News
Public education in India has to jump many hoops
Successive governments have taken out the constitutional obligation towards education out of the educational policies. This takes out the fundamental right of universal education out of the equation thus giving rise to inequalities in the system.

That the New Education Policy has created waves much before it has officially become a policy is amply clear by the media coverage that it has generated, some for the big strides it aims to take while some negative coverage for the way the policy is being handled. The latest is the war of words between Human Resource Development Minister Smriti Irani and former Cabinet Secretary T.S.R. Subramanian over the report of the New Education Policy (NEP) committee headed by him. While Subramanian is threatening to make his report public; Smriti Irani counters by saying that this can only be considered after the States have sent in their responses to it. In fact, this tug of war is symptomatic of the manner in which the entire exercise of drafting the NEP has been carried out.
Smriti Irani claimed that the Narendra Modi government’s NEP was going to be the result of a collective effort of more than 2.6 lakh consultations around 13 themes earmarked for school education at gram panchayat, block, district, State, groups of States and national levels. These consultations took place through a list of questions supplied by the HRD Ministry to elicit recommendations which would serve as inputs for each of the themes for the Draft NEP document.
Now, the questionnaire couldn’t have been drafted by experts, which explains the surprising composition of the committee itself. Headed by a former Cabinet Secretary, it includes 3 retired government Secretaries and a former Director of the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), J.S. Rajput, whose credentials are questionable since his participation in the “saffronisation” of textbooks during Murli Manohar Joshi’s tenure as HRD Minister in the previous National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government.
Available information, most of which is hearsay as the Ministry has refused to divulge any details, point out that no such scheduled meetings took place. Even if higher level meets did happen, they were orchestrated to legitimatise claims that recommendations represented “the voice of the people”, and that officials and education officers dominated proceedings at meetings where school principals, teachers, government invitees and some school management committee members were herded together. In this scenario, it is not surprising that the HRD Ministry has failed to make the content of the “people’s” recommendations publicly available. A similar lack of transparency shrouds the national and regional debates held by the University Grants Commission (UGC), the National University of Educational Planning and Administration (NUEPA), the NCERT and other national-level institutions.
This methodology shrouded in secrecy by the HRD Ministry is disturbing and problematic. Take for example the total lack of analysis of previous policies and no overview of the consequences of implementing the changes introduced by the National Policy on Education (NPE) 1986, its companion Programme of Action, and their modified versions (1992). Before the NPE, democratic goals and the guiding principles of equality and social justice articulated during the freedom struggle informed policies, although it soon became evident that successive governments failed to meet their constitutional obligations. It is no coincidence that the changes introduced by the NPE coincided with the adoption of the economic reforms programme by the Narasimha Rao government in 1991.
Since the NPE was in line with the economic reforms, it focussed on supplying the economy with employable human capital. It was through implementation of a series of missions and abhiyans to impart market-oriented “skills”, the lowest one being “functional literacy”. It needed a conceptual and curricular delinking of cognitive and aesthetic aptitudes from acquisition of the practical skills which were deemed sufficient for making the mass of citizens employable.
Completely violating the constitutional obligation to ensure universal free and compulsory education of comparable quality, the NPE introduced a policy provision for low-cost, poor quality, non-formal education (NFE) which was to be treated as “equivalent to schooling” for those children who could not “be expected to attend a full day at school”. This excluded a vast majority of children in the relevant age group from the formal system of education. With one swift stroke the NPE discriminated a large swath of students under the guise of providing employable capital.
However, NFE only prepared the ground for a policy of multitrack, discriminatory streams of education. Matters were to become far worse, as under pressure from the World Bank, the 1994 District Primary Education Programme (DPEP) introduced “low-cost” infrastructural and recruitment practices into the government school system across the country. The concept of para-teachers and contract teachers were introduced to cut costs. After the Fifth Pay Commission (1996), recruitment of permanent trained teachers was badly affected in most States. Yet, trained teachers were required to be available for official duty during Census, elections, health campaigns such as polio eradication, and now even “disaster management”. In came the Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) for improving quality and all these things resulted in driving the entire system to the brink of collapse.

Limitations of the RTE
While we read glorifying tales of the impact of RTE in the media how it is empowering the under-privileged to get their space under the education sun, the truth is that RTE has a horrible underbelly. RTE became the legal form of discrimination at every level. It excluded pre-school Early Childhood Care and Education for 0-5-year-olds. It excluded secondary education for 15-18-year-olds. It excluded the “special” government schools which were proof that governments could run schools when they were required to. But like already pointed out it provided us a peep into the future. The much-lauded and equally utilised 25% admission for children from the Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) had a salutary effect by starting a public private partnership (PPP) model which today allows transfer of crores of rupees of public funds to high-fee charging and low-budget private schools alike.
The truth is that across the political spectrum this policy perspective has either been actively contributed to—if the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) governments brought in the NPE and the RTE, the NDA brought the 86th Amendment Bill which defined the limits of the RTE and the concept of knowledge as a “tradeable commodity”, and education as a “tradeable service”—or been accepted as the model of development by all governments in power. The Modi government’s Skill Development campaign not only rests on the foundation of the NPE 1986, but also requires the changes proposed to child labour laws allowing children less than 14 years of age to participate in hereditary trades.
Quick-fix solutions
Coming back to the approach used by the HRD Ministry. It is fundamentally flawed as even after “widespread” consultation has taken place, there is no vision, principle or logic on which one set of suggestions should have precedence over other alternatives. No strategy either underlies or could be formulated out this wasteful exercise, which flies in the face of government claims that there are no funds for education and has resulted in savage cuts made in budgetary allocations over the past 2 years.
However, miraculously this does not mean that an agenda is not being advanced. If on one hand, there is no vision for reviving the stagnant public education system, on the other hand, it has to be admitted that government “policy” is herding parents to the gates of commercialised private institutes. The NGO Pratham’s Annual Status of Education Report (ASER 2012) showed that in just 2 years after the implementation of the RTE Act, there was a 5.8% increase, up from 29.8% in 2010-11, in private school enrolment for primary (Classes I–V) students.
In State after State, governments are compelled to close or merge schools because students are deserting them. Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, and even Himachal Pradesh and Kerala, once stellar examples of the success stories of the public education system, have stated that the policy is inevitable. Thousands of teachers are becoming redundant by the process of “rationalisation” because it saves public funds on paying their salaries. Holding on by a hairs length, people’s organisations in some States have been able to push back this dismantling of the state-funded and maintained school system for one more year.
Stark inequalities
Clearly, India’s education system is reproducing social inequalities and not removing them. Earlier the lack of political will to address caste, class and gender failed to universalise education, and today discriminatory policies are reinforcing inequality. Illiterate children are not a result of poverty but due to negative attitudes and misplaced priorities of policy (ASER 2015). Segregating the poor and the disadvantaged and educating them in institutions catering exclusively only to them will deny the fundamental right to education to a majority of children even as privilege masquerades as merit.
Regarding the medium of instruction, contrary to all egalitarian preferences for the mother tongue as the language of learning, fluency in English is driving even poor families to take on the crushing fee-burden of private “English medium” schools and is generating the self-defeating demand that government schools should shift from the vernacular to the English medium.
In this darkening scenario, a ray of light has been the recent landmark judgment of the Allahabad High Court (August 18, 2015) which emphasised the democratic and educational importance of shared schooling for children from all sections “. . . in changing society from grass-root level. The initial level mixing among all children will have different consequences.” It went on to say that the division of schools into “elite”, “semi-elite” and “common man’s schools” based on privilege and wealth have neither an educational basis nor social value in a democratic society.
“After more than 65 years of independence, these (common men’s) schools are still struggling to have basic amenities for children…. It is not difficult to understand why conditions of these schools have not improved. The reason is quite obvious and simple…. There is no real involvement of administration with these schools. Any person who has some capacity and adequate finances sends his child/children to elite and semi-elite primary schools. They do not even think of sending their wards for primary education to… third category schools, i.e. common men’s schools. The public administration therefore has no actual indulgence to see functioning and requirements of these schools.”
This enforced integration ordered by the court cannot be deemed a denial of “democratic choice” for the affluent elites because the judgment holds choice itself as the reason for the vast majority of India’s children being denied their fundamental right to education. The State government was thus directed to ensure that “the children/wards of government servants, semi-government servants, local bodies, representatives of people, judiciary and all such persons who receive any perk, benefit or salary, etc. from State exchequer or public fund, send their child/children/wards who are in age of receiving primary education, to primary schools run by Board… and ensure to make penal provisions for those who violate this condition”.
A resounding nod to the common school system
The judgment’s resounding endorsement of the Common School System in modern democratic societies is grounded in historical fact. No system of quality education has ever been universalised without the participation of the state. The judgment should not only be implemented forthwith in Uttar Pradesh. It should be extended to cover all States of India.
The other beacon of hope is the sustained struggle of students from numerous institutes of higher education to defend the democratic right to both knowledge and dissent.
So can we expect a radical change from the HRD Ministry? The “special touch” which the present regime has brought to the education system has more to do with bringing the system firmly under the official control of the Center with centrally sponsored Teachers’ Day events, Swachch Bharat campaigns, Sanskrit Week, compulsory sessions of the Prime Minister’s radio speeches, yoga days, and even decisions on which festivals children will be allowed to celebrate with their families.
In an underhanded style of working, historical and sociological facts are distorted to facilitate indoctrination through textbooks. Finally, Rashtriya Swayamsewak Sangh’s (RSS) student wing, the Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad (ABVP) being used to declare radical Ambedkarite, Marxist and even independent-minded university students and teachers as extremists and anti-nationals, initiating disciplinary action and even slapping charges of sedition against them are an undisguised threat to the future of the country’s educational institutions.
Clearly, the HRD Ministry has learnt nothing from its misadventures, and education and educational institutions will continue to be in turmoil.
This post is based on an article originally published here
Education
CBSE Requests Affiliated Schools to Host NIOS Public Exams in October–November 2025

The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has called on its affiliated schools to assist with the conduct of the National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) public examinations scheduled for October–November 2025.
In a recent official communication addressed to principals and heads of schools, CBSE emphasised that NIOS requires infrastructural and logistical support to conduct its biannual board examinations, which include assessments for Class 10, Class 12, and various vocational courses.
“The next Public Examinations of NIOS are scheduled to be held in October–November 2025,” the notice stated, adding that CBSE-affiliated institutions have historically played a key role in enabling NIOS to run its exams smoothly.
Schools willing to extend support have been asked to register their intent on the official NIOS website at https://exams.nios.ac.in under the section: Examination Centre > Register Now.
NIOS operates under the Ministry of Education and is the country’s largest open schooling body. It caters to learners from diverse backgrounds, offering flexibility in learning and examination schedules, especially for students who may be outside the traditional school system.
“Your assistance will help NIOS in holding Public Examinations of its learners,” the CBSE notice concluded, underlining the collaborative nature of this effort.
By participating in this initiative, CBSE schools are not only supporting a national mandate for inclusive education but also contributing to educational equity by helping millions of NIOS learners access fair and organised exam environments.
Education
No More Backbenchers: How a Simple Seating Shift Is Reimagining Learning

When was the last time you thought about where your students sit? If you think a seat is just a seat — think again.
A simple shift in seating arrangements, sparked by the Malayalam film Sthanarthi Sreekuttan, is inspiring schools in Kerala to break the age-old divide of “frontbenchers” and “backbenchers”. The Times of India recently reported how some schools have begun rethinking how rows of benches shape mindsets — often turning bright learners into passive listeners by default.
Preethi Vickram, Founder of Tapas Progressive Learning, applauded this unique approach online:
The truth is, classroom seating is more than furniture. It’s a mirror of our teaching philosophies. For decades, rigid rows have told students to sit down, face forward, and stay quiet while the teacher talks. One person speaks, everyone else absorbs. But learning doesn’t work in a straight line — it happens in loops, debates, disagreements, and those random questions that make everyone think.
It’s not just an emotional idea — there’s solid science behind it. A 2020 review in Frontiers in Psychology found that classroom layouts directly affect interaction and motivation. The Classroom Direct blog points out that flexible layouts foster collaboration, peer learning, and inclusivity. And a 2022 ESI Conference study noted that traditional seating can create power hierarchies where only frontbenchers thrive.
In India, we know this divide well. Backbenchers are often seen as mischievous or disinterested — but what if they were simply disengaged by design? Many schools still enforce outdated seating rules: girls must sit separately from boys; ‘weak’ students banished to the back; bright ones pushed to the front like prized trophies. But what are we telling children when we make them sit apart based on gender, marks or silence? That some voices matter more than others.
Architects and education designers have long championed a different approach. Rosan Bosch’s designs for Sweden’s Vittra School are modular and playful, showing that space itself can be a teacher. Danish Kurani, an expert in reimagining learning spaces, writes that the biggest mistake schools make is assuming they can modernise teaching methods without changing the physical space: “You can’t have collaborative, project-based learning in a classroom still set up for rows of passive listening.”
Kerala’s small but significant shift is a reminder that big change often starts with small, visible actions. When students sit in circles, clusters, or flexible pods, they are more likely to speak up, listen actively, and learn from one another. It helps break the silent stigma that ‘the back’ means you don’t matter.
Designers like Kurani argue that students should have a voice in how their classrooms look and feel — because when the space reflects curiosity and movement, it encourages the same in young minds. The Studio Schools Trust in the UK, the Reggio Emilia approach in Italy, and Big Picture Learning schools in the US all prove that flexible, student-centred learning environments are not “alternative” anymore — they’re the future.
And this shift doesn’t need fancy gadgets or big budgets. It’s the lowest-cost ‘edtech’ upgrade schools can make: moving a few benches, opening up a circle, creating nooks for quiet work and spaces for loud debate. It tells children: “Your voice matters, wherever you sit.”
In a world that needs more curiosity, connection, and creativity — we cannot afford to let seating stifle learning.
So let’s not just remove the backbenchers — let’s remove the very idea of front and back.
Because when every child feels seen and heard, there are no bad seats in the house.
References: * Classroom Direct Blog, 2021 * Frontiers in Psychology, 2020 * ESI Conference Proceedings, 2022 * Danish Kurani on Common Classroom Design Mistakes
Education
NEP 2020’s Panch Sankalpa to Guide Central Universities: Dharmendra Pradhan

More than 50 Vice Chancellors of India’s central universities gathered in Kevadia, Gujarat for a two-day conference to assess the implementation of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and lay the groundwork for the coming years. Organised by the Ministry of Education in collaboration with the Central University of Gujarat, the conference seeks to align higher education institutions with the broader national vision of Viksit Bharat by 2047.
Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan, addressing the gathering, outlined the Panch Sankalpa of NEP 2020—next-generation education, multidisciplinary learning, innovation, holistic development, and Bharatiya orientation—as the guiding principles for institutional transformation. He emphasised that India’s higher education ecosystem has undergone significant change over the last decade, becoming more flexible, inclusive, and innovation-driven. Student enrolment has increased by 30% since 2014–15 to reach 4.46 crore, with female enrolment growing by 38%. The gross enrolment ratio for female students now exceeds that of males, while enrolment among Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes has also improved. PhD enrolments have nearly doubled, with women registering a 136% increase.
The Minister urged Vice Chancellors to play a transformative role by redesigning curricula, improving digital infrastructure, strengthening faculty training, and promoting multidisciplinary education. He reiterated the goal of raising the gross enrolment ratio in higher education to 50% by 2035, in line with the NEP’s vision. Placing students at the centre of all reform efforts, he called on universities to foster job creators, ethical innovators, and socially responsible graduates.
Pradhan also encouraged institutions to reflect on India’s intellectual heritage while preparing for a global future, invoking the academic “Triveni Sangamam” of celebrating the past, calibrating the present, and creating the future. He recommended that each university prepare a strategy paper to fully implement NEP 2020, incorporating Indian Knowledge Systems, digital skilling initiatives, and campus-led innovations. He proposed that such review conferences be hosted at the campus level to promote decentralised engagement and exchange of ideas.
Dr. Hashmukh Adhia, Chancellor of the Central University of Gujarat, spoke about the six principles of karmayoga and the importance of Indian knowledge systems in shaping individual and collective progress. Dr. Vineet Joshi, Secretary of Higher Education, reflected on the journey since the policy’s launch and reiterated that NEP 2020 imagines universities not as degree-granting institutions, but as ecosystems of innovation, research, and holistic development. Dr. Sunil Barnwal, Additional Secretary, underlined the foundational values of access, equity, quality, affordability, and accountability, and highlighted the importance of stakeholder partnerships in driving reform.
Prof. Rama Shanker Dubey, Vice Chancellor of Central University of Gujarat, reaffirmed that all central universities are committed to advancing the vision of Viksit Bharat through concrete, on-ground measures. The conference, spread over ten thematic sessions, includes discussions on the Four-Year Undergraduate Programme, digital tools like SWAYAM and AAPAR, university governance through SAMARTH, alignment of education with the future of work, and research and innovation frameworks such as ANRF and PMRF. Other themes include equity, internationalisation, faculty development, and the integration of Indian languages and knowledge systems.
Participating universities include Jawaharlal Nehru University, University of Delhi, Tripura University, Central University of Rajasthan, Sikkim University, and many others. The outcomes of the conference are expected to help define the next phase of NEP 2020 implementation, enabling institutions to become more responsive, inclusive, and globally competitive.
Education
Less Than Half of Indian Schools Offer Skill-Based Courses for Senior Students: NCERT Survey

A recent survey conducted by NCERT’s National Assessment Centre has revealed that only 47% of schools across India currently offer any skill-based courses to students in Class 9 and above. This statistic highlights a significant gap in the availability of practical, job-ready education at the secondary level—an area that India’s New Education Policy has been aiming to strengthen.
The survey also found that student enrolment in these courses is even lower. Just 29% of students in Classes 9 and above have opted for skill-based subjects, indicating the need for better awareness, guidance, and integration of these programmes into mainstream learning.
The courses that are being offered include trending and industry-relevant subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics, Digital Marketing, and E-commerce. However, experts believe these numbers are far from adequate in a country with one of the world’s largest youth populations.
At the higher education level, there is a stronger push for integrating skills into curricula. Many skill universities now structure their programmes with a 60% to 70% skill-based component, offering students a blend of theoretical and practical knowledge designed to make them workforce-ready.
The NCERT report recommends that more schools must be brought into the fold of skill education. With the job market rapidly evolving and the demand for digital and emerging technology skills growing, strengthening school-level skill education can bridge the gap between academic learning and real-world employability.
Building robust vocational streams in schools could also help address the challenge of students dropping out after secondary education due to a lack of clear pathways into meaningful careers.
Education
UP Govt Launches Astro Labs in Government Schools to Boost Scientific Learning

Under the leadership of Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath, the state is rolling out astro labs in government schools at the block level, aiming to strengthen scientific thinking and curiosity among school children, especially in rural areas.
According to a statement issued by the government, these labs—named Amrit Kaal Learning Centres—are being developed through a public-private partnership (PPP) model and are already operational in several districts.
The initiative is designed to give students access to real-time, hands-on learning experiences using tools like Dobsonian telescopes, VR headsets, microscopes, light experiment kits, and anatomical models. These tools go beyond textbook learning, allowing students to explore astronomy, gravity, light, and the physical world through direct experimentation.
Officials say the initiative has already made significant impact. In Ballia district, for example, science labs have been established in all 17 blocks to make science more engaging and inquiry-driven.
Ballia District Magistrate Mangla Prasad Singh said the labs are aligned with the state’s broader goal of making science accessible and meaningful. “These labs are designed to foster experiential and inquiry-based learning,” he noted.
Chief Development Officer Aojaswi Raj added that each lab costs between ₹2.5 to ₹3 lakh, including both the equipment and teacher training. The inclusion of orientation sessions, video guides, and mentorship support for teachers ensures that the labs are used effectively in classrooms.
“These labs have sparked genuine curiosity among children, who now ask questions, observe the night sky, and explore concepts far beyond the standard curriculum,” said Raj.
The program is part of a larger effort to bridge the gap between urban and rural education. With access to advanced tools and teacher support, children in villages are beginning to imagine careers in space science, inspired by stories like that of Indian-origin astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla.
The UP government hopes this initiative will help build a future-ready generation, where aspiration is not defined by geography, and the boundaries of scientific exploration begin right from the classroom.
Education
Class 3 Learning Levels Show Gains Since Pandemic, But Still Below 2017: PARAKH Survey

According to the government’s latest PARAKH Rashtriya Sarvekshan report released on Monday, Class 3 students across India have yet to return to pre-COVID academic levels. The survey, conducted in December 2024, covered more than 21 lakh students from Classes 3, 6, and 9 across 74,229 schools, offering a large-scale snapshot of student learning recovery after the pandemic.
Among the three grades, Class 3 is the only one surveyed in all three rounds (2017, 2021, and 2024) — allowing for direct comparison. While there has been an uptick in scores since the 2021 assessment, they remain below the national average recorded in 2017.
In 2024, Class 3 students scored an average of 64% in language, compared to 62% in 2021 — but still lower than 66.7% in 2017. In Mathematics, the score stood at 60%, up from 57% in 2021, but below the 63% recorded in 2017.
Students were found to struggle the most in reading short stories and understanding them (60%), while performing best in everyday language usage (67%). In Maths, the lowest scores came in geometry and money concepts (50%), with the strongest performance in identifying basic shapes and number patterns (69%).
The survey’s structure is aligned with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which breaks school education into four key stages. Class 3 marks the end of the Foundational Stage, making it a crucial checkpoint for basic literacy and numeracy.
Classes 6 and 9: Scores Below 50% in Most Subjects
Students in Classes 6 and 9 showed average scores below 50% in all subjects except language, suggesting that older cohorts may be bearing the brunt of prolonged learning loss from pandemic-related school closures.
A senior official from the Ministry of Education noted that these grades missed nearly two full years of classroom instruction during a critical developmental period. Despite visible recovery since 2021, the learning gaps persist.
Why This Matters
The findings serve as a reminder of the lasting impact of the pandemic on India’s school education, especially for early learners. The report calls for targeted learning interventions, curriculum adjustments, and robust teacher support systems to help students recover foundational skills.
With only limited time before students transition into higher stages of schooling, the emphasis is now on accelerated catch-up strategies and deeper diagnostic assessments to address these persistent gaps.
Education
Punjab to Introduce Business, Marketing Education in Govt Schools for High Schoolers

The Punjab government has announced that all Class 11 and 12 students in government schools will receive skill education in business and marketing from the upcoming academic session. The initiative is being implemented under the Punjab Young Entrepreneurs Scheme.
According to Education Minister Harjot Singh Bains, the programme aims to introduce basic entrepreneurship concepts to senior secondary students. As part of this, students will be required to develop and present business ideas as subject-linked projects. The state has also invested in setting up innovation labs in schools to support product development and technical training.
The initiative was formally presented at the Business Blasters Expo 2025, where student teams from various districts showcased business models to a panel of educators, industrialists, and startup professionals. According to official information, participating teams received financial support to take their ideas forward.
Some of the student-led projects included products such as handmade goods, natural cosmetics, customised simulators, framed artwork, and cycle-based mobility solutions. In one case, a student from Mullanpur Dakha created decorative items that were later sold in the market at a significantly higher margin.
The Education Minister also cited employment data between 2014–15 and 2021–22, pointing to a gap between job applicants and job placements. The scheme, he said, is being introduced with the aim of equipping students with skills relevant to today’s economic landscape.
Initially piloted in 30 schools, the Punjab Young Entrepreneurs Scheme is now being scaled across the state. The business and marketing module is expected to cover financial literacy, product development, market analysis, and customer outreach.
The government has stated that the curriculum will align with academic requirements while also supporting practical exposure. Further partnerships with technical institutions and industry stakeholders are also being explored.
Education
Manipur Rallies Call for Disruption-Free Education Amid Ongoing Unrest
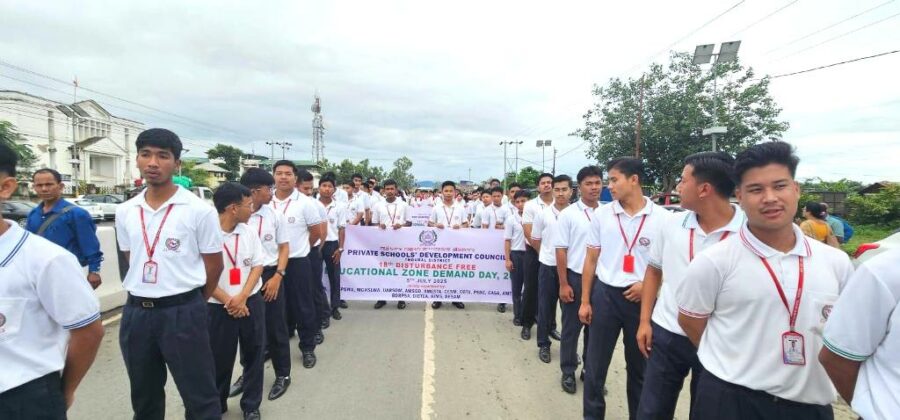

Thousands of voices echoed across the valley districts of Manipur on 5th July, as students, teachers, and civil society members marched in unison, demanding an uninterrupted and safe educational environment. Marking the 18th Disturbance-Free Education Zone Demand Day, the rallies were spearheaded by the Democratic Students’ Alliance of Manipur (DESAM), with support from over 15 civil society organisations.
Held across Imphal East, Imphal West, Kakching, Thoubal, and Bishnupur, the rallies were unified under the message: “Make Education a Disturbance Free Zone.” From THAU Ground near the Legislative Assembly to Imphal College, and similar routes in other districts, demonstrators walked with banners, placards, and resolute slogans calling for peace and protection of learning spaces.
This year’s observance comes at a particularly sensitive moment for the state, as Manipur continues to reel from over two years of ethnic conflict, political instability, and administrative disruptions. These challenges have had a disproportionate impact on the state’s education system—schools in conflict zones have been intermittently closed, exams postponed, and many children displaced from both their homes and classrooms.
Speaking to the media during the rally, DESAM President Mayengbam Somorjit urged the government to pass legislation mandating a minimum of 220 academic days per year, to ensure stability and learning continuity even during crises. He emphasized that children in Manipur must not be deprived of their right to education because of circumstances beyond their control.
Other demands included the appointment of Directors of Education from among experienced educators, and greater transparency in recruitment and promotion processes within the education department. There were also strong appeals to armed groups to abstain from placing financial or material demands on educational institutions—a practice that has led to school closures and security concerns in the past.
The rallies were largely peaceful and drew significant participation from both urban and rural communities. Protesters stressed that beyond political resolution, restoring education must become a humanitarian priority.
In the past two years, students in conflict-affected districts have faced regular school closures, sporadic internet blackouts, and mental health challenges, as families grapple with violence, displacement, and uncertainty. NGOs and local educators have warned of rising dropout rates, learning loss, and a deepening digital divide—especially in remote or vulnerable communities.
While the larger political crisis in Manipur continues to seek resolution, the message from students and educators is clear: education must be safeguarded. As one banner read during the march: “Books, not bullets. Peace, not pauses.”
Education
Tripura CM Launches School Framework, Stresses Social Work in Education

Tripura Chief Minister Dr. Manik Saha on Friday launched the ‘Tripura School Quality Assessment and Accreditation Framework (TSQAAF),’ a state-level mechanism aimed at standardising and evaluating school performance to align with national quality benchmarks.
Speaking at the launch event at Rabindra Shatabarshiki Bhavan in Agartala, Dr. Saha, who also holds the Education portfolio, emphasised that while academic knowledge is essential, it must be accompanied by values, social awareness, and holistic development.
“Textbook education can never be the standard of life,” the Chief Minister stated, adding, “Along with education, children should also be engaged in social work.”
The TSQAAF is expected to serve as an evaluative framework that not only sets indicators for school infrastructure, teaching practices, and learning outcomes but also focuses on co-curricular and value-based education. According to officials, the framework will allow schools across Tripura to be assessed, accredited, and guided for improvement on measurable parameters of quality.
Saha acknowledged that the state education department is adapting to the evolving needs of learners and aligning with national initiatives like the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. He highlighted the importance of uniformity in curriculum and assessment to ensure students across India are prepared for central-level competition.
“If there is a uniform question paper, our children can also compete centrally,” he said.
The CM also spoke about the broader responsibilities of teachers in shaping character, ethics, and social consciousness among students. He encouraged the inclusion of practical subjects that address social problems and life skills, going beyond syllabus-bound instruction.
Reaffirming the state’s commitment to education reforms, Saha said quality teachers are being recruited through the Teacher Eligibility Test (TET), and more appointments are planned to strengthen the system further.
Senior officials, including Special Secretary of the Education Department Raval Hemendra Kumar, Director of Education N C Sharma, and SBI Foundation CEO Sanjay Prakash, were present at the event. The SBI Foundation has also extended support to the state’s education initiatives.
The TSQAAF initiative marks another step in Tripura’s education reform roadmap, aimed at creating a comprehensive schooling environment that prepares students for academic success while also cultivating civic responsibility.
Education
“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space

Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla, currently stationed aboard the International Space Station (ISS), answered questions from schoolchildren during a live interaction hosted under ISRO’s Vidyarthi Samvad Program.
The session, designed to bring students closer to the realities of space science, turned into a heartwarming and humorous conversation about food, sleep, and the sheer wonder of viewing Earth from space.
When asked how astronauts sleep in zero gravity, Shukla smiled and explained: “There is no floor or ceiling in space. Some of us sleep on the wall, some on the ceiling. We have to tie ourselves down so we don’t float away while sleeping.”
The conversation became sweeter when Shukla revealed that he brought familiar Indian flavours with him into orbit. “I have carried gajar ka halwa, moong dal halwa, and mango juice with me from India,” he said, to the delight of the young audience. He clarified that the halwa was specially medicated for space missions, not made at home — a detail that sparked laughter and curiosity alike.
The astronaut also spoke about daily life aboard the ISS, including how exercise is essential to counter microgravity. “We ride bicycles here, but there are no seats. We strap ourselves in with belts,” he told the children, who were both fascinated and amused by the image.
For Shukla, however, the highlight of being in space remains the view of Earth. “That blue sphere, that light mist… seeing Earth from here is the most beautiful experience. It’s hard to describe in words.”
Addressing mental well-being, he shared how astronauts stay connected with their families. “Technology helps bridge the distance. We can talk to our loved ones, and that keeps us grounded — even when we’re not.”
Also present during the interaction was Group Captain Angad Pratap, a fellow member of the Gaganyaan mission crew, who encouraged students to consider careers in aviation and space science.
For many students, the session was a dream come true. “It felt like science fiction,” said one participant. “Now I believe I can go to space one day.”
As India continues its rapid progress in space exploration, conversations like these serve as reminders that inspiration is as critical as infrastructure — and that sometimes, a simple chat with an astronaut can launch the imagination of an entire generation.
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoBanu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature





















































































