News
Lucknow’s Shubh Agrawal scores 1590 / 1600 (the highest) in SAT in India
Shubh Agrawal, a Class 11 student, has made Lucknow proud by scoring 1590 out of 1600 on SAT for admission in undergraduate programs of universities or colleges in the United States. SAT (originally called the Scholastic Aptitude Test) is an entrance exam created by the College Board, USA.

Shubh Agrawal, a Class 11 student, has made Lucknow proud by scoring 1590 out of 1600 on SAT for admission in undergraduate programs of universities or colleges in the United States. SAT (originally called the Scholastic Aptitude Test) is an entrance exam created by the College Board, USA and is used by many colleges and universities globally to make admission decisions.
This is for the first time that any student from Lucknow has achieved this feat and this is probably the highest score in India for SAT, which was held on January 21 this year.
“I can look forward to not only successfully applying to the most elite colleges in the US, including Stanford, CalTech, Harvard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and others but will also get substantial scholarship,” a jubilant Shubh, a student of City Montessori School, Gomti Nagar branch, told Hindustan Times.
Shubh, scored 800 out of 800 in the maths section and 790 out of 800 in the evidence-based reading and writing in English section. The 16-year-old’s marks are the second highest score possible on the test.
His overall score of 1590 represented the highest percentile rank of 99+ in India, said Abha Anant, principal of CMS Gomti Nagar.
The test comprised 4 sections, two from English (reading and writing) and two from mathematics. The result is in the form of a score ranging from a minimum of 400 to a maximum of 1600, in intervals of 10 points.
If you are looking for more information on SAT, Click Here
Education
Supreme Court’s Landmark Judgment for Schools: Menstrual Health is a Fundamental Right
In a transformative judgment delivered on January 30, 2026, the Supreme Court of India has unequivocally placed menstrual health within the ambit of fundamental rights, linking dignity, education, and equality in classrooms across the country. This ruling goes beyond infrastructure mandates to address stigma, awareness, and school culture—reshaping how institutions must support adolescent girls. ScooNews breaks down what the judgment says and what it now requires every school leader to do.

In a landmark judgment that firmly connects constitutional law with everyday classroom realities, the Supreme Court of India has declared menstrual health a fundamental right, placing it squarely within the ambit of Article 21 (Right to Life with dignity) and Article 21A (Right to Education).
Delivered on January 30, 2026, by a Bench of Justices J.B. Pardiwala and R. Mahadevan, the ruling in Jaya Thakur vs Union of India goes far beyond symbolic recognition. It lays down clear, enforceable obligations for schools—government and private alike—transforming menstrual hygiene from a welfare measure into a constitutional duty.
For school leaders, this judgment marks a decisive shift: menstrual dignity is no longer optional, charitable, or discretionary. It is a core educational standard.
Why the Court Intervened
The Court acknowledged what educators and parents have long known but systems have often ignored:
lack of menstrual hygiene support is a direct barrier to girls’ education.
Absenteeism, discomfort, fear of embarrassment, inadequate toilets, and social stigma collectively push many girls out of classrooms—sometimes temporarily, sometimes permanently. By recognising menstrual health as integral to dignity and learning, the Court affirmed that no girl should ever have to choose between her education and her period.
What the Court Said
The judgment rests on three powerful principles:
- Menstrual health is inseparable from dignity and bodily autonomy, which are central to the Right to Life.
- Education cannot be meaningful if menstruation becomes a reason for exclusion, discomfort, or discrimination.
- Infrastructure alone is insufficient—social stigma, silence, and male insensitivity must also be addressed.
In a telling observation, the Court noted that “ignorance breeds insensitivity” and warned that menstrual facilities will remain underused unless schools actively dismantle stigma.
What Schools Must Now Do
The Court’s directions are both practical and time-bound, with a three-month implementation window. They fall into two clear buckets: infrastructure and ecosystem change.
-
Physical Infrastructure: The Non-Negotiables
All schools—government and private—must ensure:
- Free provision of biodegradable sanitary pads, with a preference for discreet access such as vending machines.
- Functional, gender-segregated toilets with running water, soap, privacy, and regular maintenance.
- Disabled-friendly sanitation facilities, ensuring inclusivity for all students.
- Safe and hygienic disposal systems, including covered bins and environmentally compliant solutions.
- Creation of a Menstrual Hygiene Management (MHM) Corner stocked with emergency supplies such as spare uniforms, innerwear, and hygiene kits.
The Court made it clear that absence of these facilities amounts to denial of constitutional rights.
-
Cultural & Educational Shift: The Ecosystem Solution
Perhaps the most progressive aspect of the ruling is its insistence that menstrual health is not a “girls-only issue.”
Schools are now expected to:
- Sensitise boys about menstruation as a normal biological process, removing shame, jokes, and harassment from school spaces.
- Train male teachers and staff to respond empathetically to menstruation-related needs, without interrogation or embarrassment.
- Integrate age-appropriate, gender-responsive content on menstruation and puberty into health and wellness curricula, in line with NCERT/SCERT guidance.
- Foster a school culture where menstruation is discussed openly, respectfully, and without euphemism.
The message is unambiguous: pads without dignity do not equal access.
A Clear Warning to Private Schools
The Supreme Court issued a firm caution to private institutions:
non-compliance can lead to de-recognition.
By linking menstrual hygiene directly to the Right to Education, the Court has placed accountability squarely on school managements. Compliance is no longer a matter of reputation—it is a legal obligation.
Why This Judgment Matters
This ruling represents a rare moment where law, education, health, and gender equity intersect meaningfully.
It acknowledges that:
- Equality in education requires both facilities and acceptance
- Silence around menstruation is itself a form of discrimination
- Boys and men must be part of the solution—not bystanders
For school leaders, this is an opportunity to lead with empathy, foresight, and constitutional responsibility.
The Bottom Line
The Supreme Court has drawn a clear line:
menstrual dignity is a right, not a favour.
Schools that act decisively now will not only meet compliance requirements but will also create environments where every student feels safe, supported, and respected—every day of the month.
Education
Beyond the First Bell: 5 Key Takeaways for School Leaders from Economic Survey 2025–26
The Economic Survey 2025–26 signals a definitive pivot in India’s education strategy. While infrastructure goals have largely been met, the focus now shifts to bridging the higher secondary gap and fixing a vocational training deficit that remains under 1%. For school leaders, success is no longer measured by enrolment, but by measurable competencies, digital wellness, and global readiness.

The Economic Survey 2025–26, tabled in Parliament on January 29, 2026, presents an arresting paradox. India has successfully built one of the world’s largest schooling systems—educating 24.69 crore students—yet only six out of ten learners complete higher secondary education.
For school leaders, the Survey’s message is unambiguous: the national focus is shifting from inputs (getting children into school) to impact (ensuring they learn, progress, and stay). What follows are five findings that matter most inside the school gate.
1. The “Leaky Bucket”: Transitioning from Middle to Secondary
While primary enrolment is near-universal (90.9%), the Survey identifies a structural drop-off after Class 8.
Reality check: The Net Enrolment Rate (NER) at the secondary level stands at just 52.2%.
The rural gap: Only 17.1% of rural schools offer secondary education, compared to 38.1% in urban areas. Longer travel distances and higher costs lead to significant transition losses.
What this means for schools:
- The Survey strongly backs Composite Schools (K–12 models) to reduce dropout risk.
- Schools serving Classes 6–10 should prioritise transition counselling, parent engagement, and academic bridging.
Leader takeaway: Retention, not recruitment, is now the real leadership challenge.
2. Learning Outcomes: The PARAKH Recovery Story
Post-pandemic recovery is visible, particularly in foundational years—but learning quality remains uneven across states and school types.
Encouraging gains:
- Grade III Mathematics proficiency has risen to 65%, up from 42% in 2021.
What’s next:
- The Survey proposes a PISA-like, competency-based assessment at the end of Class 10, signalling a decisive move away from rote learning.
What this means for schools:
- Internal assessments will increasingly need to mirror National Achievement Survey (NAS) benchmarks.
- Performance-linked accountability is no longer hypothetical—it is imminent.
Leader takeaway: Assessment literacy will become as important as curriculum delivery.
3. The Skilling Crisis: Addressing the 1%
Perhaps the most candid section of the Survey exposes a stark education–employment mismatch.
The 1% problem: Only 0.97% of students aged 14–18 have received formal institutional skilling.
Structural issue: Education and skilling continue to operate in parallel silos, leaving most learners academically qualified but workplace-unready.
What this means for schools:
- Vocational exposure must be embedded within Classes 9–12, not offered as an optional or external add-on.
- Partnerships with local industry, NSDC-aligned providers, and apprenticeship platforms will become critical.
Leader takeaway: Schools that integrate skills early will future-proof their students—and their relevance.
4. Digital Exposure: Pedagogy vs. Addiction
In a significant first, the Economic Survey flags digital addiction as a threat to student wellbeing, learning focus, and social capital.
The paradox:
- 89% of rural youth now have access to smartphones.
- 75% use them primarily for social media, contributing to sleep deprivation, reduced attention spans, and anxiety.
What this means for schools:
- The Survey recommends introducing a Digital Wellness Curriculum, covering:
- Screen-time literacy
- Cyber safety
- Responsible AI and social media use
Leader takeaway: Digital fluency must now include digital restraint.
5. Global Ambitions: Stemming the Student Exodus
India is on track to become the world’s largest source of international students, with outbound numbers expected to reach 18 lakhs by 2025. Yet, international students form just 0.10% of domestic enrolment.
The strategy:
- The Survey promotes “Internationalisation at Home”—inviting foreign campuses, enabling joint degrees, and ensuring mutual recognition of qualifications.
Key enablers already in place:
- Academic Bank of Credit (ABC)
- APAAR IDs (with 2.2 crore already issued)
What this means for schools:
- Senior secondary students should be actively guided on credit portability, interdisciplinary choices, and global pathways.
Leader takeaway: Global readiness is no longer optional—it is systemic.
The Bigger Shift: Learning Over Schooling
The Economic Survey 2025–26 makes one thing clear: India’s education mission has entered its second phase. Infrastructure and access have largely been achieved. The next frontier is retention, relevance, and real learning.
For school leaders, success will no longer be measured by enrolment numbers alone, but by:
- Meaningful learning outcomes
- Student wellbeing and digital balance
- Employability and global mobility
The bell has rung. What happens after it now matters more than ever.
News
Inclusive Education Summit 2026: Designing the Future of “Learner-Centric” Education
The Inclusive Education Summit 2026 gained significant momentum on Day 2, moving from policy vision to practical implementation. Focused on “Inclusive Education Pathways,” the session highlighted the transformative PRASHAST 2.0 digital screening tool and groundbreaking state models from Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal. Industry experts from NCERT, NIOS, and UNICEF emphasized a critical shift from mere “classroom access” to “academic achievement” through Universal Design for Learning (UDL). By integrating assistive technology, specialized teacher training, and inclusive sports, the summit is redefining how India supports Children with Special Needs, ensuring that every learner has a personalized path to success.
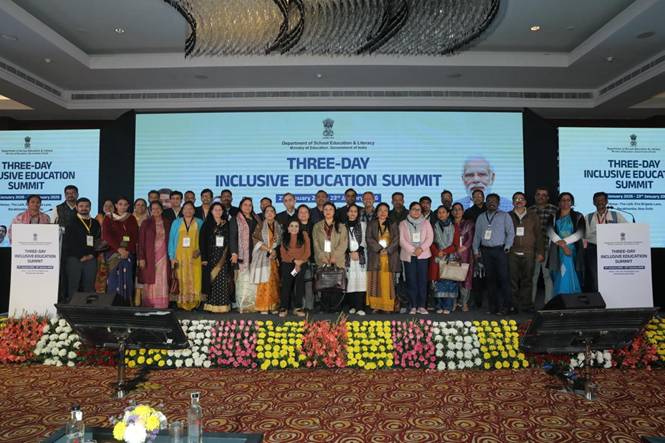

New Delhi | January 22, 2026 – As the three-day Inclusive Education Summit 2026 enters its second day, the conversation has shifted from policy theory to tangible pathways. Organised by the Ministry of Education (DoSEL) at The Lalit, New Delhi, the summit is setting a high bar for how India intends to align with NEP 2020 and the RPwD Act 2016.
While Day 1 set the stage, Day 2 focused on the “how”—the digital tools, pedagogical shifts, and inter-sectoral collaborations required to ensure no child is left behind.

1. Digital Transformation: PRASHAST 2.0 Takes Center Stage
The most significant tech highlight was the unveiling and live demonstration of PRASHAST 2.0. Introduced by Ms. Ira Singhal (Deputy Secretary, DoSEL), this revamped disability screening tool is designed to move the needle on early identification.
-
Integrated Ecosystem: The tool now integrates directly with UDISE+, allowing for real-time tracking and data-driven interventions.
-
The Goal: Moving away from guesswork toward evidence-based planning at the school level.
2. Scalable Success: Lessons from the States
The summit showcased that inclusion isn’t just a national mandate; it’s a local reality. Two states shared blueprints that other school leaders can learn from:
-
Andhra Pradesh: Highlighted the transformative impact of their 125 Autism Support Centres.
-
West Bengal: Showcased a model of strengthening resource rooms to provide child-centric interventions immediately after identification.
3. Reimagining Pedagogy and Teacher Training
A recurring theme throughout the day was that “access” to a classroom is not the same as “achievement” in learning.
-
NCERT’s New Framework: Dr. Sharad Sinha presented an 8-module framework designed to mainstream inclusive pedagogy. The focus is on training teachers to manage diverse classrooms as the norm, not the exception.
-
NCTE & NIOS: Discussions led by Prof. Pankaj Arora (NCTE) and Prof. Akhilesh Mishra (NIOS) highlighted the shift toward flexible admission systems, accessible e-content, and a national mentoring mission to support inclusive practices in everyday schooling.
4. Beyond the Classroom: Sports and Language
Inclusion was also discussed through the lens of holistic development:
-
Inclusive Sports: Representatives from Special Olympics Bharat and the Indian Blind Sports Association emphasized that sports are a primary vehicle for building confidence and independence in children with intellectual and visual impairments.
-
The Power of Words: Ms. Amita Tandon (UNICEF) reminded delegates that disability-inclusive language is the first step in reducing stigma.
Innovator’s Spotlight: Prof. Bharti Kaushik (CIET, NCERT) showcased the “Kitaab Ek, Padhe Anek” project. Based on Universal Design for Learning (UDL), this initiative allows a single textbook to offer multiple accessible pathways, proving that “one size fits all” is a thing of the past.

Key Takeaways for School Leaders
As the summit concludes its second day, the message to the Indian education fraternity is clear:
-
Screen Early: Use tools like PRASHAST 2.0.
-
Train Often: Move toward inclusive pedagogy, not just special education.
-
Build Infrastructure: Invest in resource rooms and UDL-compliant materials.
Education
AI to Become a Core Subject from Class 3: India’s Big Leap Toward a Future-Ready Generation
In a landmark move to make India’s school system future-ready, the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSE&L), Ministry of Education, has announced that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computational Thinking (CT) will be introduced as part of the school curriculum from Class 3 onwards, beginning in the academic year 2026–27.
The initiative marks a major step in preparing students for an AI-driven world, ensuring early exposure to technological literacy, ethics, and problem-solving. The curriculum, currently being developed through a consultative process with CBSE, NCERT, KVS, NVS, and States/UTs, will fall under the National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) 2023, in alignment with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
A stakeholder consultation held on 29th October 2025 brought together education leaders, including Prof. Karthik Raman from IIT Madras, who heads the CBSE expert committee responsible for shaping the AI & CT curriculum. The focus is on designing a meaningful, inclusive framework that integrates AI not as an advanced elective but as a foundational skill — comparable to literacy and numeracy in importance.
Shri Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, DoSE&L, emphasised that AI education should be viewed as a universal skill closely linked to real-world applications. “Every child’s distinct potential is our priority. Policymakers must define minimum thresholds and evolve them with changing needs,” he said. He also stressed on teacher training as the backbone of successful implementation, with modules under NISHTHA, and resource materials being prepared by NCERT and CBSE.
The Ministry plans to release AI handbooks and digital resources by December 2025, followed by a grade-specific rollout supported by video-based learning materials and structured training.
By embedding AI education from the foundational years, India aims to nurture a generation that understands, creates, and applies technology ethically — transforming the vision of AI for Public Good into everyday classroom reality.
Education
Dharav Utsav to Celebrate Rajasthan’s Cultural Heritage and Local Talent

Education
Beyond the Syllabus: School Teachers’ Insights on Project-Based Learning

How classroom experiences are being reshaped through projects, inquiry, and authentic learning
As the classroom grows beyond the boundaries of textbooks and blackboards, so too does the role of the teacher, and the very meaning of learning. Project-Based Learning (PBL), once considered a niche innovation, is increasingly being embraced by educators across schools in India. But what happens when PBL moves from theory to practice?
To answer this, we turned to the people at the heart of the learning experience: teachers.
In conversations with educators from diverse school contexts, one theme was clear: PBL is not just a teaching strategy; it’s a transformation in how students learn, engage, and grow.
From Worksheets to Real-World Work: How PBL Differs from Traditional Homework
One of the clearest contrasts teachers observed was how PBL moves learning from repetition to relevance. Traditional homework often reinforces information through rote exercises. PBL, by contrast, asks students to apply their knowledge to solve problems, create products, or investigate issues that matter to them.
One teacher shared how using PBL to raise student awareness about water pollution was a hit in the class. Instead of just assigning problems, the students were made to create awareness posters, conduct surveys in their neighbourhood, and suggest solutions through group presentations. The teacher also noted how the students took the lead, and had an ownership over this project that they usually don’t showcase.
The shift from repetition to application fosters deeper engagement. Several teachers noted that students who previously struggled to stay motivated with homework showed renewed interest when asked to take on real-world challenges.
Changing Roles: Teachers as Facilitators, Not Just Instructors
Project-Based Learning also changes the role of the teacher, who went from being the sole source of knowledge to a guide who supports inquiry and exploration.
One common change teachers noticed was on how they had to let go of control in the classroom. Naturally, the students now had to work on projects on their own, and could only come to the teacher for guidance and help. The teachers noted that they helped their students ask the right questions, find credible sources, and evaluate their work, instead of completely placing the burden of learning on the teacher themselves.
This change isn’t always easy. It requires a shift in mindset and in many cases, rethinking how time is used in class. But most teachers agree: the shift is worth it. PBL has encouraged interdisciplinary approaches, made space for collaborative learning, and created more meaningful student-teacher interactions.
Unlocking Student Potential: What PBL Offers Beyond Academics
Academic performance remains important, but a lot of teachers repeatedly pointed out that PBL nurtures a broader set of skills, like critical thinking, collaboration, communication, and creativity. One teacher particularly noted on how their quietest students became ‘leaders’, and became outspoken when it came to presenting their ideas and projects. While not directly, PBL helped these students find their voices, and find confidence in their effort and abilities.
Students learn to manage time, negotiate roles, and solve problems, skills that aren’t always reflected in exam scores but are vital for life beyond school. For many teachers, the most rewarding aspect of PBL was watching students take initiative, work through failure, and reflect on their learning.
Widening the Circle: Strategies for Scaling PBL in More Classrooms
While the benefits are clear, teachers acknowledged that implementing PBL at a large scale comes with challenges, like limited time, rigid curriculum structures, and unfamiliarity among teachers.
They offered a few practical suggestions for schools and educators considering wider adoption:
- Start Small and Build Confidence: Starting with short projects aligned to the unit you are already teaching introduces PBL in an easy manner. This way, teachers do not have to worry about overhauling their curriculum, or for making huge changes to their current teaching methods.
- Encourage Collaboration Among Teachers: Joint planning across subjects makes projects richer and more integrated. This also promotes interdisciplinary skills among students, and allows them to craft solutions using different subjects and skillsets.
- Make Time for Reflection: Embedding opportunities for students to present, critique, and reflect helps solidify learning. By reflecting on their projects and mistakes, they can understand how they can improve their approach to PBL.
- Support Professional Development: Teachers emphasized the need for ongoing training, not just one-off workshops but long-term spaces for peer sharing and mentorship. This continuous development would cement and solidify the methods and outcomes that will maximise using PBL for student benefits
Looking Ahead: Redefining Success in Education
PBL challenges traditional ideas of what learning looks like. It pushes students to move beyond memorization, and it challenges teachers to rethink their methods. But more than anything, it opens up the classroom to ideas, to communities, and to possibilities. No longer are students just preparing for exams, but also for the complex world outside school.
As educators continue to navigate the changing landscape of education, the insights from teachers point us toward a hopeful future, where learning is meaningful, relevant, and rooted in real-world experience.
This article is authored by Mrs. Padmashini M Patro, Principal, Air Force School Bamrauli
Education
Over 1 Lakh Single-Teacher Schools Educate 33 Lakh Students Across India: MoE Data
Education
Over 3 Lakh Schools Join Hands for India’s Largest-Ever Innovation Challenge: Viksit Bharat Buildathon 2025

In a historic moment for Indian education, more than 3 lakh schools across the country came together to participate in the Viksit Bharat Buildathon (VBB) 2025, the largest live school innovation challenge ever organised in India. The nationwide event was inaugurated in New Delhi by Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, marking a significant milestone in the Government’s efforts to embed creativity, innovation, and problem-solving into the school ecosystem.
The Viksit Bharat Buildathon, organised by the Department of School Education & Literacy (DoSEL) in collaboration with Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), NITI Aayog, and AICTE, saw over one crore students from Classes 6 to 12 working simultaneously during a 120-minute live innovation session. Students teamed up in groups of three to five to design prototypes and propose solutions under four themes — Atmanirbhar Bharat, Swadeshi, Vocal for Local, and Samriddhi.
While inaugurating the event, Minister Pradhan interacted virtually with students of PM SHRI Government High School, Khorda, Odisha, and later visited Delhi Public School, Mathura Road, and Kendriya Vidyalaya No. 2, Delhi Cantt. Commending students for their creativity, he said, “The vision of Viksit Bharat will be realised through the innovative spirit of our young learners. These ideas will not only address domestic challenges but also create global models for change.”
The event drew widespread participation, with Uttar Pradesh leading the numbers (78,206 schools), followed by Maharashtra (41,198), Gujarat (20,017), and Madhya Pradesh (18,129). Other states like Tamil Nadu (16,370), Bihar (15,732), Odisha (12,344), and Haryana (11,567) also recorded impressive engagement, showing the growing momentum for grassroots innovation across regions. Even smaller territories like Ladakh (358), Puducherry (149), and Andaman & Nicobar Islands (171) participated actively, reflecting the nationwide reach of the initiative.
According to Sanjay Kumar, Secretary, DoSEL, this unprecedented participation signals a transformation in how Indian students approach learning. “This one-of-a-kind movement strengthens innovative thinking and enhances the problem-solving capabilities of students across India,” he said. Deepak Bagla, Mission Director of AIM, called the initiative a “mass movement connecting schools in remote villages with those in metropolitan cities through innovation.”
A New Chapter for Indian Education
The Viksit Bharat Buildathon signifies more than just a hackathon — it reflects a systemic shift in Indian education towards experiential and innovation-led learning. As schools across the country engage in design thinking, tinkering, and collaboration, students are being equipped not just with knowledge, but with the mindset and skills needed to build a self-reliant India.
By nurturing creativity from an early age and fostering partnerships between schools, government bodies, and industry, the Buildathon is shaping a generation ready to contribute to the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047 — a developed, empowered, and innovation-driven India.
Education
17-year-old Innovator Designs Learning Tools for the Visually Impaired

At just 17, Singapore-based student Ameya Meattle is proving that age is no barrier to impact. What began as a small idea to make education more accessible has evolved into a mission that is transforming how visually impaired learners experience learning and skill development.
Ameya founded Earth First at the age of 14 — a social enterprise that helps visually impaired individuals “earn and learn” by creating sustainable, eco-friendly products. Working with eight NGOs across India and Singapore, the initiative has trained more than 100 visually impaired students and launched over 23 sustainable product lines, from tote bags and jute placemats to macramé planters. Each design is adapted to provide hands-on learning opportunities and help trainees gain confidence in both craft and enterprise.
Beyond social entrepreneurship, Ameya has focused deeply on education and technology. He led a Python programming course for 50 visually impaired students, designing custom training modules that made coding accessible through screen readers and tactile tools. By introducing technology as a viable career pathway, Ameya hopes to help students move from manual tasks to high-skill, digital opportunities.
His work also extends into assistive technology research. Under the mentorship of Dr. Pawan Sinha at MIT, Ameya developed a VR-based diagnostic game to assess visual acuity in children — turning the process into an interactive experience rather than a clinical test. The tool is being piloted at MIT’s Sinha Lab and with Project Prakash in India, helping doctors evaluate and track visual development before and after eye surgeries.
In addition, during his internship at the Assistech Lab at IIT Delhi, Ameya worked on designing tactile STEM teaching aids, such as accessible periodic tables and coding tutorials for visually impaired learners. His goal, he says, is not just to innovate but to make scientific learning inclusive and joyful for all.
Ameya’s work highlights how education, empathy, and innovation can intersect to create a more equitable future — one where technology serves not just progress, but people.
Education
Ministry of Education Urges Schools to Adopt UPI for Digital Fee Payments, Promoting Ease of Schooling

-

 Inspiration3 months ago
Inspiration3 months agoUmeed: A Ray of Hope for Better Tomorrow
-

 Knowledge2 months ago
Knowledge2 months agoBuilding a Healthier India: Why School Health Programs Are Essential
-

 Inspiration2 months ago
Inspiration2 months agoBefore the Nobel, There Was a Teacher
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoWhat the Indian Army Teaches Our Children Beyond Textbooks
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoInclusive Education Summit 2026: Designing the Future of “Learner-Centric” Education
-

 Education1 month ago
Education1 month agoBeyond the First Bell: 5 Key Takeaways for School Leaders from Economic Survey 2025–26
-

 Education1 month ago
Education1 month agoSupreme Court’s Landmark Judgment for Schools: Menstrual Health is a Fundamental Right
-

 Education2 weeks ago
Education2 weeks agoTapas Project Shaala 2026 to Spark National Dialogue on Autonomy, Curiosity and Community in Education
-

 Education3 weeks ago
Education3 weeks agoJudicial Guardrails: How the J&K High Court’s Fee Regulation Verdict Redraws the Rules for Private Schools
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoDaring to Dream: Six Years in the Heart of Rural Rajasthan