Inspiration
Read this to know more about Prof. Sugata Mitra and his work in education
Best known for his Hole in the Wall experiment and widely cited in works on literacy and education, Prof Sugata Mitra’s belief in the power of self-organized learning to shape the future of education is immensely inspiring.
Published
7 years agoon
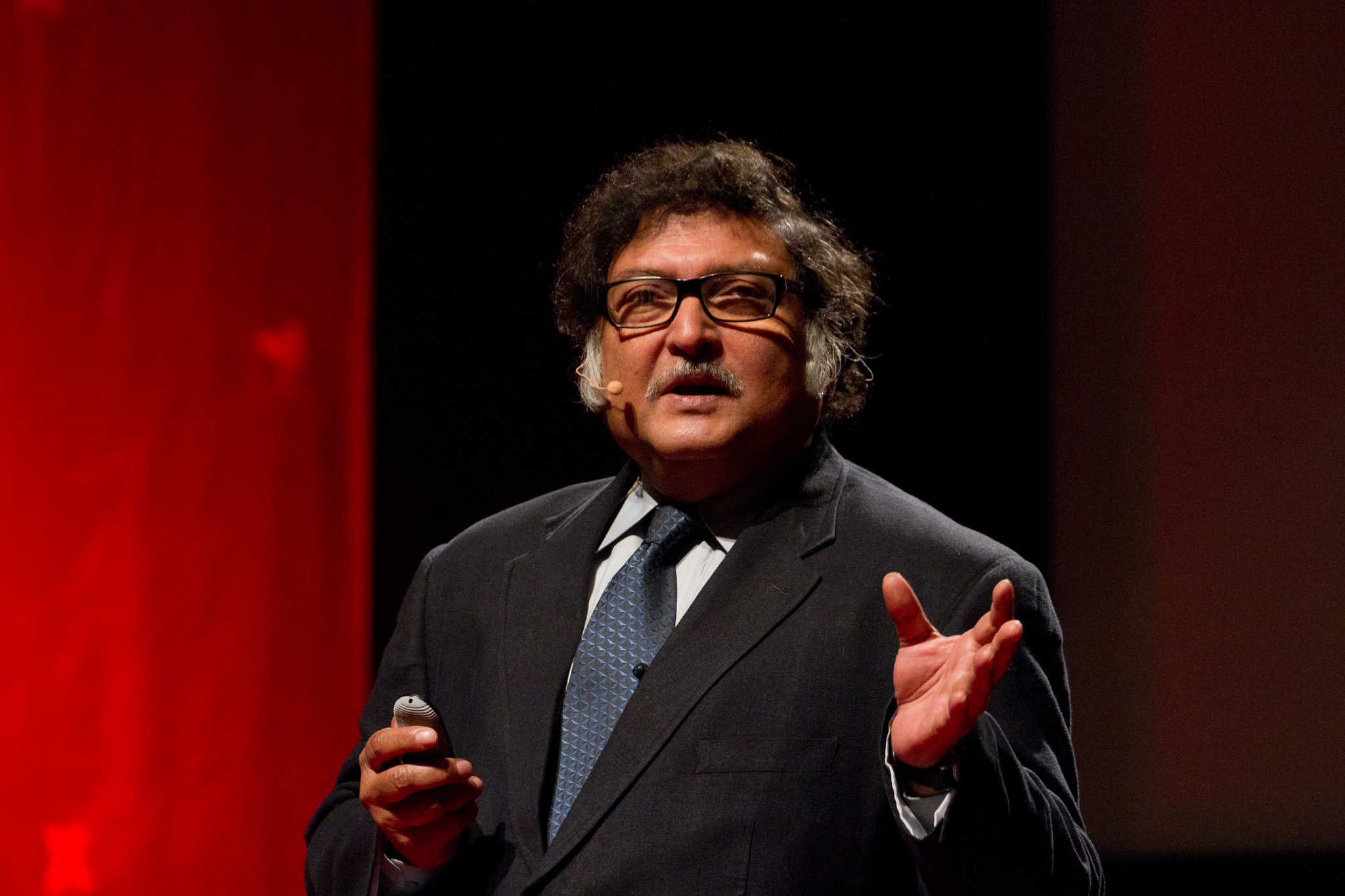

Education scientist and researcher, Professor Sugata Mitra is a name that gets anyone and everyone in the field of education and pedagogy excited and thrilled. He is synonymous with adjectives like out of the box, fresh and innovative. He is best known for his Hole in the Wall experiment, which proves that it is high time we break the barriers of conventional rote learning and teach with the use of advancements in technology and the internet to impart education and make our children self-sufficient learners.
A strong proponent of ‘Just in Time’ learning, he believes that the role of teachers is indispensable but what they need to do is not teach from textbooks.
He avers, “Teachers need to enable children to do ‘Just in Time’ learning. How to learn quickly, accurately, how to search for the right thing – this is our job! So the job is changing. If teachers could realise that, then they wouldn’t have this attitude of ‘Technology is evil, technology will take away my job!’ We have to understand, technology doesn’t remain technology.
You don’t think my clothes are technology, do you? It was once upon a time huge technology! My watch, my shoes, they used to be technology – they are not technology anymore. To the generation that is growing up, the internet and smartphones are not technology; they are things that you live with. If children have interest, then education happens.”
Prof Sugata believes that we can achieve better outcomes with minimally invasive education – i.e. when children can teach themselves.
He says, “It's quite fashionable to say that the education system is broken — it's not broken, it's wonderfully constructed. It's just that we don't need it anymore. It's outdated.”
Currently, he is Professor of Educational Technology at the School of Education, Communication and Language Sciences at Newcastle University, UK. Simultaneously, he pursues his passion for implementation of minimally invasive education in the economically backward sections of society in India.
He is the winner of TED Prize, 2013.

Early life and education
Prof Sugata Mitra was born to a Bengali family in Calcutta. He finished schooling from St. Xavier’s High School, Delhi in 1969. He went on to do a Bachelor of Science (BSc.) with honours in Physics from Jadavpur University, Calcutta, in 1973. He completed his Master of Science (MSc.) in Physics with specialisation in Solid State Electronics, Acoustic Holography and Quantum Biology from the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi in 1975. He earned a Ph.D. in Theoretical Solid State Physics of Organic Semiconductors, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi in 1978.
He went on to research battery technology at the Centre for Energy Studies in the IIT, and later at the Technische Universität, Vienna. He published a paper on a zinc-chlorine battery and a speculative paper on why the human sense organs are located where they are.
Hole in the Wall experiment and its reception
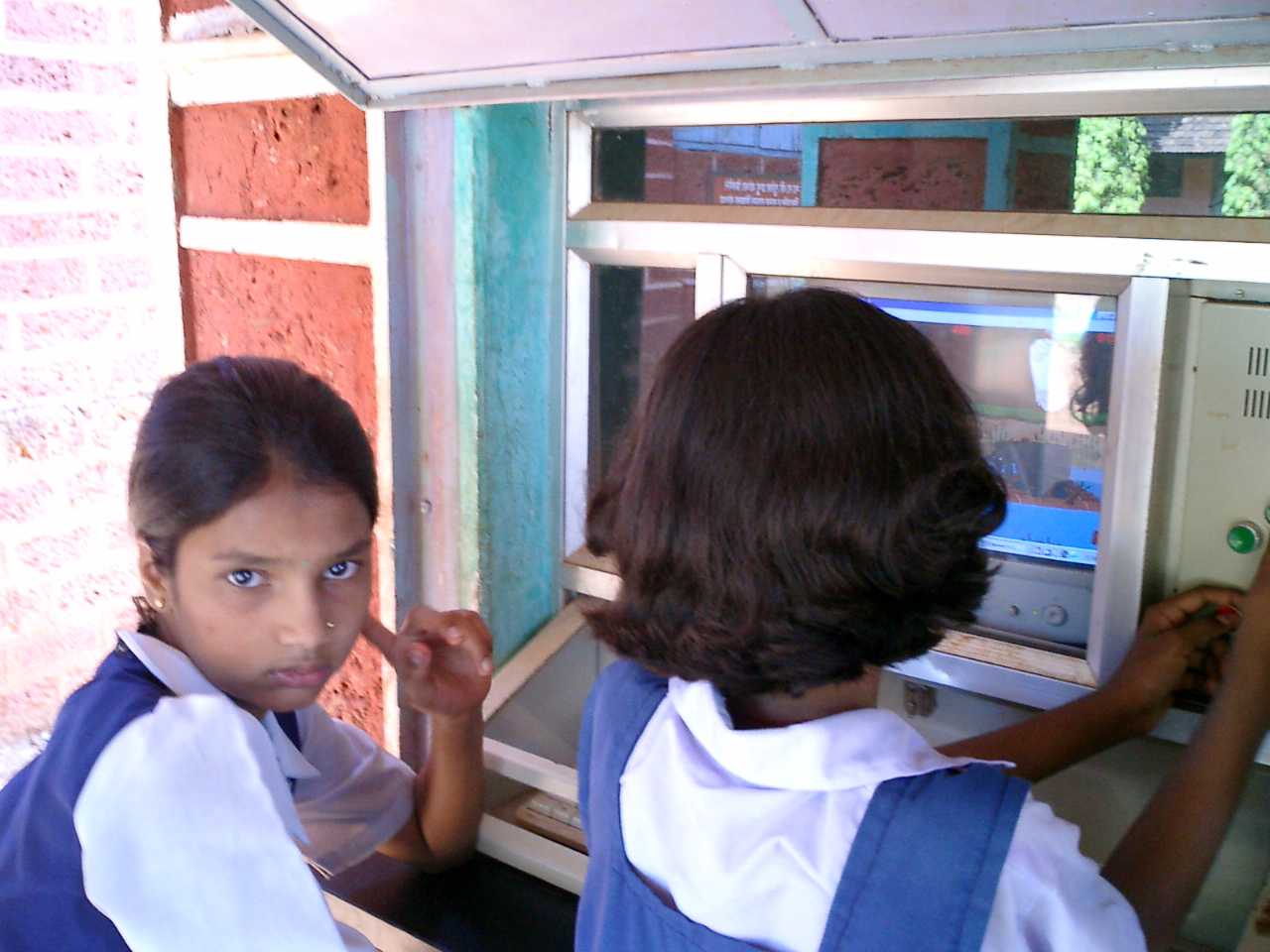
On January 26, 1999, in collaboration with the Delhi government, a team led by Dr. Sugata Mitra, then Chief Scientist at National Institute of Information Technology (NIIT), carved open a section of a wall adjoining the NIIT campus and placed a computer with internet there. This was used by children, without supervision, from the adjacent slum in Kalkaji, New Delhi and thus Hole in the Wall was born.
He found that children using learning stations like these required little or no inputs from teachers and learnt on their own by the process of exploration, discovery and peer coaching. The idea of Minimally Invasive Education (MIE) has crystallised over a period of time-based on observations and educational experiments conducted at NIIT. Minimally Invasive Education is defined as a pedagogic method that uses the learning environment to generate an adequate level of motivation to induce learning in groups of children, with minimal, or no, intervention by a teacher. Within a month, the children knew how the internet worked.
MIE uses children's natural curiosity and focuses on providing an enabling environment where they can learn on their own. Children, in the process of freely experimenting with the Learning Station, pick up critical problem-solving skills. It also provides a collaborative setting where children can share their knowledge and in the process, develop better group dynamics, all in a highly natural environment.
MIE's uniqueness is its ability to attract children towards the Learning Station driven purely by their own interests. Conventional pedagogy, on the other hand, focuses on the teacher's ability to disseminate information in a classroom setting. MIE thus complements the formal schooling system by providing a much-needed balance for children to learn on their own and provides a holistic learning experience.
In the 18 years that have passed since, the Hole in the Wall concept has spread to Kerala, Maharashtra and more states across India. In Delhi, these computers have been set up in Lajpat Nagar and Alipur. The project was also the inspiration behind the novel Q and A by Vikas Swarup, an IFS officer. This novel led to the Oscar-winning Slumdog Millionaire. The project is truly lighting the spark of learning in children all over India.
For children, it is an extension of their playground where they can play together, teach each other new things, and more importantly, just be themselves.
Prof Mitra is expanding his project to UK primary schools, using the same techniques to help children in Gateshead as he used in India. He believes that it can be used in failing schools that aren't attracting the best teachers. His idea has been implemented in a Mexican school with great effect. The class went from a 0 to 63 percent in the excellent category on the Maths exam while failing scores went from 45 percent down to 7 percent.
Across the nation, children with access to Learning Stations showed improved academic scores!
A national research programme was started, in which Learning Stations were set up in 23 locations across rural India. In 2004, the Hole in the Wall reached Cambodia through the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India.
In an internal restructuring, in July 2013, NIIT Foundation (NF) which started in 2004 as a not for profit society with a mandate to reach the unreached, uncared and unattended for, ensuring inclusive development in India has been entrusted to implement the Hole in the Wall Education Project (HiWEP).
With this, HiWEP is now poised to scale up the idea of Hole in the Wall to make a significant contribution to improving elementary education and life skills of children across the world, especially those in disadvantaged communities in rural areas and urban slums.
Since then it has already implemented more than 100 Hole in the Wall Learning Stations in India as a part of CSR initiatives of various corporates.
School in the Cloud and SOLEs (Self-Organised Learning Environments)
In addition to opening physical learning stations of varying sizes, Prof Mitra is creating a Granny Cloud, a global network of retired teachers who support kids through an online School in the Cloud platform. Granny Cloud is a platform where children interact with online 'grannies' to engage in a wide range of informal activities.
His goal is to share the Self-Organised Learning Environments (SOLE) method with parents, teachers, after-school programmes, and communities worldwide, and transform the way kids learn.
What makes this work is the universal 'grandmother' approach, where children get to interact with a person who is encouraging and appreciates their efforts, and in doing so enables them to learn what they need and also find out more about what interests them.
The need for the Granny Cloud became apparent during the preliminary experiences in the SOLEs. The SOLEs were originally initiated to provide educational support for children in remote, disadvantaged settings in rural and urban areas in India.
The SOLE approach appealed to many educators worldwide and is now used by many teachers and schools in their own classrooms. The School in the Cloud joins these two components together and will bring in the Grannies who will use the SOLE approach in these settings.
In November 2013, the first School in the Cloud learning lab — located inside a high school in Killingworth, England — opened its doors to students. Since then, six more learning labs have been built — one more in the UK and five across India.
Mitra has also launched the School in the Cloud platform which ensures that anyone, anywhere, can experiment with self-organised learning. As of 2016, more than 16,000 SOLE sessions have taken place globally, with partner learning labs and programmes scattered across the world — including in Pakistan, Colombia, and Greece. Newcastle University opened SOLE Central in 2014, as a global hub for research on self-organised learning. The platform is managed at the university's culture lab. He wishes to help design the future of learning by supporting children all over the world to tap into their innate sense of wonder. He says, “Help me build the School in the Cloud, a learning lab in India, where children can embark on intellectual adventures by engaging and connecting with information and mentoring online. I also invite you, wherever you are, to create your own miniature child-driven learning environments and share your discoveries.”
Thousands of people from Colombia to South Africa have also downloaded his SOLE toolkit for use in their homes and classrooms, experimenting with his learning method on the ground. They are also sharing their discoveries to help advance his research.
School in the Cloud is the subject of a documentary by director Jerry Rothwell, winner of TED Prize Filmmaker Award.

Digital Learning and the Shift
He explains that we humans have a tendency to approach something critically, especially when it is new. He says sadly many approach the internet and digital learning that way. Before the internet or books were around, we were taught by people who knew the subject. To explain his point, he says “Why do you have to be taught? Because you don’t have access to that information easily. This was the case, for example, in the 15th century, where if you wanted to learn something, you had to find an expert and ask him or her to please explain it to you. So that’s where the teaching bit comes. When books came, which was the first sort of impact of technology, suddenly the teacher’s knowledge could be tapped into a non-human form – the book. And there was equal controversy, I believe, at that time about the fact that books were going to ruin the education system! ‘What will teachers now do? Children will just pick up the book and they will figure it out!’
Then the teachers said, ‘No, that’s not going to happen because how do you know which book you have to read? The teacher will tell you!’ So, the curriculum, the library, the books, that kind of system came in. This happens for the first 17 years of your life because after that, once you get into your job, you don’t have access to all those books. You can’t carry your library on your head – you have to have it inside your head! So if you are lost, you are stuck, you are on a ship going somewhere and you want to know where you are, you use your sextant, point to a star, you use your knowledge of trigonometry, you look at your watch and you figure it out. All this you learnt in the first 17 years. But what happens when you can carry the library with you?
That’s the shift that we are going through. Not just the library, you can carry everything with you! So, if you’re now stuck on a ship, the new generation looks at a sextant and says, ‘What is this?’ Then you say ‘Well, trigonometry…’ and he says, ‘What is that?’ And you say, ‘But how will you find out where you are?’ And the new generation will say, ‘Here’s my phone’. We have to make that shift.
“Thanks to the internet, packing your head for the first 17 years of your life, like a suitcase for a journey, is no longer required. The stuff is available everywhere – whenever you need it, you can have it.”
He believes, “It is high time we change our approach to teaching. We need to make children curious about something so that they look it up and learn, thereby reversing the process of learning. This generation doesn’t take orders, not because they are indisciplined – we often think they are indisciplined but every generation says this about the next! Nobody is indisciplined, we are just adjusting and living in our time. So we need to make that change and adapt.”

Conclusion
To us at ScooNews, Prof Mitra is not just the brain behind several brilliant and innovative learning experiments and methods. He has been a mentor and he has been constantly supportive of our work. He was even gracious enough to be the keynote speaker at the ScooNews Global Educators Fest 2017. He inspires us to think out of the ordinary and come up with new and fresh ideas in the realm of education.
In the current education scenario, students are rewarded for memorisation, not imagination or resourcefulness. Prof Mitra is an inspiration to educators worldwide and we hope that his ideas can revolutionise the learning system and pedagogy in India, thereby producing better results. We need to follow his advice and make changes in our system to make it more efficient for our children, particularly to impart primary education. The concept of pointless memorisation, which is undoubtedly a burden for the students, needs to come to an end and “real learning” needs to start. We can make it happen.
Like he rightly said, “Knowing is NOT the most important thing. To be able to FIND OUT is more important than knowing.”
This story was published in ScooNews April 2018 special issue dedicated to Prof. Sugata Mitra and his work.
All images used for representational purposes only and are the copyright of their respective owners.
You may like
-


No More Backbenchers: How a Simple Seating Shift Is Reimagining Learning
-


NEP 2020’s Panch Sankalpa to Guide Central Universities: Dharmendra Pradhan
-


Less Than Half of Indian Schools Offer Skill-Based Courses for Senior Students: NCERT Survey
-


The Woman Who Refused to Disappear – Aditi Sharma’s Quiet Fight for Education
-


UP Govt Launches Astro Labs in Government Schools to Boost Scientific Learning
-


Class 3 Learning Levels Show Gains Since Pandemic, But Still Below 2017: PARAKH Survey
-


Manipur Rallies Call for Disruption-Free Education Amid Ongoing Unrest
-


Tripura CM Launches School Framework, Stresses Social Work in Education
-


“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space
-


A Structural Proposal to Transform School Education in Bihar
Education
The Woman Who Refused to Disappear – Aditi Sharma’s Quiet Fight for Education
Published
2 days agoon
July 10, 2025
In a quiet corner of Karnal, Haryana, Aditi Sharma runs a small school for underprivileged children. She is the founder, principal, and often, the only teacher. As a transgender woman in North India, her journey has been marked by resistance and isolation — but also by unwavering commitment. Her school may lack formal recognition or resources, but it stands as a space of learning, inclusion, and quiet resilience.
Aditi is not just the founder and principal of Haryana Public School. She is also a transgender woman who dared to imagine a different kind of North India — one where prejudice makes way for possibility, and education belongs to everyone.

But dreams, she learned early on, come at a cost.
Born and raised in Delhi, Aditi was no stranger to the stereotypes that shadow the transgender community.
“Even educated people carry the assumption that all trans people beg or perform ceremonial rituals. That’s the stereotype I grew up seeing around me,” she says.
It disturbed her and lit the fuse of quiet rebellion.
Leaving Delhi behind, she moved to Karnal with one goal: to build a school not just for visibility, but for children who had nowhere else to go. Her father, unaware she had come out, gave her a 1,200-square-yard plot to build on. “At the time, I hadn’t fully come out. Had they known I was transgender, they wouldn’t have named it to me.”
What she built wasn’t just a school — it was a statement.
In the beginning, there were no teachers, no steady funds, and no blueprint. “I doubted whether I could run a school at all. I had no confidence. But slowly, a few children started coming in. Then a few more. At one point, we had 60–70 students.”
That number dropped, not due to a lack of dedication, but constant harassment. Neighbours let their dogs loose outside. Parents were warned, “Why send your child there? This isn’t a real school.” Some believed her identity disqualified her from leadership, from teaching, from existing with dignity.
She persisted anyway.
Aditi never set out to run a school for underprivileged children. It wasn’t a strategic choice or a targeted mission. It was simply what remained when everyone else walked away. Families who could afford higher fees refused to send their children to a school run by a transgender woman. Teachers quit under social pressure. So she opened her doors to those who had nowhere else to go — children whose families could pay ₹100 a month, sometimes just ₹50, and often nothing at all. “If they don’t learn here, they won’t learn anywhere,” she says. And so she teaches — not because it’s easy, but because no one else will.

Her day begins at 4 AM — cleaning, prepping, sourcing supplies. By 8 AM, she’s teaching English, guiding students through computing tasks, or painting with them on borrowed desktops. She buys second-hand books herself. There are no permanent staff members. Most teachers leave within weeks. “They say, ‘My family doesn’t want me working here.’ The social pressure is immense.”
Once, a neighbour handed her a one-day-old baby and walked away. Aditi cared for her. When the child fell ill, she spent 12 days at the hospital with her — and the other children. Alone. “They don’t speak to me anymore,” she says of her family. “I’ve learned to let go. If someone doesn’t want to stay in touch, that’s okay. You still have to be happy.”
Haryana Public School is still not recognised by the state government. Despite its large plot, authorities claim she doesn’t meet the criteria. “Other schools on smaller land get recognised,” she says. “But because I’m transgender, they say no.” Her case is currently being reviewed by the Human Rights Commission. Justice Lalit Batra, in a hearing, reportedly said:
“If she doesn’t meet your current rule, change the rule.”
Meanwhile, the children continue to learn — with donated books, basic tools, and the irrepressible will of one woman. Aditi has even built two giant model airplanes — one stretching 20 feet — from scrap and wood. “They don’t fly, but they spark curiosity. Ten children can sit inside. It makes them dream.”

And dreams are something she insists on, even when the world offers no applause. “One child had developmental issues. No school would take him. People told me I was wasting my time. But he deserved a chance.”
Sometimes, appreciation is scarce. Respect even more so. “When parents don’t respect you, neither do their children,” she admits. “When your own life is a constant struggle, it becomes hard to build emotional bonds.”
But she still shows up every day. Reporters ask why so many people visit her school. “Because we’re doing something that shakes the norms,” she tells the children. “This school is special.”
And they believe her. Because children don’t discriminate. Adults do.
Her message to the transgender community is clear:
“Don’t wait for society to accept you. Build your own path. Even if you’re the only one walking it.”
Aditi Sharma may be the only openly transgender woman in North India running a school. But she’s not asking for sympathy. Just space. Just dignity. Just the right to show up — and not disappear.
“Even if only one child comes,” she says,
“I’ll keep the doors open.”
Read the full story in our latest Teacher Warriors issue: https://scoonews.com/magazines/scoonews-june-july-2025-digital-edition/
Education
A Vision Beyond Sight – How Aarti Takawane is Rewriting Futures for Blind Girls
Published
3 days agoon
July 9, 2025
Sometimes, the most extraordinary journeys begin with an ordinary restlessness — that nagging sense that comfort isn’t enough. For Aarti Takawane, that quiet realisation led her to walk away from a secure corporate job, and towards a mission she never imagined for herself.
Aarti’s early career looked like everything most people might aspire to: a steady job, good salary, and the kind of stability that makes parents proud. But deep down, she felt a pull that numbers and meetings just couldn’t satisfy. With a background in psychology and a genuine desire to help others, she always knew her purpose lay in people, not just profit.
That spark turned into a flame when she met Mrs Meera Badve, founder of Niwant, an organisation supporting blind students in higher education. A casual encounter at a social event became a life-changing conversation. Aarti took a leap of faith and began volunteering at Niwant — and for the first time, she felt what it was like to make an impact where it truly mattered.

Her path eventually led her to the National Federation of the Blind’s Jagriti School for Blind Girls in Pune — a place that today houses 110 blind girls, 99% of whom come from rural areas. Here, the girls don’t just study; they live, learn, and grow together in an environment that believes in what they can do, rather than what they can’t.
When Aarti joined Jagriti, she began as a psychologist, focusing on the social and emotional development of the girls. But the more she listened to their dreams and struggles, the more she saw the barriers waiting for them after school. “When you give them the right tools, you’re not just giving them a skill — you’re giving them back their choice,” she reflects.
Visually-challenged girls face a stark reality once they step out into the world. Apart from limited government quota jobs in banks or insurance, there were few opportunities that truly matched their abilities. So, Aarti decided to do something about it.
“True empowerment means they can live with dignity, not just survive.”
She founded the Skill Development Centre inside Jagriti School — a space where blind girls could learn practical, job-ready skills that tap into their real strengths. Many of the students have remarkable listening and verbal abilities. So the Centre offers courses that play to these strengths: voice modulation, foreign languages, recruitment training, and more. There are also classes in computer literacy, digital accessibility testing, and even coaching for competitive exams.

But the real magic lies in how the Centre stays rooted in reality. The team works closely with organisations like Vision-Aid India and inclusive employers to keep training aligned with what the industry actually wants. Each student’s strengths and interests are mapped out with care, so the training feels personal and purposeful.
Equally important is what happens beyond the classroom. Many girls arrive at Jagriti shy, anxious, or unsure of themselves. They may have never used a screen reader, travelled alone, or spoken up in public. So the Centre pairs technical skills with confidence-building: mobility training, decision-making workshops, life skills, and emotional support.
“They didn’t need sympathy — they needed direction, support and opportunity,”
Funding is always a tightrope act — a mix of donations, CSR partnerships, and the occasional government grant keeps the Centre alive. It covers trainer salaries, hostel facilities, assistive technology, and learning materials. The school is committed to full transparency with its supporters, many of whom return year after year because they can see exactly where their help is going.

Aarti knows that none of this would be possible without the right people leading the way. Every teacher or trainer goes through orientation in assistive technology and inclusive education. Sensitisation workshops and regular feedback from students make sure the environment stays supportive and respectful.
As the world changes, so do Aarti’s dreams for the Centre. She hopes to introduce advanced digital modules, remote work training, and a stronger network of inclusive employers. But what excites her most is the chance to rewrite how society sees disability, not as a barrier, but as a different kind of potential waiting to be unlocked.
For the 110 girls who call Jagriti School home, Aarti Takawane is more than just a teacher. She’s proof that sometimes, the best things really do happen by accident — and that true vision is not about what we see, but what we choose to do about what we can’t.
Read the full story in our issue of Teacher Warriors 2025 at https://scoonews.com/magazines/scoonews-june-july-2025-digital-edition/
Education
“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space
Published
1 week agoon
July 4, 2025
Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla, currently stationed aboard the International Space Station (ISS), answered questions from schoolchildren during a live interaction hosted under ISRO’s Vidyarthi Samvad Program.
The session, designed to bring students closer to the realities of space science, turned into a heartwarming and humorous conversation about food, sleep, and the sheer wonder of viewing Earth from space.
When asked how astronauts sleep in zero gravity, Shukla smiled and explained: “There is no floor or ceiling in space. Some of us sleep on the wall, some on the ceiling. We have to tie ourselves down so we don’t float away while sleeping.”
The conversation became sweeter when Shukla revealed that he brought familiar Indian flavours with him into orbit. “I have carried gajar ka halwa, moong dal halwa, and mango juice with me from India,” he said, to the delight of the young audience. He clarified that the halwa was specially medicated for space missions, not made at home — a detail that sparked laughter and curiosity alike.
The astronaut also spoke about daily life aboard the ISS, including how exercise is essential to counter microgravity. “We ride bicycles here, but there are no seats. We strap ourselves in with belts,” he told the children, who were both fascinated and amused by the image.
For Shukla, however, the highlight of being in space remains the view of Earth. “That blue sphere, that light mist… seeing Earth from here is the most beautiful experience. It’s hard to describe in words.”
Addressing mental well-being, he shared how astronauts stay connected with their families. “Technology helps bridge the distance. We can talk to our loved ones, and that keeps us grounded — even when we’re not.”
Also present during the interaction was Group Captain Angad Pratap, a fellow member of the Gaganyaan mission crew, who encouraged students to consider careers in aviation and space science.
For many students, the session was a dream come true. “It felt like science fiction,” said one participant. “Now I believe I can go to space one day.”
As India continues its rapid progress in space exploration, conversations like these serve as reminders that inspiration is as critical as infrastructure — and that sometimes, a simple chat with an astronaut can launch the imagination of an entire generation.
Education
Banu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature
Published
2 months agoon
May 22, 2025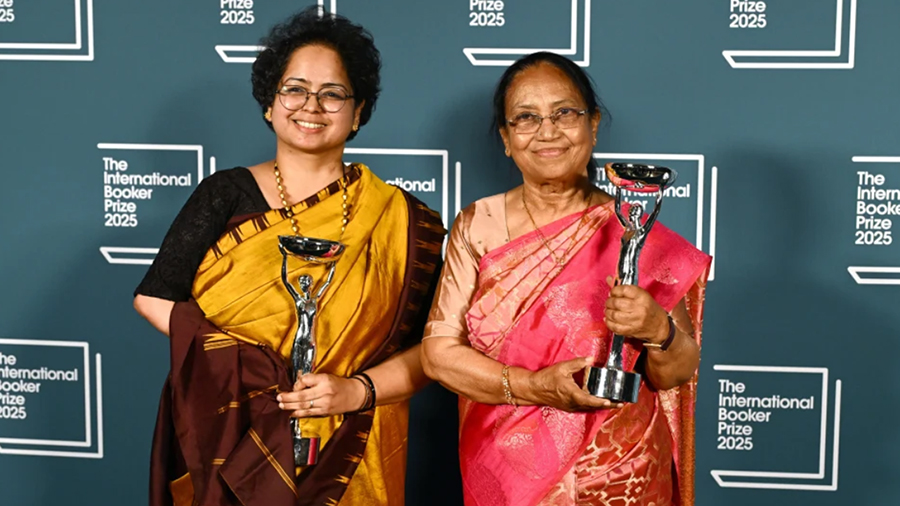
When Banu Mushtaq became the first Kannada author to win the prestigious International Booker Prize for her short story collection Heart Lamp, she didn’t just make literary history—she reignited a conversation about the role of literature in shaping society, and the way schools can nurture future writers not just as hobbyists, but as cultural forces.
Mushtaq, along with translator Deepa Bhasthi, was honoured for Heart Lamp, a collection of stories chronicling the lives of Muslim women in Karnataka across three decades. The stories are rooted in resistance, critique of religious and patriarchal structures, and everyday courage. The recognition was not just for the literary craft, but for the emotional and moral clarity the stories offer—a kind of truth that is rarely rewarded in global spaces. But the International Booker did just that.
And yet, how many students in Indian classrooms today know what the Booker Prize even is? While the Grammys, Oscars and even YouTube Play Buttons are common cultural currency among young people, literary awards often pass under the radar. This needs to change.
The International Booker Prize is one of the most prestigious literary honours in the world, recognising the finest works of fiction translated into English. It opens up space for voices that often remain local to reach a global stage. For students in India, this is an opportunity to understand that writing, especially in regional languages, is not a dead-end path. Yes, it may not offer the instant gratification of a viral video or influencer deal—but as Mushtaq’s life proves, it can shape public discourse, win global accolades, and leave behind a legacy that matters.
For educators, this is a teaching moment. Banu Mushtaq’s story is as much about literary merit as it is about resilience. She wrote in Kannada, a language she adopted over her native Urdu. She survived deep personal trauma, including a suicide attempt, and faced social backlash for her activism. She was a councillor, a journalist, and a lifelong advocate for women’s rights. These are the kinds of role models classrooms should be spotlighting—especially for young girls who need to see that stories, quite literally, can change lives.
Heart Lamp may not be appropriate for every age group, but its themes—identity, voice, justice—can be introduced in many ways. Schools should consider book discussions, literary circles, or even creative writing prompts inspired by such works to encourage students to find their voice, in whatever language or form it may come.
This win is also a reminder that educators need to broaden the definition of success they present to students. STEM, coding, and commerce continue to dominate career conversations, but it’s equally crucial to show that the arts—especially literature—have their own path to impact and influence. We hope for a time when young writers are not asked “what else do you do?” but are valued for what their words bring to the world.
Banu Mushtaq’s Booker Prize win is not just an individual triumph—it’s a collective opportunity. For schools, for students, and for all of us who believe that a powerful story can change minds, communities, and someday, the world.
Education
John King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
Published
2 months agoon
May 7, 2025
For John B. King Jr., former U.S. Secretary of Education, school wasn’t just a place—it was a lifeline. In his newly released memoir, Teacher By Teacher: The People Who Change Our Lives, King traces his journey from a grief-stricken child in New York to the corridors of educational leadership in Washington, D.C. But while the book is rooted in the American educational experience, its messages about the impact of teachers resonate far beyond U.S. borders.
In an exclusive interview with Education Week’s Sam Mallon on May 5, 2025, King reflected on his memoir, the teachers who shaped his life, and the ongoing challenges educators face worldwide.
A Childhood Saved by Teachers
King’s story is a testament to the power of mentorship. Following the death of his mother and his father’s battle with Alzheimer’s, school became King’s sanctuary. “Teachers saved my life,” he shared, recalling how educators believed in him, nurtured his potential, and gave him hope even when the world outside seemed dark.
From those formative years, King went on to earn degrees from Harvard, Columbia, and Yale. His career as a teacher, school principal, education policymaker, and eventually, U.S. Secretary of Education became a journey of giving back. The memoir celebrates not only King’s personal resilience but the quiet heroism of teachers everywhere.

Former Secretary of U.S Education John King. Image Source- EducationWeek
While King’s book is anchored in American education, the messages it carries are universally relevant. Teachers worldwide are grappling with challenges—overcrowded classrooms, mental health issues among students, and ever-changing education policies. In his interview with Education Week, King highlighted how schools must be more than academic factories. They must be safe havens, places of healing, and hubs of inspiration.
King advocates for “trauma-informed practice”—an approach where teachers are equipped to understand and support students facing emotional challenges. This is a lesson that transcends borders, as schools globally encounter rising mental health concerns among students.
Teacher Evaluations and Policy Pressures
King’s time as U.S. Secretary of Education was marked by ambitious reforms—from implementing the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) to pushing for more rigorous teacher evaluation systems. But looking back, he acknowledges a key lesson: change cannot be forced without teacher buy-in.
“Teachers can’t be bombarded with reforms,” he explained. Change must be gradual, and educators must feel a sense of ownership over new policies.
King’s narrative is ultimately about hope. In his memoir, he shares how a single teacher’s encouragement can change a student’s life trajectory. He recalls how his father’s legacy as New York’s first Black deputy schools chief was kept alive by a former student who, years later, shared how impactful his father’s teaching was.
Teaching is more than a job—it is a calling. It is a force for social good, a platform for mentorship, and a means to nurture the next generation of thinkers, leaders, and dreamers. King’s Teacher By Teacher is a reminder that educators everywhere have the power to transform lives, often without even knowing it.
Though written from an American perspective, Teacher By Teacher is a love letter to educators everywhere. It is a call to support teachers, to understand the pressures they face, and to recognise the life-changing impact they can have on their students.
For a world that often takes teachers for granted, John King’s memoir is a reminder of the heroes who stand at the front of every classroom, ready to make a difference.
Excerpts referenced in this article were taken from John King's exclusive interview with Education Week on May 5, 2025, in Washington, conducted by Sam Mallon for Education Week.
Education
Rewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
Published
3 months agoon
April 14, 2025
Ambedkar Jayanti Special | ScooNews
Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar. Most students in India recognise the name—largely as the “Father of the Indian Constitution.” If you ask a Class 10 student what Ambedkar stood for, you’ll likely get a respectable summary: chairperson of the Drafting Committee, architect of constitutional equality, and perhaps a passing reference to his fight against untouchability. But that’s where it ends.
This is not a failure of our students. This is a failure of our books.
Because Babasaheb Ambedkar was not just a jurist or a political figure to be summarised in three bullet points under Civics. He was one of the most radical, intellectually fierce, and unapologetically liberal minds India has ever known. And if we are talking about modern India—its democracy, its dissent, its diversity, its demands for dignity—then Dr. Ambedkar isn’t just relevant, he is foundational.
And yet, he remains tragically under-read and under-taught.
The Man We Didn’t Read Enough About
Ambedkar’s life is a masterclass in resilience, intellect, and reform. Born into the most marginalised community in India, he went on to become the first Indian to pursue a doctorate in economics from Columbia University, studied law at the London School of Economics, and returned to a country that still wouldn’t allow him to sit beside upper-caste students.
But Ambedkar did not stop at personal success. He turned his education into ammunition. His writings dissected caste not just as a social issue but as an economic and psychological reality. In works like Annihilation of Caste, he boldly challenged not just the religious orthodoxy but also Mahatma Gandhi—a sacred figure for many—in ways that were considered almost blasphemous at the time. And even today.
Unlike Gandhi, who sought reform within the caste system, Ambedkar demanded its demolition. Where Gandhi appealed to morality, Ambedkar appealed to reason, law, and modernity.
This discomfort with Ambedkar’s sharp, unflinching views is perhaps why our textbooks package him safely—as the dignified lawyer with a pen, not the roaring revolutionary with a voice.
More Than a Constitution-Maker
To say Ambedkar gave us the Constitution is both true and painfully incomplete.
- He gave us the right to constitutional morality, the idea that the Constitution isn’t just a set of rules but a living document that must be interpreted in the spirit of liberty, equality, and justice.
- He envisioned reservations not as charity but as corrective justice.
- He believed that a true democracy must have “social democracy” at its base—not just the right to vote but the right to dignity in everyday life.
- And he warned, prophetically, that political democracy without social democracy would be India’s downfall. He was not just designing India’s governance system, but was rather trying to develop India’s moral spine.
A Voice for Individual Freedom—Louder Than We Knew
“I measure the progress of a community by the degree of progress which women have achieved.”- Bhim Rao Ambedkar
Ambedkar’s liberalism was far ahead of his time. He consistently advocated for individual rights in the truest sense. There’s documented evidence that he argued for the decriminalisation of same-sex relationships, seeing it as an issue of individual freedom long before such conversations entered our legal discourse.
His economic ideas—rarely taught—favoured state-led industrialisation, fair wages, and social security decades before these became policy buzzwords. His writings on women’s rights were equally progressive, particularly through the Hindu Code Bill, which sought to grant women equal property rights, rights to divorce, and freedom in marriage—a bill so radical for its time that it was shelved, only to return years later in diluted forms.
Why Today’s Students Need Ambedkar—Unfiltered
In an age where freedom of speech is contested, when marginalised voices still struggle for space, when gender and sexuality are still debated as ‘issues’ instead of identities—Ambedkar is the teacher we didn’t know we needed.
We need to stop sanitising him for our syllabus. We need high schoolers to read Annihilation of Caste in their literature classes and understand the intersections of caste, religion, and gender in history—not just from an upper-caste nationalist lens but from the view of the people who fought to be seen as human.
We need Ambedkar in economics classrooms, debating his views against today’s neoliberal models.
We need to introduce him as an intellectual, a radical thinker, a critic of Gandhi, a reformer of Hindu personal law, a journalist, a linguist, a labour rights advocate, a rebel with a cause.
Because the freedoms we enjoy today—freedom of religion, freedom of expression, freedom to love, to choose, to protest, to dream—all have Ambedkar’s fingerprints on them.
If our education system truly believes in nurturing critical thinkers and empathetic citizens, then Dr. Ambedkar cannot remain a footnote or a ceremonial portrait garlanded on April 14th.
He must be read. He must be debated. He must be understood. Because the more we know about Ambedkar, the more we know about ourselves—and the democracy we’re still trying to build.
Education
“Be the Change in a Changing World”: Anita Karwal and Anju Chazot Reflect on NEP 2020
Published
4 months agoon
March 27, 2025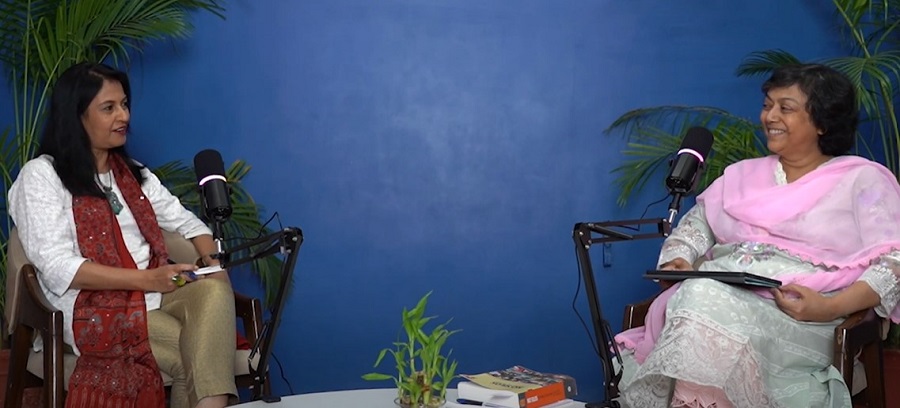
In a deeply reflective and engaging episode of the NEP Tunes podcast, Dr. Anju Chazot, education reformer and founder of Mahatma Gandhi International School (MGIS), Ahmedabad, sat down with Mrs. Anita Karwal, former Secretary of School Education, Government of India, to explore one fundamental question: How do we prepare children for a rapidly changing world?
Titled “Be the Change in the Changing World,” the episode offers a powerful conversation between two veterans of Indian education who have shared a decades-long friendship—and a mutual vision for a holistic and transformative school system.
“You can’t prepare children for tomorrow with the pedagogy of the day before yesterday.”
Drawing inspiration from John Dewey’s famous words, the episode begins by addressing the urgent need for policy literacy among stakeholders in education. Mrs. Karwal and Dr. Chazot underscore that the pace of global change—technological, environmental, economic, and emotional—has far outstripped the ability of traditional education systems to keep up. “We are in a VUCA world—volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous,” Karwal reminds listeners, calling for schools to adapt to this reality rather than resist it.
Decolonising the Classroom
A significant portion of the conversation focused on the historical context of schooling in India. Dr. Chazot draws parallels between today’s school system and Michel Foucault’s “cell and bell” model, which mirrors the prison system—marked by uniforms, bells, and rigid structures. Tracing the roots of modern schooling to the Prussian military model and colonial-era policies introduced by Lord Macaulay, both speakers lamented how education was once used as a tool to produce clerks for the Empire, rather than creative, entrepreneurial individuals.
“Colonialism didn’t just take away our resources; it colonised our minds,” Chazot observed. Karwal added, “The gurukul system was rooted, contextual, and sustainable. The colonial model replaced it with standardisation and control.”
Disruptions and the Call for Change
From climate change to AI, from the gig economy to rising mental health challenges—today’s youth are living in an era of non-stop disruptions. Mrs. Karwal shared a poignant insight: on the very day she retired from her government service (30 November 2022), OpenAI launched ChatGPT. “As a senior citizen, I would have felt useless had I not tried to understand this disruption,” she said, urging listeners to stay updated with technological trends.
Mental health also featured prominently in the discussion. The World Health Organization reports a 25% increase in global anxiety and depression cases, especially among the youth. Schools, Karwal said, must acknowledge and address this invisible epidemic, and create environments that are nurturing—not anxiety-inducing.
Why NEP 2020 Is a Game Changer
Against this backdrop, both educators believe the National Education Policy 2020 is a timely and visionary document. “It’s not just about academics—it’s about the whole child,” said Chazot, pointing to NEP’s focus on holistic development across cognitive, emotional, physical, and ethical domains.
Key elements of the NEP and the newly released National Curriculum Framework (NCF) discussed in the podcast include:
-
A shift from rote learning to competency-based, experiential learning
-
Focus on Indian traditions and cultural rootedness
-
Moving away from exam-centric teaching, especially in early years
-
Recognition of multilingualism and contextual learning
-
Encouragement of critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability
“Learning to learn is the most essential skill of the future,” Karwal stressed. “Children must be ready to unlearn and relearn throughout life.”
The Future of Jobs
To illustrate the rapidly changing employment landscape, both speakers listed a host of emerging careers—from Prompt Engineers and Drone Fleet Managers to Climate Data Analysts and Digital Detox Specialists. “Just imagine,” Chazot quipped, “if I were a child again, I’d become a Prompt Engineer and finally fulfil my parents’ dreams of being an engineer—with a creative twist!”
Karwal, on the other hand, expressed a desire to become a Human-Machine Team Manager—a futuristic role bridging collaboration between people and machines.
Their message was clear: the world our children are entering is drastically different from the one their parents and teachers grew up in. And education must keep up.
A Takeaway Challenge for Listeners
To wrap up the episode, the hosts offered a unique call-to-action: ask yourself what job you would pick today if you could go back in time again. Then, explore new professions with your family or students. From LinkedIn job listings to the World Economic Forum’s reports, Karwal recommended several tools to research emerging careers. They invited listeners to write in with their findings and reflections.
“This exercise is not just for students,” said Dr. Chazot. “It’s for parents, teachers, and policy-makers alike. We must all become learners again.”
Final Thoughts
In an era where the only constant is change, the NEP Tunes podcast is a timely resource to help educators, parents, and students reimagine the purpose of schooling. With leaders like Anju Chazot and Anita Karwal at the helm of the conversation, the journey towards meaningful transformation in Indian education seems not only possible—but exciting.
🟡 This article is adapted from the NEP Tunes podcast hosted by Dr. Anju Chazot. You can listen to the full episode on YouTube. Here is the video-
Education
Sunbeam Indiranagar Shines in Academics, Arts, and Sports, Cementing Its Legacy of Holistic Education
Published
4 months agoon
March 18, 2025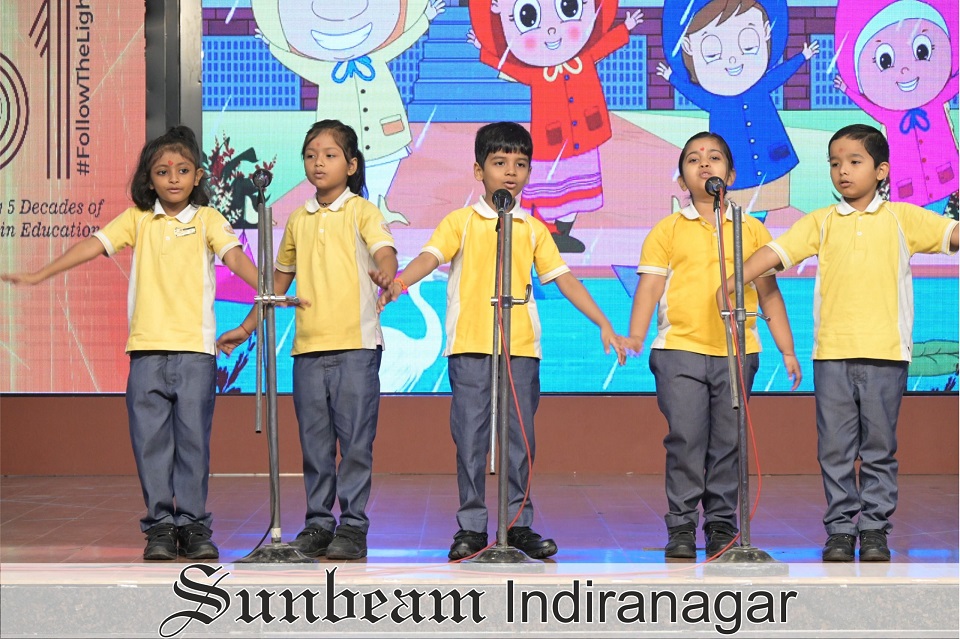
Varanasi: Sunbeam Indiranagar, Varanasi, has emerged as a dynamic centre for academic excellence, cultural enrichment, and sporting achievements, reinforcing its commitment to holistic education. In a year marked by significant accomplishments, students and faculty have demonstrated a dedication to intellectual growth, creative expression, and leadership development, embodying the rich legacy of the Sunbeam Group.
The school’s approach extends beyond traditional academics, encouraging students to engage in parallel activities that nurture a well-rounded skill set. From literature festivals to classical dance championships, Sunbeam Indiranagar has provided students with platforms to explore, innovate, and excel.
Students had the opportunity to engage with global thought leaders through their participation in prestigious events such as the Jaipur Literature Festival and the Great Indian Learning Festival (GILF) at Daly College, organised by ScooNews. These experiences enabled them to explore contemporary literary and intellectual discussions, sharpening their analytical and creative abilities.
The performing arts department also made a mark with theatrical performances at Banaras Hindu University (BHU) and the Krishnamurti Foundation, under the guidance of renowned dramaturgist Mukherjee P.. The school’s commitment to developing critical thinking and communication skills was further reflected in students’ achievements in quizzes, creative writing, Olympiads, debates, and visual arts competitions, underscoring a culture of academic inquiry and artistic exploration.
Sunbeam Indiranagar’s focus on all-round development was evident in the State Level Kathak Championship, where students showcased their prowess in Indian classical dance. The school’s sporting achievements were equally impressive, with students excelling in the East Zone Skating Championship 2024 and the Open District Roller Championship 2024, securing both individual and team accolades. The school’s impact extends beyond student achievements, with its leadership being recognised for their visionary contributions to education. The Principal of Sunbeam Indiranagar was honoured with the Distinguished Educator for Future-Ready Skills award, securing All India Rank (AIR) 6 in the School Leader’s category by CENTA and receiving the Nari Shakti Sammaan for contributions towards empowering students through progressive learning methodologies.
Sunbeam Indiranagar’s standing as a leading educational institution was reaffirmed when it was ranked 5th among the Best Co-Ed Day Schools in Varanasi.
With its continued emphasis on holistic development, Sunbeam Indiranagar remains dedicated to shaping young minds, reinforcing its reputation as an institution that values learning in all its forms.
Education
Nagaland Schools Launch ‘Adolescent Girls Club’ to Empower Young Girls Under Mission Shakti
Published
5 months agoon
February 27, 2025
Adolescence is a pivotal phase in a child’s development, marked by rapid physical and psychological transformations. It is a time of exploration, self-discovery, and, often, vulnerability. To provide structured guidance and empower young girls during this crucial stage, Nagaland has introduced ‘Adolescent Girls Clubs’ in both government and private schools for girls aged 10-19 years under Mission Shakti.
On 5th October 2024, the first Adolescent Girls Club was launched at Don Bosco Higher Secondary School, Wokha, Nagaland, with 50 adolescent girls as its founding members. The initiative aims to equip girls with essential skills, knowledge, and support systems to navigate challenges, make informed choices, and build a strong foundation for their future. With the motto “Live the Promise,” the clubs aspire to develop confident, informed, and compassionate leaders of tomorrow.
The initiative is designed with key objectives to educate, uplift, and empower adolescent girls:
The Adolescent Girls Club will engage its members in workshops, mentorship programmes, health camps, community service projects, and creative expression activities. Additionally, a special adolescent toolkit is being developed to serve as a guide for both adolescent girls and their parents. The toolkit will include informational materials on menstrual hygiene management (MHH), mental health, teenage pregnancy prevention, child abuse awareness, and emergency helpline numbers.
Teachers and counsellors are actively working on IEC (Information, Education, and Communication) materials tailored to adolescent needs. The clubs will also conduct monthly activities to ensure continuous engagement, provide a platform for girls to discuss their concerns, and create a safe space for their growth and development.
This initiative under Mission Shakti is expected to positively impact thousands of young girls across Nagaland, equipping them with the necessary tools to navigate adolescence with confidence and resilience.Objectives of the Adolescent Girls Club
Education
Saudi Teacher Mansour bin Abdullah Al-Mansour Wins $1 Million Global Teacher Prize
Published
5 months agoon
February 13, 2025
In a heartwarming recognition of dedication and innovation in education, Saudi Arabian teacher Mansour bin Abdullah Al-Mansour has been awarded the prestigious $1 million GEMS Education Global Teacher Prize. Announced at the World Governments Summit in Dubai, the award celebrates Al-Mansour’s transformative work in empowering students from low-income families, including hundreds of gifted orphans, and his 3,000+ hours of community service.
Al-Mansour, a teacher at Prince Saud bin Jalawi School in Al-Ahsa, has spent over two decades uplifting students facing academic challenges, disabilities, and financial hardships. His efforts include establishing mentorship programmes, innovation incubators, and financial literacy initiatives, enabling students to achieve global recognition. Notably, he plans to use the prize money to build a school for talented orphans, furthering his mission to provide quality education to underprivileged children.

(Image: Mansour Al Mansour- 2025 Global Teacher Prize Winner)
Beyond the classroom, Al-Mansour has authored 21 educational books, trained over 300 educators, and led literacy programmes for prison inmates, helping reduce sentences for some. His work has earned him accolades as an international ambassador for educational excellence.
The Global Teacher Prize, now in its ninth year, recognises exceptional educators who make a profound impact on their communities. Al-Mansour was selected from over 5,000 nominations across 89 countries, joining a prestigious list of global educators.
Sunny Varkey, Founder of the Global Teacher Prize, praised Al-Mansour’s “passion, dedication, and the life-changing power of education.” Stefania Giannini, UNESCO Assistant Director-General for Education, highlighted the importance of investing in teachers to build a sustainable future.
As the world faces challenges like inequality and climate change, Al-Mansour’s story serves as a beacon of hope, reminding us of the transformative power of education and the unsung heroes shaping our future.
Newsletter

No More Backbenchers: How a Simple Seating Shift Is Reimagining Learning

NEP 2020’s Panch Sankalpa to Guide Central Universities: Dharmendra Pradhan

Less Than Half of Indian Schools Offer Skill-Based Courses for Senior Students: NCERT Survey

The Woman Who Refused to Disappear – Aditi Sharma’s Quiet Fight for Education

A Vision Beyond Sight – How Aarti Takawane is Rewriting Futures for Blind Girls

UP Govt Launches Astro Labs in Government Schools to Boost Scientific Learning

Class 3 Learning Levels Show Gains Since Pandemic, But Still Below 2017: PARAKH Survey

Design and the Future of Learning: How Architecture is Shaping Next-Gen Schools

Punjab to Introduce Business, Marketing Education in Govt Schools for High Schoolers

Manipur Rallies Call for Disruption-Free Education Amid Ongoing Unrest

Tripura CM Launches School Framework, Stresses Social Work in Education

“We Sleep on Walls Here”: Shubhanshu Shukla Talks to Indian Students from Space

A Structural Proposal to Transform School Education in Bihar

NIIT Foundation and YuWaah, UNICEF Launch Free Online Digital Marketing Course for Youth

National Conference Pushes for Common Standards Across School Boards

Maharashtra: Over 8,000 Villages Lack Schools, CCTV Compliance Still Patchy

Haryana to Offer Free After-School Coaching for JEE, NDA Aspirants

Telangana CM Calls for Overhaul of Intermediate Education in Telangana

Indian Astronaut Shubhanshu Shukla to Connect with School Students Live from Space

Are 4-Year Degrees Dead? Nikhil Kamath and the WEF Say Lifelong Learning Is Here to Stay

UGC Cracks Down on 89 Institutes Over Anti-Ragging Failures

Government Doubles Down on Coaching Centres: New Panel Signals Stronger Regulation Ahead

CBSE To Conduct Board Exams Twice for Class 10 from 2026

How to Win Back Wandering Minds: Post-Summer Edition
Tripura Becomes Third Indian State to Achieve Full Literacy

CBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools

Is Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?

Maharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020

MAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
China Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035

John King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education

CBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020

Rewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution

CBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme

Banu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature

India Bids Farewell to NEP Architect Dr K. Kasturirangan

Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar 2025: Nominations Now Open for India’s Young Achievers

NCERT Class 7 Textbooks Updated: Mughals Removed, Focus on Indian Ethos and Pilgrimage

Delhi Government Cracks Down on Dummy Schooling; Over 600 Schools Inspected, 10 Issued Notices

Delhi Approves Landmark Bill to Regulate School Fees Across 1,677 Institutions

Harvard Stands Its Ground: Harvard Faces ₹18,400 Crore Funding Freeze After Rejecting Trump Administration’s Demands

Operation Sindoor and Operation Abhyaas: Navigating School Safety and Student Well-being Amid Rising Tensions

CUET-UG 2025 Likely to be Postponed, Fresh Dates Expected Soon

Aalamaram 2025: Where Indian Educators Came Together to Grow, Reflect, and Lead

Trump Signs Executive Order to Promote AI Integration in U.S. K-12 Education

Mizoram Declared First Fully Literate State in India

Indian Students Flock to Singapore, Ireland, and Dubai for Higher Studies: 38% Surge Recorded

OpenAI Academy Launches in India to Democratise AI Education for Students, Teachers, and Startups

UK’s New Immigration Rules: What They Mean for Indian Students

Private School Fees Surge by 50–80% in Three Years, National Survey Finds
SGEF2023 | Special Address by Rama Datt, Trustee, Maharaja Sawai Man Singh II Trust, Jaipur

ScooNews | After Movie | ScooNews Global Educators Fest 2023

Aftermovie | NIES2 UP Chapter | 21 Jan 2023

WEBINAR | Gamification in Education: How Digital Badges Can Boost Student Motivation and Engagement

ScooNews | WEBINAR| Importance of Physical Activity for Children at School | Plaeto

SCOONEWS | WEBINAR | WHY DIGITIZING YOUR SCHOOL IS A MUST | TEACHMINT

Keynote Address | Lakshyaraj Singh Mewar

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, CBSE at SGEF2022

How schools can nurture every student’s genius

Aftermovie | SGEF2022 | Jaipur

Li Andersson | Minister of Education | Finland

Anurag Tripathi, Secretary, Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) discusses NEP2020

ScooNews | Early Ed Asia 2019 | Aftermovie
#PodarECEconf : Pursuing quality ECE

#CBSE Class XII #Results #Highlights

The interesting story of India’s educational system | Adhitya Iyer

A young scientist’s quest for clean water

The Danger of Silence: Clint Smith

National Digital Library of India is an initiative by HRD Ministry

Remembering Kalpana Chawla on her birthday!

Message from Sadhguru for Students!
Message from Sadhguru for Students!

The Untapped Genius That Could Change Science for the Better

Eddy Zhong: How school makes kids less intelligent TEDxYouth@Beacon

#TEDxCanberra : What if every child had access to music education…
Trending
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoCBSE’s ‘Sugar Boards’ Initiative: Tackling the Sweet Crisis in Indian Schools
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoIs Your School Following These Mandatory CBSE Committees?
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMaharashtra to Regulate Pre-Primary Education with New Law Aligned to NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoMAHAJYOTI’s Book Distribution Scheme to Empower 7,000 OBC Students Preparing for JEE/NEET & MHT-CET
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoChina Embarks on Ambitious AI-Driven Education Reform to Build a ‘Strong Education Nation’ by 2035
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoJohn King’s Book ‘Teacher By Teacher’: A Global Tribute to the Transformative Power of Education
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Introduces Mandatory Bridge Course for Classes 6 to 12 in Chhattisgarh Under NEP 2020
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoRewriting Ambedkar: Why Students Must Know the Man Beyond the Constitution
-

 Education3 months ago
Education3 months agoCBSE Mandates 50-Hour Annual Training for Teachers, Declares STEM as 2025 Theme
-

 Education2 months ago
Education2 months agoBanu Mushtaq’s International Booker Win Is a Wake-Up Call for Indian Schools to Reclaim Literature






