baalpan ki Kavita’ Initiative Launched to Restore Indian Rhymes for Young Learners
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution





